Abstract
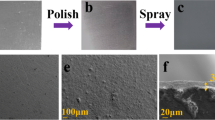
In this study, laser cleaning of blue and red polyurethane paint on aluminum alloy surface were investigated by using a nanosecond pulsed laser at 1.8, 3.2 and 8.0 J/cm2. The surface topography after laser cleaning was analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the paint removal process was recorded by high-speed camera (HSC) and spectrophotometer. It was found that the cleaning results and phenomena of the two paints were significantly different. After cleaned at 1.8 J/cm2, the blue residual paint is a uniform and flat paint layer while the red residual paint presents a loose mesh morphology. Although both red paint and blue paint could be removed at 3.2 and 8.0 J/cm2, the surface of the substrate shows different topography. It could be observed by HSC that the blue paint detached from the substrate by being vaporized and the red paint was disintegrated into pieces and ejected from the substrate. This phenomenon was caused by the difference in the absorption coefficient of the two paints to the laser. To illustrate this, an energy distribution model was established considering Beer-Lambert’s law and the temperature distribution of paint and thermal stress of substrate were calculated. Under laser irradiation, blue paint was more likely to be ablated and vaporized, while red paint was subject to greater thermal stress. For blue paint removal, vaporization, spallation and combustion are the dominated mechanisms and the red paint was mainly erupted by thermal stress of substrate.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.M. Mostafa, A.A. Menazea, Laser-assisted for preparation ZnO/CdO thin film prepared by pulsed laser deposition for catalytic degradation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 176, 109020 (2020)
A.A. Menazea, N.S. Awwad, Antibacterial activity of TiO2 doped ZnO composite synthesized via laser ablation route for antimicrobial application. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 9434–9441 (2020)
S.M. Bedair, H.P. Smith, Atomically clean surfaces by pulsed laser bombardment. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 4776–4781 (1969)
Y. Koh, I. Sarady, Removal of adhesives and coatings on iron artifacts using pulsed TEA CO2 and Nd:YAG lasers. Laser Tech. Syst. Art Conserv. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics. (2001)
G. Zhu, S. Wang, W. Cheng, Y. Ren, D. Wen, Corrosion and wear performance of aircraft skin after laser cleaning, Opt. Laser Technol. 132, 106475 (2020)
Q.H. Tang, D. Zhou, Y.L. Wang, G.F. Liu, Laser cleaning of sulfide scale on compressor impeller blade. Appl. Surf. Sci. 355, 334–340 (2015)
G.X. Chen, T.J. Kwee, K.P. Tan, Y.S. Choo, M.H. Hong, Laser cleaning of steel for paint removal. Appl. Phys. A 101, 249–253 (2010)
M.K.A. Abdul, R.M.S. Jaafar, A.A. Rahman, S.A. Saidi, Identification of optimum operatives parameters for Pulse Nd:YAG laser in paint removal on different types of car coated substrate. Int. J. Edu. Res. 2, 47–64 (2014)
M.K.A.A. Razab, M.S. Jaafar, A.A. Rahman, S.A. Saidi, Estimation of threshold fluence, absorption coefficient and thermal loading of car coated substrate in laser paint removal. App. Mec. Mat. 554, 439–443 (2014)
Y. Lu, L. Yang, Y. Wang, H. Chen, B. Guo, Z. Tian, Paint Removal on the 5A06 aluminum alloy using a continuous wave fiber laser. Coatings 9, 488 (2019)
Z. Li, D. Zhang, X. Su, S. Yang, J. Xu, R. Ma, D. Shan, B. Guo, Removal mechanism of surface cleaning on TA15 titanium alloy using nanosecond pulsed laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 139, 106998 (2021)
X. Xie, Q. Huang, J. Long, Q. Ren, S. Liu, A new monitoring method for metal rust removal states in pulsed laser derusting via acoustic emission techniques. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 275, 116321 (2019)
Y. Lu, Y. Ding, M. Wang, L. Yang, Y. Wang, An environmentally friendly laser cleaning method to remove oceanic micro-biofoulings from AH36 steel substrate and corrosion protection. J. Clean. Prod. 314, 127961 (2021)
G. Zhang, X. Hua, Y. Huang, Y. Zhang, F. Li, C. Shen, J. Cheng, Investigation on mechanism of oxide removal and plasma behavior during laser cleaning on aluminum alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 506, 144666 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144666
H. Li, S. Costil, V. Barnier, R. Oltra, O. Heintz, C. Coddet, Surface modifications induced by nanosecond pulsed Nd:YAG laser irradiation of metallic substrates. Surf. Coat. Tech. 201, 1383–1392 (2006)
K.G. Watkins, Mechanisms of laser cleaning. Proc. SPIE-The Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 3888, 165–174 (2000)
F. Brygo, C. Dutouquet, F. Le Guern, R. Oltra, A. Semerok, J.M. Weulersse, Laser fluence, repetition rate and pulse duration effects on paint ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 2131–2138 (2006)
M. Kumar, P. Bhargava, K.A. Biswas, S. Sahu, Epoxy-paint stripping using TEA CO2 laser: determination of threshold fluence and the process parameters. Opt. Laser Technol. 46, 29–36 (2013)
X. Li, Q. Zhang, X. Zhou, D. Zhu, Q. Liu, The influence of nanosecond laser pulse energy density for paint removal. Optik 156, 841–846 (2017)
H. Zhao, Y. Qiao, D. Xian, S. Wang, Q. Zhang, Y. Zang, X. Liu, Laser cleaning performance and mechanism in stripping of Polyacrylate resin paint. Appl. Phys. A (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03551-0
J.H. Brannon, A.C. Tam, R.H. Kurth, Pulsed laser stripping of polyurethane-coated wires: a comparison of KrF and CO2 lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 70, 3881–3886 (1991)
D.E. Roberts, Pulsed laser coating removal by detachment and ejection. Appl. Phys. A 79, 1067–1070 (2004)
Y.F. Lu, Laser-induced temperature rise in anisotropic substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 72, 4893–4900 (1992)
A.V. Bulgakov, N.M. Bulgakova, Thermal model of pulsed laser ablation under the conditions of formation and heating of a radiation-absorbing plasma. Quantum Electron 29, 433–437 (1999)
L. Yue, Z. Wang, L. Li, Modeling and simulation of laser cleaning of tapered micro-slots with different temporal pulses. Opt. Laser Technol. 45, 533–539 (2013)
B. Majaron, L. ŠuŠterči, M. Lukač, U. Skalerič, N. Funduk, Heat diffusion and debris screening in Er: YAG laser ablation o4f hard biological tissues. Appl. Phys. B. 66, 479–487 (1998)
Y.G. Yingling, P.F. Conforti, B.J. Garrison, Theoretical investigation of laser pulse width dependence in a thermal confinement regime. Appl. Phys. A. 79, 4–6 (2004)
F. Brygo, A. Semerok, R. Oltra, J. Weulersse, S. Fomichev, Laser heating and ablation at high repetition rate in thermal confinement regime. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 8314–8318 (2006)
A. Lamikiz, J.A. Sánchez, L.N.L. de Lacalle, J.L. Arana, Laser polishing of parts built up by selective laser sintering. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manu. 47, 2040–2050 (2007)
T.L. Perry, D. Werschmoeller, X. Li, F.E. Pfefferkorn, N.A. Duffie, Pulsed laser polishing of micro-milled Ti6Al4V samples. J. Manuf. Process. 11, 74–81 (2009)
G. Raciukaitis, M. Brikas, P. Gecys, M. Gedvilas, Accumulation effects in laser ablation of metals with high-repetition-rate lasers, Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics. (2008)
S. Eaton, H. Zhang, P. Herman, F. Yoshino, L. Shah, J. Bovatsek, A. Arai, Heat accumulation effects in femtosecond laser-written waveguides with variable repetition rate. Opt. Express. 13, 4708–4716 (2005)
F. Bauer, A. Michalowski, T. Kiedrowski, S. Nolte, Heat accumulation in ultra-short pulsed scanning laser ablation of metals. Opt. Express. 23, 1035 (2015)
J. Han, X. Cui, S. Wang, G. Feng, G. Deng, R. Hu, Laser effects based optimal laser parameter identifications for paint removal from metal substrate at 1064nm: a multi-pulse model. J. Mod. Optic. 64, 1–13 (2017)
J.S. Chickos, W.E. Acree, J.F. Liebman, Estimating solid-liquid phase change enthalpies and entropies. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data. 28, 1535–1673 (1999)
J.S. Chickos, Enthalpies of vaporization of organic and organometallic compounds, 1880–2002. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data. 32, 519–878 (2003)
Z. Zhiyan, Z. Jingyuan, W. Yibo, Z. Shusen, L. Xuechun, L. Xinyang, Removal of paint layer by layer using a 20 kHz 140 ns quasi-continuous wave laser. Optik 174, 46–55 (2018)
Y. Lu, L. Yang, M. Wang, Y. Wang, Improved thermal stress model and its application in ultravioletnanosecond laser cleaning of painting. Appl. Opt. 59(25), 7652–9 (2020)
Z. Tian, Z. Lei, X. Chen, Y. Chen, L. Zhang, J. Bi, J. Liang, Nanosecond pulsed fiber laser cleaning of natural marine micro-biofoulings from the surface of aluminum alloy. J. Clean. Prod. 244, 118724 (2020)
Y.F. Lu, W.D. Song, B.W. Ang, M.H. Hong, D.S.H. Chan, T.S. Low, A theoretical model for laser removal of particles from solid surfaces. Appl. Phys. A 65, 9–13 (1997)
Y. Lu, L. Yang, M. Wang, Y. Wang, Simulation of nanosecond laser cleaning the paint based on the thermal stress. Optik. 227, 165589 (2021)
Y.F. Lu, M. Takai, S. Komuro, T. Shiokawa, Y. Aoyagi, Surface cleaning of metals by pulsed-laser irradiation in air. Appl. Phys. A 59, 281–288 (1994)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Guangdong Province Introduction of Innovative R&D Team (Grant No. 2018B090905003) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U19A2077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 12756 KB)
Supplementary file2 (MP4 6376 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 7125 KB)
Supplementary file4 (MP4 8119 KB)
Supplementary file5 (MP4 13638 KB)
Supplementary file6 (MP4 8381 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Xu, J., Li, Z. et al. Removal mechanisms of nanosecond pulsed laser cleaning of blue and red polyurethane paint. Appl. Phys. A 128, 170 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05296-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05296-4