Abstract
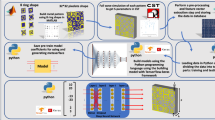
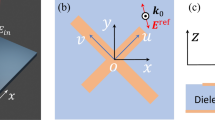
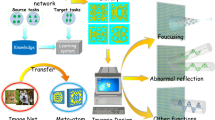
Compared to the conventional metasurface design, machine learning-based methods have recently created an inspiring platform for an inverse realization of the metasurfaces. Here, we have used the Deep Neural Network (DNN) for the generation of desired output unit cell structures for both TE and TM polarized waves which its working frequency can reach up to 45 GHz. To automatically generate metasurfaces over wide frequencies, we deliberately design 8 annular models; thus, each generated meta-atoms in our dataset can produce different notches in our desired working frequency. Compared to the general approach, whereby the final metasurface structure may be formed by any randomly distributed “0” and “1”, we propose here a confined output configuration. By confining the output, the number of calculations will be decreased and the learning speed will be increased. Establishing a DNN-confined output configuration based on the input data for both TE and TM polarized waves is the novelty to generate the desired metasurface structure for dual orthogonal polarizations. Moreover, we have demonstrated that our network can attain an accuracy of 92%. Obtaining the final unit cell directly without any time-consuming optimization algorithms for both TE and TM polarized waves, and high average accuracy, open beneficial ways for the inverse metasurface design; thus, the designer is required only to focus on the design goal.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
H. Rajabalipanah, A. Abdolali, J. Shabanpour, A. Momeni, A. Cheldavi, Asymmetric spatial power dividers using phaseamplitude metasurfaces driven by Huygens principle. ACS Omega 4, 14340–14352 (2019)
J. Shabanpour, Full manipulation of the power intensity pattern in a large space-time digital metasurface: from arbitrary multibeam generation to harmonic beam steering scheme. Ann. Phys. 532, 2000321 (2020)
M. Di Renzo, et al. Smart radio environments empowered by reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: How it works, state of research, and the road ahead. IEEE J. Selected Areas Commun. 38.11, 2450–2525 (2020)
M. Di Renzo, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces versus relaying: differences, similarities, and performance comparison. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 1, 798–807 (2020)
J. Shabanpour, Programmable anisotropic digital metasurface for independent manipulation of dual-polarized THz waves based on a voltage-controlled phase transition of VO 2 microwires. J. Mater. Chem. 8, 7189–7199 (2020)
J. Shabanpour, S. Beyraghi, A. Cheldavi, Ultrafast reprogrammable multifunctional vanadium-dioxide-assisted metasurface for dynamic THz wavefront engineering. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–14 (2020)
J. Shabanpour, S. Beyraghi, F. Ghorbani, H. Oraizi, Implementation of conformal digital metasurfaces for THz polarimetric sensing. OSA Continuum 4, 1372–1380 (2021)
J. Shabanpour, et al. Real-time multi-functional near-infrared wave manipulation with a 3-bit liquid crystal based coding metasurface. Opt. Express 29.10, 14525–14535 (2021)
N.I. Landy, S. Sajuyigbe, J.J. Mock, D.R. Smith, W.J. Padilla, Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 207402 (2008)
J. Shabanpour, S. Beyraghi, H. Oraizi, Reconfigurable honeycomb metamaterial absorber having incident angular stability. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–8 (2020)
Gu, M., & Goi, E. Holography enabled by artificial intelligence. In Holography, Diffractive Optics, and Applications X (Vol. 11551, p. 1155102). International Society for Optics and Photonics (2020)
F. Ghorbani, et al. Deep neural network-based automatic metasurface design with a wide frequency range. Sci. Rep. 11.1, 1–8 (2021)
F. Ghorbani, et al. EEGsig: an open-source machine learning-based toolbox for EEG signal processing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.12877 (2020)
F. Ghorbani, S. Hossein, S. Mohammad, Deep learning approach for target locating in through-the-wall radar under electromagnetic complex wall. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.07990 (2021)
S. An et al., A deep learning approach for objective-driven all-dielectric metasurface design. ACS Photon. 6, 3196–3207 (2019)
L. Cui, Y. Zhang, R. Zhang, Q.H. Liu, A modified efficient KNN method for antenna optimization and design. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68, 6858–6866 (2020)
Y. Sharma, H.H. Zhang, H. Xin, Machine learning techniques for optimizing design of double T-shaped monopole antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68, 5658–5663 (2020)
A. Bacigalupo, et al., Machine-learning techniques for the optimal design of acoustic metamaterials. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1–24 (2019)
R.-T. Wu, et al., Design of one-dimensional acoustic metamaterials using machine learning and cell concatenation. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 1–25 (2021)
H.M. Yao, et al., Machine learning methodology review for computational electromagnetics. 2019 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium-China (ACES). Vol. 1. IEEE, 2019
H.M. Yao, E. I. Wei, J. Lijun, Two-step enhanced deep learning approach for electromagnetic inverse scattering problems. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 18.11, 2254–2258 (2019)
T. Qiu et al., Deep learning: a rapid and efficient route to automatic metasurface design. Adv. Sci. 6, 1900128 (2019)
Q. Zhang et al., Machine-learning designs of anisotropic digital coding metasurfaces. Adv. Theory Simul. 2, 1800132 (2019)
T. Shan, X. Pan, M. Li, S. Xu, F. Yang, Coding programmable metasurfaces based on deep learning techniques. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Topics Power Electron 10, 114–125 (2020)
X. Shi, T. Qiu, J. Wang, X. Zhao, S. Qu, Metasurface inverse design using machine learning approaches. J. Phys. D. 53, 275105 (2020)
I. Sajedian, H. Lee, J. Rho, Double-deep Q-learning to increase the efficiency of metasurface holograms. Sci. Rep. 9, 1–8 (2019)
Y. Kiarashinejad, A. Sajjad, A. Ali, Deep learning approach based on dimensionality reduction for designing electromagnetic nanostructures. npj Comput. Mater. 6.1, 1–12 (2020)
M.V. Zhelyeznyakov, S. Brunton, A. Majumdar, Deep learning to accelerate scatterer-to-field mapping for inverse design of dielectric metasurfaces. ACS Photon. 8(2), 481–488 (2021)
C. Yeung, et al., Elucidating the behavior of nanophotonic structures through explainable machine learning algorithms. ACS Photon. 7.8, 2309–2318 (2020)
J. Jiaqi, C. Mingkun, A.F. Jonathan, Deep neural networks for the evaluation and design of photonic devices. Nat. Rev. Mater. 1–22 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no con ict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghorbani, F., Shabanpour, J., Beyraghi, S. et al. A deep learning approach for inverse design of the metasurface for dual-polarized waves. Appl. Phys. A 127, 869 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05030-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05030-6