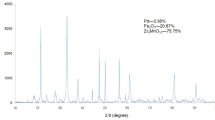
Abstract
Fabrication of gas sensors is witnessing great advancements due to recent progress in synthesis of metal-oxide nanoparticles with custom designed characteristics. Composition of nanoparticles allows access to the chemical features of the surface nanoparticles and utilization of physical features of the core nanoparticles. Furthermore, it enables formation of p − n heterojunctions among nanoparticles with depletion layers that enables to control the follow of charge carriers. Herein, nanoparticles of Fe3O4 and PdO are synthesized using a coprecipitation process and explored for their implementation for gas sensor applications. The mean grain sizes are 7.7 ∓ 2.3 nm and 6.4 ∓ 1.5 nm for Fe3O4 and PdO, respectively. The sensor devices are produced by depositing nanoparticles (dispersed) on substrates with pre-deposited interdigitated electrodes. Electrical characteristics are examined using impedance spectroscopy that enables calculation of the activation energy Ea = 0.66 ± 0.04 eV. The produced sensors are selective for both H2 and H2S within different concentration ranges, where their minimum responses at ambient temperature are 1200 and 10 ppm for H2 and H2S gases, respectively. The gas sensor devices fabricated in this work exhibit potential for practical implementation because of their numerous advantages that incorporate simplified fabrication technique, low power consumption due to their functionality at ambient temperature, extraordinary sensitivity, practical response time, as well as their core that consists of magnetic nanoparticles which simplify their recycling.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Haija, M. Chamakh, I. Othman, F. Banat, A.I. Ayesh, Fabrication of H2S gas sensors using ZnxCu1-xFe2O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 126, 489 (2020)
W. Jaeschke, H. Claude, J. Herrmann, Sources and sinks of atmospheric H2S. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans 85, 5639–5644 (1980)
A.I. Ayesh, A.A. Alyafei, R.S. Anjum, R.M. Mohamed, M.B. Abuharb, B. Salah, M. El-Muraikhi, Production of sensitive gas sensors using CuO/SnO 2 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 125, 1–8 (2019)
A.I. Ayesh, A.F. Abu-Hani, S.T. Mahmoud, Y. Haik, Selective H2S sensor based on CuO nanoparticles embedded in organic membranes. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 231, 593–600 (2016)
A.F. Abu-Hani, Y.E. Greish, S.T. Mahmoud, F. Awwad, A.I. Ayesh, Low-temperature and fast response H2S gas sensor using semiconducting chitosan film. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 253, 677–684 (2017)
M.A. Haija, A.F. Abu-Hani, N. Hamdan, S. Stephen, A.I. Ayesh, Characterization of H2S gas sensor based on CuFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 690, 461–468 (2017)
R.B. Gupta, Hydrogen fuel: Production, Transport, and Storage, Crc Press, 2008
A.I. Ayesh, S.T. Mahmoud, S.J. Ahmad, Y. Haik, Novel hydrogen gas sensor based on Pd and SnO2 nanoclusters. Mater. Lett. 128, 354–357 (2014)
A.I. Ayesh, Linear hydrogen gas sensors based on bimetallic nanoclusters. J. Alloy. Compd. 689, 1–5 (2016)
M.A. Haija, A.I. Ayesh, S. Ahmed, M.S. Katsiotis, Selective hydrogen gas sensor using CuFe2O4 nanoparticle based thin film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 369, 443–447 (2016)
J. Van Lith, A. Lassesson, S. Brown, M. Schulze, J. Partridge, A. Ayesh, A hydrogen sensor based on tunneling between palladium clusters. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 181910 (2007)
G.A. Poda, Hydrogen sulfide can be handled safely, archives of environmental health: an. Int. J. 12, 795–800 (1966)
A.I. Ayesh, Metal/metal-oxide nanoclusters for gas sensor applications. J. Nanomater. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2359019
A.I. Ayesh, M.A. Haija, A. Shaheen, F. Banat, Spinel ferrite nanoparticles for H2S gas sensor. Appl. Phys. A 123, 682 (2017)
M. Rosenberg, G. Kulkarni, A. Bosy, C. McCulloch, Reproducibility and sensitivity of oral malodor measurements with a portable sulphide monitor. J. Dent. Res. 70, 1436–1440 (1991)
E. Comini, G. Faglia, G. Sberveglieri, Z. Pan, Z.L. Wang, Stable and highly sensitive gas sensors based on semiconducting oxide nanobelts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 1869–1871 (2002)
M. Gaidi, Nanostructured SnO 2 thin films: effects of porosity and catalytic metals on gas-sensing sensitivity. Appl. Phys. A 124, 725 (2018)
E.R. Kumar, P.S.P. Reddy, G.S. Devi, S. Sathiyaraj, Structural, dielectric and gas sensing behavior of Mn substituted spinel MFe2O4 (M=Zn, Cu, Ni, and Co) ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 398(2016), 281–288 (2016)
Y. Wu, N. Huang, J. Wang, Sensitive characteristics of ZnO nano gas sensor based on dynamic temperature modulation. Results Phys. 18, 103241 (2020)
C.-J. Huang, F.-M. Pan, H.-Y. Chen, Li-Chang, Growth and photoresponse study of PdO nanoflakes reactive-sputter deposited on SiO 2. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 053105 (2010)
J. Hinojosa, A. Jose, H.H. Kan, J.F. Weaver, Molecular chemisorption of O2 on a PdO (101) thin film on Pd (111). J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 8324–8331 (2008)
S. Specchia, E. Finocchio, G. Busca, P. Palmisano, V. Specchia, Surface chemistry and reactivity of ceria–zirconia-supported palladium oxide catalysts for natural gas combustion. J. Catal. 263, 134–145 (2009)
T. Nunome, H. Irie, N. Sakamoto, O. Sakurai, K. Shinozaki, H. Suzuki, N. Wakiya, Magnetic and photocatalytic properties of n-and p-type ZnFe2O4 particles synthesized using ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 121, 26–30 (2013)
H. Singh, J. Du, P. Singh, G.T. Mavlonov, T.H. Yi, Development of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via direct conjugation with ginsenosides and its in-vitro study. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 185, 100–110 (2018)
N. Nakagiri, M. Manghnani, L. Ming, S. Kimura, Crystal structure of magnetite under pressure. Phys. Chem. Miner. 13, 238–244 (1986)
O. Glemser, G. Peuschel, Beitrag zur kenntnis des systems PdO/H2O. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 281, 44–53 (1955)
L.A. Al-Sulaiti, B. Salah, A.I. Ayesh, Investigation of flexible polymer-Tl2O3 nanocomposites for x-ray detector applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 489, 351–357 (2019)
V. Josh, M.Y. Haik, A.I. Ayesh, M.A. Mohsin, Y. Haik, Electrical properties of sorbitol doped PVA-PAA polymer membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 128, 3861–3869 (2012)
A.I. Ayesh, Electronic transport in Pd nanocluster devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 133108 (2011)
A. Shaheen, M.A. Haija, M. Chamakh, G.A. Assayed, F. Banat, A.I. Ayesh, Fabrication and characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol)–Glycerol–Spinel ferrites flexible membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 137(24), 48821 (2019)
M. Chamakh, A.I. Ayesh, M.F. Gharaibeh, Fabrication and characterization of flexible ruthenium oxide-loaded polyaniline/poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 137(38), 49125 (2020)
A.I. Ayesh, A.F.S. Abu-Hani, S.T. Mahmoud, Y. Haik, Selective H2S sensor based on CuO nanoparticles embedded in organic membranes. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 231, 593–600 (2016)
N. Yamazoe, New approaches for improving semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 5, 7–19 (1991)
N.D. Hoa, N. Van Quy, H. Jung, D. Kim, H. Kim, S.-K. Hong, Synthesis of porous CuO nanowires and its application to hydrogen detection. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 146, 266–272 (2010)
A. Chapelle, M.H. Yaacob, I. Pasquet, L. Presmanes, A. Barnabé, P. Tailhades, J.D. Plessis, K. Kalantar-zadeh, Structural and gas-sensing properties of CuO–CuxFe3−xO4 nanostructured thin films. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 153, 117–124 (2011)
A.I. Ayesh, A.A. Alyafei, R.S. Anjum, R.M. Mohamed, M.B. Abuharb, B. Salah, M. El-Muraikhi, Production of sensitive gas sensors using CuO/SnO 2 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 125, 550 (2019)
F.E. Annanouch, Z. Haddi, S. Vallejos, P. Umek, P. Guttmann, C. Bittencourt, E. Llobet, Aerosol-assisted CVD-grown WO3 nanoneedles decorated with copper oxide nanoparticles for the selective and humidity-resilient detection of H2S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 6842–6851 (2015)
C. Wang, Y. Zhang, X. Sun, Y. Sun, F. Liu, X. Yan, C. Wang, P. Sun, G. Lu, Preparation of Pd/PdO loaded WO3 microspheres for H2S detection. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 321, 128629 (2020)
C. Balamurugan, Y.J. Jeong, D.W. Lee, Enhanced H2S sensing performance of a p-type semiconducting PdO-NiO nanoscale heteromixture. Appl. Surf. Sci. 420, 638–650 (2017)
N.S. Ramgir, C.P. Goyal, P.K. Sharma, U.K. Goutam, S. Bhattacharya, N. Datta, M. Kaur, A.K. Debnath, D.K. Aswal, S.K. Gupta, Selective H2S sensing characteristics of CuO modified WO3 thin films. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 188, 525–532 (2013)
J. Liu, X. Huang, G. Ye, W. Liu, Z. Jiao, W. Chao, Z. Zhou, Z. Yu, H2S Detection sensing characteristic of CuO/SnO2 sensor. Sensors 3, 110–118 (2003)
Y.-J. Chen, F.-N. Meng, H.-L. Yu, C.-L. Zhu, T.-S. Wang, P. Gao, Q.-Y. Ouyang, Sonochemical synthesis and ppb H2S sensing performances of CuO nanobelts. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 176, 15–21 (2013)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration, Hydrogen Sulfide, in: Safety and Health Topics, United States Department of Labour USA
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Qatar University under Grant Number, IRCC-2019-003. The TEM, SEM, EDS, and XRD measurements were accomplished in the Central Laboratories unit at Qatar University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayesh, A.I., Salah, B. Production of selective gas sensors based on nanoparticles of PdO/Fe3O4. Appl. Phys. A 127, 843 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05004-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05004-8