Abstract
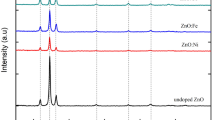
In the current work, the effect of zinc doping on the structural and optical properties of iron oxide has been explored for optoelectronic applications. Undoped and different (2–10 wt%) Zn-doped iron oxide (Fe2O3/Zn) nanostructured films (nFs) were successfully prepared via spray pyrolysis technique. The structural, morphological, bonds vibrations and optical properties of the prepared films were examined using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), FT-IR and UV-Vis-NIR spectroscopy techniques, respectively. The XRD measurements reveal the formation of the rhombohedral hematite phase structure of iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) for all prepared films. The FT-IR spectra analysis exhibits the existence of absorption bands corresponded to the stretching and bending vibrations of Fe–O and O–Fe–O bonds, respectively. The UV–Vis–NIR measurements of the prepared samples indicate the significant effect of Zn doping on various optical properties of Fe2O3 films. The achieved optical bandgap of Fe2O3/Zn nFs is tuned from 2.38 eV (undoped Fe2O3) to 2.83 eV (10 wt% of Fe2O3/Zn). These findings are explained on the basis of the created localized energy levels and Burstein–Moss effect. As a novel result of this study, Fe2O3/Zn nFs are well-qualified for the use in modern optoelectronic applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Badawi, M.G. Althobaiti, Effect of Cu-doping on the structure, FT-IR and optical properties of Titania for environmental-friendly applications. Ceram. Int. 47(8), 11777–11785 (2021)
A. Badawi, S.S. Alharthi, M.G. Althobaiti, A.N. Alharbi, H. Assaedi, H.I. Alkhammash, N. Al-Hosiny, Structure investigation and optical bandgap tuning of La-doped CuO nanostructured films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. Appl. Phys. A 127(4), 235 (2021)
A. Badawi, M.G. Althobaiti, S.S. Alharthi, A.M. Al-Baradi, Tailoring the optical properties of CdO nanostructures via barium doping for optical windows applications. Phys. Lett. A 411, 127553 (2021)
S. Kurtaran, M. Kellegöz, S. Köse, Characterization of Gd doped CeO2 thin films grown by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Opt. Mater. 117, 111144 (2021)
P. Albert, J. Narayanan, T. Arockiadoss, Indium-tin oxide regulated band gap of nitrogen-doped titanium oxide thin films for visible light photocatalyst. Appl. Phys. A 127(12), 900 (2021)
S. Roy, M.P. Ghosh, S. Mukherjee, Introducing magnetic properties in Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 127(6), 451 (2021)
Suman S. Chahal, A. Kumar P. Kumar (2020), Zn Doped α-Fe2O3: an efficient material for UV driven Photocatalysis and electrical Conductivity Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des. 10(4), 273
S. Guo, H. Wang, W. Yang, H. Fida, L. You, K. Zhou, Scalable synthesis of Ca-doped α-Fe2O3 with abundant oxygen vacancies for enhanced degradation of organic pollutants through peroxymonosulfate activation. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 262, 118250 (2020)
R. Sivaranjani, A. Thayumanavan, S. Sriram, Photocatalytic activity of Zn-doped Fe2O3 nanoparticles: a combined experimental and theoretical study. Bull. Mater. Sci. 42(4), 185 (2019)
R. Nikam, S. Rayaprol, S. Mukherjee, S.D. Kaushik, P.S. Goyal, P.D. Babu, S. Radha, V. Siruguri, Structure and magnetic properties of Mn doped α-Fe2O3. Phys B: Condens. Matter 574, 411663 (2019)
A. Akbar, S. Bashir, S. Riaz, S. Naseem (2015), Magnetic Properties of Co-doped Fe2O3 Thin Films. Mater. Today: Proc. 2 (10, Part B), 5674–5678
A.M. El Sayed, W.M. Morsi, α-Fe2O3 /(PVA + PEG) Nanocomposite films; synthesis, optical, and dielectric characterizations. J. Mater. Sci. 49(15), 5378–5387 (2014)
M. Sharmin, J. Podder, Influence of Al doping on the structure and properties of Fe2O3 thin films: high transparency, wide band gap, ferromagnetic behavior. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 34(7), 075033 (2019)
R.R. Salunkhe, C.D. Lokhande, Effect of film thickness on liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) sensing properties of SILAR deposited CdO thin films. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 129(1), 345–351 (2008)
B. Sahin, Y. Gülen, F. Bayansal, H.A. Çetinkara, H.S. Güder, Structural and optical properties of Ba-doped CdO films prepared by SILAR method. Superlattices Microstruct. 65, 56–63 (2014)
N.E. Makori, I.A. Amatalo, P.M. Karimi, W.K. Njoroge, Optical and electrical properties of CdO: Sn thin films for solar cell applications. Int. J. Optoelectron. Eng. 4(1), 11–15 (2014)
C.L.E. Aquino, M.D.L. Balela, Thermally grown Zn-doped hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanostructures for efficient adsorption of Cr(VI) and Fenton-assisted degradation of methyl orange. SN Appl. Sci. 2(12), 2099 (2020)
A. Abdel-Galil, M.S.A. Hussien, I.S. Yahia, Synthesis and optical analysis of nanostructured F-doped ZnO thin films by spray pyrolysis: transparent electrode for photocatalytic applications. Optic. Mater. 114, 110894 (2021)
M. Vigneshwaran, R. Chandiramouli, B.G. Jeyaprakash, D. Balamurugan, Physical properties of spray deposited Mg doped CdO thin films. J. Appl. Sci. 12, 1754–1757 (2012)
R.J. Deokate, S.M. Pawar, A.V. Moholkar, V.S. Sawant, C.A. Pawar, C.H. Bhosale, K.Y. Rajpure, Spray deposition of highly transparent fluorine doped cadmium oxide thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254(7), 2187–2195 (2008)
U. Khan, A. Akbar, H. Yousaf, S. Riaz, S. Naseem (2015), Ferromagnetic properties of al-doped Fe2O3 thin films by sol-gel. Mater. Today: Proc. 2 (10, Part B), 5415–5420
A. Badawi, E.M. Ahmed, N.Y. Mostafa, F. Abdel-Wahab, S.E. Alomairy, Enhancement of the optical and mechanical properties of chitosan using Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28(15), 10877–10884 (2017)
B. Jansi Rani, G. Ravi, R. Yuvakkumar, S. Ravichandran, F. Ameen, S. AlNadhary, Sn doped α-Fe2O3 (Sn=0,10,20,30 wt%) photoanodes for photoelectrochemical water splitting applications. Renew Energy 133, 566–574 (2019)
A. Lassoued, Synthesis and characterization of Zn-doped α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic activities. J. Mol. Struc. 1239, 130489 (2021)
M.T. Rahman, M.A. Hoque, G.T. Rahman, M.M. Azmi, M.A. Gafur, R.A. Khan, M.K. Hossain, Fe2O3 nanoparticles dispersed unsaturated polyester resin based nanocomposites: effect of gamma radiation on mechanical properties. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 174(5–6), 480–493 (2019)
N.H.A. Ngadiman, A. Idris, M. Irfan, D. Kurniawan, N.M. Yusof, R. Nasiri, γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles filled polyvinyl alcohol as potential biomaterial for tissue engineering scaffold. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 49, 90–104 (2015)
P Scherrer (1918). Bestimmung der Größe und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen Math Klasse, 29, 98–100
V.V. Jadhavar, V.D. Mote, B.S. Munde, Study of structural, optical, and paramagnetic properties of Zn1−xCoxS nanoparticles prepared via co-precipitation. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 17297–17306 (2020)
A. Badawi, Enhancement of the optical properties of PVP using Zn1-xSnxS for UV-region optical applications. Appl. Phys. A 127(1), 51 (2021)
A. Badawi, Engineering the energy bandgap of lead cobalt sulfide quantum dots for visible light optoelectronics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31(20), 17726–17735 (2020)
A. Badawi, A.H. Al Otaibi, A.M. Albaradi, N. Al-Hosiny, S.E. Alomairy, Tailoring the energy band gap of alloyed Pb1−xZnxS quantum dots for photovoltaic applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29(24), 20914–20922 (2018)
A. Badawi, Tunable energy band gap of Pb1-xCoxS quantum dots for optoelectronic applications. Superlattices Microstruct. 125, 237–246 (2019)
H.M.H. Zakaly, H.A. Saudi, S.A.M. Issa, M. Rashad, A.I. Elazaka, H.O. Tekin, Y.B. Saddeek, Alteration of optical, structural, mechanical durability and nuclear radiation attenuation properties of barium borosilicate glasses through BaO reinforcement: experimental and numerical analyses. Ceram. Int. 47(4), 5587–5596 (2021)
A. Badawi, Effect of the non-toxic Ag2S quantum dots size on their optical properties for environment-friendly applications. Phys E 109, 107–113 (2019)
R. Al-Gaashani, S. Radiman, N. Tabet, A.R. Daud, Rapid synthesis and optical properties of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanostructures using a simple thermal decomposition method. J. Alloy. Compd. 550, 395–401 (2013)
H.M. Zidan, E.M. Abdelrazek, A.M. Abdelghany, A.E. Tarabiah, Characterization and some physical studies of PVA/PVP filled with MWCNTs. J. Market. Res. 8(1), 904–913 (2019)
A.A. Atta, M.M. El-Nahass, K.M. Elsabawy, M.M. Abd El-Raheem, A.M. Hassanien, A. Al Huthali, A. Badawi, A. Merazga, Optical characteristics of transparent samarium oxide thin films deposited by the radio-frequency sputtering technique. Pramana 87(5), 72 (2016)
A. Bouzidi, K. Omri, W. Jilani, H. Guermazi, I.S. Yahia, Influence of TiO2 Incorporation on the Microstructure, Optical, and Dielectric Properties of TiO2/Epoxy Composites. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 28(3), 1114–1126 (2018)
O.G. Abdullah, S.B. Aziz, M.A. Rasheed, Structural and optical characterization of PVA:KMnO4 based solid polymer electrolyte. Results Phys. 6, 1103–1108 (2016)
N. Badi, Y. Al-Douri, S. Khasim, Effect of nitrogen doping on structural and optical properties of MgxZn1-xO ternary alloys. Opt. Mater. 89, 554–558 (2019)
K. Gherab, Y. Al-Douri, U. Hashim, R. Khenata, A. Bouhemadou, M. Ameri, Temperature effect to investigate optical and structural properties of AZO nanostructures for optoelectronics. Bull. Mater. Sci. 44(1), 39 (2021)
A. Badawi, S.S. Alharthi, H. Assaedi, A.N. Alharbi, M.G. Althobaiti, Cd0.9Co0.1S nanostructures concentration study on the structural and optical properties of SWCNTs/PVA blend. Chem. Phys. Lett. 775, 138701 (2021)
A. Badawi, Engineering the optical properties of PVA/PVP polymeric blend in situ using tin sulfide for optoelectronics. Appl. Phys. A 126(5), 335 (2020)
A. Badawi, S.S. Alharthi, H. Assaedi, N. Al-Hosiny, Effect of the solar irradiation on the structure and optical properties of Gafchromic films. Appl. Phys. A 127(4), 272 (2021)
Z.K. Heiba, M.B. Mohamed, A. Badawi, Structure, optical and electronic characteristics of iron-doped cadmium sulfide under nonambient atmosphere. Appl. Phys. A 127(3), 166 (2021)
H. Benamra, H. Saidi, A. Attaf, M.S. Aida, A. Derbali, N. Attaf, Physical properties of Al-doped ZnS thin films prepared by ultrasonic spray technique. Surf. Interfaces 21, 100645 (2020)
B. Yan, Y. Wang, T. Jiang, X. Wu, Synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic property of La-doped CuO nanostructures by electrodeposition method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27(5), 5389–5394 (2016)
P.K. Manoj, B. Joseph, V.K. Vaidyan, D.S.D. Amma, Preparation and characterization of indium-doped tin oxide thin films. Ceram. Int. 33(2), 273–278 (2007)
R. Ranjithkumar, A. Albert Irudayaraj, G. Jayakumar, A. Dhayal Raj, S. Karthick, R. Vinayagamoorthy, Synthesis and properties of CdO and Fe doped CdO nanoparticles. Mater. Today: Proc. 3(6), 1378–1382 (2016)
A.T. Ravichandran, A. Robert Xavier, K. Pushpanathan, B.M. Nagabhushana, R. Chandramohan, Structural and optical properties of Zn doped CdO nanoparticles synthesized by chemical precipitation method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27(3), 2693–2700 (2016)
Z.K. Heiba, M.B. Mohamed, H. El Shimy, A. Badawi, Modifying the electronic and optical properties of nano-ZnS via doping with Mn and Fe. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 12358–12370 (2021)
T. Ahmad, S. Khatoon, K. Coolahan, S.E. Lofland, Structural characterization, optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped CdO dilute magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. 28(9), 1245–1253 (2013)
E. Jalali-Moghadam, Z. Shariatinia, Al3+ doping into TiO2 photoanodes improved the performances of amine anchored CdS quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Mater. Res. Bull. 98, 121–132 (2018)
A. Javed, A. Qurat ul, M. Bashir, Controlled growth, structure and optical properties of Fe-doped cubic π- SnS thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 759, 14–21 (2018)
P. Velusamy, R. Ramesh Babu, K. Ramamurthi, E. Elangovan, J. Viegas, Effect of La doping on the structural, optical and electrical properties of spray pyrolytically deposited CdO thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 708, 804–812 (2017)
A. Moharana, D. Kumar, A. Kumar, Synthesis of Ni doped iron oxide nanoparticles and their dielectric properties. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1531, 012113 (2020)
K. Kaviyarasu, E. Manikandan, P. Paulraj, S.B. Mohamed, J. Kennedy, One dimensional well-aligned CdO nanocrystal by solvothermal method. J. Alloy. Compd. 593, 67–70 (2014)
H. Lin, J. Long, Q. Gu, W. Zhang, R. Ruan, Z. Li, X. Wang, In situ IR study of surface hydroxyl species of dehydrated TiO2: towards understanding pivotal surface processes of TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation of toluene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14(26), 9468–9474 (2012)
A. Singh, V. Goyal, J. Singh, M. Rawat, Structural, morphological, optical and photocatalytic properties of green synthesized TiO2 NPs. Current Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 3, 100033 (2020)
P. Concepción, in Infrared Spectroscopy - Principles, Advances, and Applications (IntechOpen, 2018).
R. Mehdizadeh, L.A. Saghatforoush, S. Sanati, Solvothermal synthesis and characterization of α-Fe2O3 nanodiscs and Mn3O4 nanoparticles with 1,10-phenanthroline. Superlattices Microstruct. 52(1), 92–98 (2012)
R. Kant, D. Kumar, V. Dutta, High coercivity α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles prepared by continuous spray pyrolysis. RSC Adv. 5(65), 52945–52951 (2015)
S.A. Mansour, A.H. Farha, M.F. Kotkata, Sol–gel synthesized Co-doped anatase TiO2 Nanoparticles: structural, optical, and magnetic characterization. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 29(4), 1375–1382 (2019)
A. El Mragui, Y. Logvina, L. Pinto da Silva, Synthesis of Fe- and Co-doped TiO(2) with improved photocatalytic activity under visible irradiation toward carbamazepine degradation. Materials 12(23), 3874 (2019)
A. Badawi, N. Al-Hosiny, S. Abdallah, S. Negm, H. Talaat, Tuning photocurrent response through size control of CdTe quantum dots sensitized solar cells. Sol. Energy 88, 137–143 (2013)
M. Thambidurai, N. Muthukumarasamy, A. Ranjitha, D. Velauthapillai, Structural and optical properties of Ga-doped CdO nanocrystalline thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 86, 559–563 (2015)
A. Garzon-Roman, C. Zuñiga-Islas, E. Quiroga-González, Immobilization of doped TiO2 nanostructures with Cu or In inside of macroporous silicon using the solvothermal method: morphological, structural, optical and functional properties. Ceram. Int. 46(1), 1137–1147 (2020)
P.K. Chakraborty, G.C. Datta, K.P. Ghatak, The simple analysis of the Burstein-Moss shift in degenerate n-type semiconductors. Physica B 339(4), 198–203 (2003)
C. Aydın, O.A. Al-Hartomy, A.A. Al-Ghamdi, F. Al-Hazmi, I.S. Yahia, F. El-Tantawy, F. Yakuphanoglu, Controlling of crystal size and optical band gap of CdO nanopowder semiconductors by low and high Fe contents. J. Electroceram. 29(2), 155–162 (2012)
R. Leelavati, R. Kumar, Kumar, Structural and optical studies of Mn2+ substituted CdO nano-particles. Appl. Phys. A 127(4), 249 (2021)
S.H. Mohamed, R. Drese, Structural and optical properties of direct current sputtered zinc aluminum oxides with a high Al concentration. Thin Solid Films 513(1), 64–71 (2006)
S.H. Mohamed, O. Kappertz, J.M. Ngaruiya, T. Niemeier, R. Drese, R. Detemple, M.M. Wakkad, M. Wuttig, Influence of nitrogen content on properties of direct current sputtered TiOxNy films. Physica Status Solidi (a) 201(1), 90–102 (2004)
A.A. Aboud, A. Mukherjee, N. Revaprasadu, A.N. Mohamed, The effect of Cu-doping on CdS thin films deposited by the spray pyrolysis technique. J. Market. Res. 8(2), 2021–2030 (2019)
H. Ben Jbara, D. Abdelkader, F. Chaffar Akkari, M. Kanzari, M. Arab Pour Yazdi, A. Billard, Preparation of Cu–Fe–O thin films via post oxidation of iron/copper bilayers: structural, optical and electrical properties. Optic. Quantum Electro. 51(4), 99 (2019)
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/248), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badawi, A., Althobaiti, M.G., Alharthi, S.S. et al. Effect of zinc doping on the structure and optical properties of iron oxide nanostructured films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. Appl. Phys. A 128, 123 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05154-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05154-9