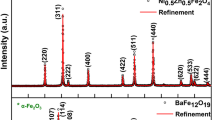
Abstract
In this article, we report on the synthesis as well as structure, microstructure, and magnetic properties of nanocomposites NiFe2O4/PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 (NFO/PZT) with weight ratio (40%(NFO):60%(PZT)). They are synthesized in two types of connectivity (0–0) and (0–3) connectivity by standard mixing and modified two-step sol–gel techniques, respectively. Single-phase NFO and PZT are also prepared by sol–gel and hydrothermal techniques, respectively. This study aims to merely understand the effect of different connectivity on the composite properties. X-ray and electron diffraction results confirm the presence of tetragonal and cubic phases for PZT and NFO, respectively, in (0–0) and (0–3) 0.4NFO/0.6PZT nanocomposites. The size-strain analysis results showed that (0–3) 0.4NFO/0.6PZT has a higher microstrain than (0–0) 0.4NFO/0.6PZT. The microstructural and morphological properties were recognized by high-resolution transmission electron microscope. The spectrums of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and magnetic properties are affected by the difference in the connectivity. The saturation magnetization Ms of (0–3) 0.4NFO/0.6PZT is higher than (0–0) 0.4NFO/0.6PZT, while the coercive field Hc of (0–3) 0.4NFO/0.6PZT is lower than (0–0) 0.4NFO/0.6PZT due to the lower value of porosity. Also, the relative initial permeability of (0–3) 0.4NFO/0.6PZT is higher than the (0–0) 0.4NFO/0.6PZT, and the Curie temperatures of both nanocomposites are significantly increased relative to the single-phase NFO. In general, the (0–3) connectivity shows remarkable physical and magnetic properties over the (0–0) connectivity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Lottermoser, D. Meier, Phys. Sci. Rev. 6, 2 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1515/psr-2020-0032
M. Yu, J. Hu, J. Liu, S. Li, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 326, 31 (2013)
N. Hur, S. Park, P.A. Sharma, J.S. Ahn, S. Guha, S.-W. Cheong, Nature 429, 392 (2004)
N.A. Hill, J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 6694 (2000)
R.E. Newnham, D.P. Skinner, L.E. Cross, Mater. Res. Bull. 13, 525 (1978)
K. UCHINO, Advanced Piezoelectric Materials Woodhead Publishing Limited, Abington Hall, Granta Park, Great Abington, Cambridge CB21 6AH, UK (2010)
M.I. Bichurin, Magnetoelectric Composites, 1st edn. (Jenny Stanford Publishing, 2019)
A.A. Bukharaev, A.K. Zvezdin, A.P. Pyatakov, Y.K. Fetisov, Uspekhi Fiz. Nauk 188, 1288 (2018)
M.M. Vijatović-Petrović, A. Džunuzović, J.D. Bobić, N. Ilić, I. Stijepović, B.D. Stojanović, Process. Appl. Ceram. 14, 9 (2020)
J. Zhang, W. Zhu, D. Chen, H. Qu, P. Zhou, M. Popov, L. Jiang, L. Cao, G. Srinivasan, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 473, 131 (2019)
N. Barrett, I. Gueye, G. Le Rhun, O. Renault, E. Defay, Thin Solid Films 715, 138423 (2020)
M. Atif, S. Ahmed, M. Nadeem, M.N. Khan, J. Alloys Compd. 735, 880 (2018)
J.H. Peng, M. Hojamberdiev, H.Q. Li, D.L. Mao, Y.J. Zhao, P. Liu, J.P. Zhou, G.Q. Zhu, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 378, 298 (2015)
M.A. Ashmawy, A.A. Sattar, H.M. El-Sayed, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1253, 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1253/1/012017
R. Pandey, B.R. Meena, A.K. Singh, J. Alloys Compd. 593, 224 (2014)
X. Yao, Y. Yang, J.-P. Zhou, X.-M. Chen, P.-F. Liang, C. You, J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 51, 55002 (2018)
X. Yao, Y. Yang, X.-L. Zhang, Q. Liu, J.-P. Zhou, X.-M. Chen, G.-B. Zhang, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 501, 166410 (2020)
J.-L. Chen, Z. Xu, S.-B. Qu, X.-Y. Wei, X.-H. Liu, Ceram. Int. 34, 803 (2008)
T. Cheng, L.F. Xu, P.B. Qi, C.P. Yang, R.L. Wang, H.B. Xiao, J. Alloys Compd. 602, 269 (2014)
C. Elena, M. Airimioaei, V. Nica, L.M. Hrib, O.F. Caltun, A.R. Iordan, C. Galassi, L. Mitoseriu, M. N. Palamaru 32, 3325 (2012)
M. Zeng, J.G. Wan, Y. Wang, H. Yu, J.M. Liu, X.P. Jiang, C.W. Nan, J. Appl. Phys. 95, 8069 (2004)
V.M. Laletin, N.N. Poddubnaya, Tech. Phys. Lett. 43, 114 (2017)
R.A. Islam, V. Bedekar, N. Poudyal, J.P. Liu, S. Priya, J. Appl. Phys. 104, 8 (2008)
D. Wu, W. Gong, H. Deng, M. Li, J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 40, 5002 (2007)
W.R. Agami, M.A. Ashmawy, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 126, 1 (2020)
R.M. Piticescu, R.R. Piticescu, D. Taloi, V. Badilita, Nanotechnology 14, 312 (2003)
B. Su, T.W. Button, C. B. Ponton 9, 6439 (2004)
G. Xu, W. Jiang, M. Qian, X. Chen, Z. Li, G. Han, Cryst. Growth Des. 9, 13 (2009)
V. Corral-Flores, D. Bueno-Baqués, R.F. Ziolo, Acta Mater. 58, 764 (2010)
J.B. Nelson, D.P. Riley, Proc. Phys. Soc. 57, 160 (1945)
Dipti, J.K. Juneja, S. Singh, K.K. Raina, R.K. Kotnala, C. Prakash, Ferroelectr. Lett. Sect. 42, 97 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/07315171.2015.1026201
S.N. Kallaev, G.G. Gadzhiev, I.K. Kamilov, Z.M. Omarov, S.A. Sadykov, L.A. Reznichenko, Phys. Solid State 48, 1169 (2006)
W.R. Agami, M.A. Ashmawy, A.A. Sattar, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23, 604 (2014)
C.P. Fernández, F.L. Zabotto, D. Garcia, R.H.G.A. Kiminami, Ceram. Int. 42, 3239 (2016)
E.B. Araújo, C.A. Guarany, K. Yukimitu, J.C.S. Moraes, J.A. Eiras, Ferroelectrics 337, 145 (2006)
J.T. Last, Phys. Rev. 105, 1740 (1957)
B. Himmetoglu, A. Janotti, H. Peelaers, A. Alkauskas, C.G. Van De Walle, Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 90, 1 (2014)
S. Sahoo, M.S. Hu, C.W. Hsu, C.T. Wu, K.H. Chen, S. Sahoo, M.S. Hu, C.W. Hsu, C.T. Wu, K.H. Chen, L.C. Chen, A.K. Arora, S. Dhara, Appl. Phys. Lett 93, 233116 (2008)
R.D. Waldron, Phys. Rev. 99, 1727 (1955)
B. D. Cullity and C. D. Graham, Introduction to Magnetic Materials, Wiley (2011).
V. Šepelák, I. Bergmann, A. Feldhoff, P. Heitjans, F. Krumeich, D. Menzel, F.J. Litterst, S.J. Campbell, K.D. Becker, J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 5026 (2007)
J. Smit and H. P. J. Wijn, Ferrites (N. V. Philips (Holland), 1959).
W.H. Gong, M. Li, Z. Shi, H.J. Deng, C.W. Nan, Key Eng. Mater. 336–338, 238 (2007)
Z.P. Niu, Y. Wang, F.S. Li, J. Mater. Sci. 41, 5726 (2006)
G. Srinivasan, R. Hayes, C.P. DeVreugd, V.M. Laletsin, N. Paddubnaya, Appl. Phys. A 80, 891 (2003)
O.M. Hemeda, A. Tawfik, A. Al-Sharif, M.A. Amer, B.M. Kamal, D.E. El Refaay, M. Bououdina, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 4118 (2012)
J.-P. Zhou, L. Lv, Q. Liu, Y.-X. Zhang, P. Liu, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 13, 045001 (2012)
Funding
This work was not funded by any institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashmawy, M.A., Sattar, A.A. & El-Sayed, H.M. Physical and magnetic properties for two types of connectivity of NiFe2O4/PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 (NFO/PZT) composite. Appl. Phys. A 127, 566 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04711-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04711-6