Abstract
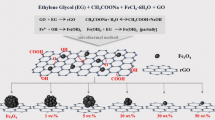
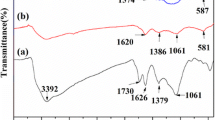
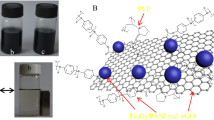
The three-dimensional Fe3O4/rGO/ZnO composite was successfully fabricated with a two-step method. Particularly, with rGO as the substrate, spindle-shaped ZnO nanorods and magnetic nanoparticles Fe3O4 are uniformly dispersed on the surface of rGO. Various equipments are used to test the structure, morphology and performance of the composite. Compared with single Fe3O4 nanoparticles and Fe3O4/rGO composite, the Fe3O4/rGO/ZnO composite has excellent EMWA performance. The minimum RL of the Fe3O4/rGO/ZnO composite is − 58.7 dB and the effective absorption bandwidth less than − 10 dB is 5.4 GHz (effective absorption bandwidth, RL ≤ − 10 dB, 12.6–18.0 GHz) with a thickness of 2 mm. It is believed that multi-layered hierarchical Fe3O4/rGO/ZnO composite can be used as an electromagnetic wave absorber and is a prospective material in these technical fields.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Yang, Y. Zhang, M. Li, L. Yang, J. Liu, Y. Hou et al., Surface architecture of Ni-based metal organic framework hollow spheres for adjustable microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2(12), 7888–7897 (2019)
X. Cui, X. Liang, J. Chen, W. Gu, G. Ji, Y. Du, Customized unique core-shell Fe2N@N-doped carbon with tunable void space for microwave response. Carbon 156, 49–57 (2020)
Q. Liu, Q. Cao, H. Bi, C. Liang, K. Yuan, W. She et al., CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 28(3), 486–490 (2016)
N. Yang, Z.X. Luo, S.C. Chen, G. Wu, Y.Z. Wang, Fe3O4 nanoparticle/N-Doped carbon hierarchically hollow microspheres for broadband and high-performance microwave absorption at an ultralow filler loading. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(16), 18952–18963 (2020)
D. Liu, Y. Du, F. Wang, Y. Wang, L. Cui, H. Zhao et al., MOFs-derived multi-chamber carbon microspheres with enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 157, 478–485 (2020)
D. Xu, J. Liu, P. Chen, Q. Yu, J. Wang, S. Yang et al., In situ growth and pyrolysis synthesis of super-hydrophobic graphene aerogels embedded with ultrafine β-Co nanocrystals for microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 7(13), 3869–3880 (2019)
J.B. Cheng, H.G. Shi, M. Cao, T. Wang, Y.Z. Wang, Porous carbon materials for microwave absorption. Mater. Adv. 8(1), 2631–2645 (2020)
J. Li, S. Yang, P. Jiao, Q. Peng, W. Yin, Y. Yuan et al., Three-dimensional macroassembly of hybrid C@CoFe nanoparticles/reduced graphene oxide nanosheets towards multifunctional foam. Carbon 157, 427–436 (2020)
I. Abdalla, A. Elhassan, J.Y. Yu, Z.L. Li, B. Ding, A hybrid comprised of porous carbon nanofibers and rGO for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 157, 703–713 (2020)
D. Liu, Y. Du, P. Xu, F. Wang, X. Han, Rationally designed hierarchical N-doped carbon nanotubes wrapping waxberry-like Ni@C microspheres for efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 5086–5096 (2021)
C. Ji, Y. Liu, Y. Li, X. Su, J. Xu, L. Lu, Facile preparation and excellent microwave absorption properties of cobalt-iron/porous carbon composite materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 20(527), 167776 (2021)
X. Zhang, X. Ren, C. Wang, N. Chen, N. Song, Synthesis of layered Fe3O4 nanodisk and nanostructure dependent microwave absorption property. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 4404–4415 (2021)
M. Green, A.T.V. Tran, R. Smedley, A. Roach, X. Chen, Microwave absorption of magnesium/hydrogen-treated titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Nano Mater. Sci. 1(1), 48–59 (2019)
T.S. Mahule, J. Das, V.V. Srinivasu, Low-field microwave absorption in Zn(1–x)(Mn:Fe(Ni))xO (x=0.02) system: hysteresis, line shapes and powdering effects. Appl. Phys. A 125(4), 231 (2019)
M.Y. Kong, Z.R. Jia, B.B. Wang, J.L. Dou, G.L. Wu, Construction of metal-organic framework derived Co/ZnO/Ti3C2Tx composites for excellent microwave absorption. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 26(14), 00219 (2020)
M.T. Qiao, D. Wei, X.W. He, X.F. Lei, Q.Y. Zhang, Novel yolk–shell Fe3O4@void@SiO2@PPy nanochains toward microwave absorption application. J. Mater. Sci. 56(2), 1–16 (2021)
M. Cai, A. Shui, X. Wang, C. He, B. Du, A facile fabrication and high-performance electromagnetic microwave absorption of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 842, 155638 (2020)
M. Qiao, J. Li, D. Wei, X. He, X. Lei, J. Wei et al., Chain-like Fe3O4@void@mSiO2@MnO2 composites with multiple porous shells toward highly effective microwave absorption application. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 314, 110867 (2021)
Y.H. Cui, K. Yang, J.Q. Wang, T. Shah, B.L. Zhang, Preparation of pleated RGO/MXene/Fe3O4 microsphere and its absorption properties for electromagnetic wave. Carbon 172, 1–14 (2021)
F. Ebrahimi Tazangi, H. Hekmatara, Y.J. Seyed, Remarkable microwave absorption of GO-SiO2/Fe3O4 via an effective design and optimized composition. J. Alloy. Compd. 854, 157213 (2021)
Y. Liang, Y. Yuan, B. Wang, Y. Wang, S. Wei, Microstructure and microwave absorption properties of ZnO with different surfactants by hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 6, 1–11 (2021)
G.H. He, Y.P. Duan, H.F. Pang, J.J. Hu, Superior microwave absorption based on ZnO capped MnO2 Nanostructures. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 7(15), 2000407 (2020)
L. Zhou, J. Yu, M. Chen, H. Wang, X. Su, Influence of particle size on the microwave absorption properties of FeSiAl/ZnO-filled resin composite coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(3), 2446–2453 (2020)
J.H. Luo, K. Zhang, M.L. Cheng, M.M. Gu, X.K. Sun, MoS2 spheres decorated on hollow porous ZnO microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 380, 122625 (2020)
J.S. Li, H. Huang, Y.J. Zhou, C.Y. Zhang, Z.T. Li, Research progress of graphene-based microwave absorbing materials in the last decade. J. Mater. Res. 32, 1–18 (2017)
Q.L. Sun, Y.Y. Cai, L. Sun, W. Ye, X.Y. Long, S.J. Xu et al., Preparation of sandwich-like CNs@rGO nanocomposites with enhanced microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Sci. 56(2), 1492–1503 (2021)
F. Li, L. Zhuang, W.W. Zhan, M.X. Zhou, X.P. Yang, Desirable microwave absorption performance of ZnFe2O4@ZnO@rGO nanocomposites based on controllable permittivity and permeability. Ceram. Int. 46(13), 21744–21751 (2020)
Z.H. Du, X.B. Chen, Y.W. Zhang, X.Y. Que, M.L. Zhai, One-pot hydrothermal preparation of Fe3O4 decorated graphene for microwave absorption. Materials 13(14), 3065 (2020)
H. Han, Z.B. Zhao, Z. Quan, Y. Gogotsi, J.S. Qiu, The role of microwave absorption on formation of graphene from graphite oxide. Carbon 50(9), 3267–3273 (2012)
Y.C. Yin, H. Zhang, Y. Li, N.N. Yang, G.K. Wei, Facile synthesis of monodisperse ultrasmall Fe3O4 nanoparticles on graphene nanosheets with excellent microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04954-8
C. Wu, Z.F. Chen, M.L. Wang, X. Cao, Y.Z. Huang, Microwave absorption: confining tiny MoO2 clusters into reduced graphene oxide for highly efficient low frequency microwave absorption. Small 16(30), 2001686 (2020)
X.F. Liu, Y.X. Chen, C.C. Hao, J.R. Ye, R.H. Yu, D.Q. Huang, Graphene-enhanced microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4/SiO2 nanorods. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 89, 40–46 (2016)
H.Q. Zhao, Y. Cheng, Z. Zhang, B.S. Zhang, G.B. Ji, Biomass-derived graphene-like porous carbon nanosheets towards ultralight microwave absorption and excellent thermal infrared properties. Carbon 173, 501–511 (2021)
D.D. Zhi, T. Li, J.Z. Li, H.S. Ren, F.B. Meng, A review of three-dimensional graphene-based aerogels: synthesis, structure and application for microwave absorption. Compos. B Eng. 211, 108642 (2021)
D.J. Zhang, Y.J. Liao, Z.H. Wang, X.F. Zhang, Z.P. Wang, Highly ordered, ultralight three-dimensional graphene-like carbon for high-frequency electromagnetic absorption. J. Mater. Sci. 56(6), 1–11 (2021)
N.A. Pohan, M.H. Wahid, Z. Zainal, N.A. Ibrahim, Pickering-emulsion-templated synthesis of 3D hollow graphene as an efficient oil absorbent. RSC Adv. 11, 3963–3971 (2021)
L. Wang, B. Wen, H.B. Yang, Y. Qiu, N.R. He, Hierarchical nest-like structure of Co/Fe MOF derived CoFe@C composite as wide-bandwidth microwave absorber. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 135, 105958 (2020)
X.C. Di, Y. Wang, Y.Q. Fu, X.M. Wu, P. Wang, Wheat flour-derived nanoporous carbon@ZnFe2O4 hierarchical composite as an outstanding microwave absorber. Carbon 173, 174–184 (2021)
X.H. Ren, X.L. Pu, H.F. Yin, Y. Tang, H.D. Yuan, H.Q. Fan, Fabrication of hierarchical PANI@W-type barium hexaferrite composites for highly efficient microwave absorption. Ceram. Int. 47, 12122–12129 (2021)
J. Ding, L.G. Cheng, X.T. Zhang, Q.F. Liu, Synthesis of multilayered micro flower NiCo2O4/GN/Fe3O4 composite for enhanced electromagnetic microwave (EM) absorption performance. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 8864–8875 (2019)
W.S. Hummers, R.E. Offeman, Preparation of graphitic oxide. Am. Chem. Soc. 208, 1334–1339 (1958)
L. Wang, H.L. Xing, Z.F. Liu, Z.Y. Shen, X. Sun, G.C. Xu, Synthesis and excellent microwave absorption properties of ZnO/Fe3O4/MWCNTs Composites. Nano 11(12), 1650139–1650150 (2016)
P. Sadhukhan, M. Kundu, S. Rana, R. Kumar, J. Das, P.C. Sil, Microwave induced synthesis of ZnO nanorods and their efficacy as a drug carrier with profound anticancer and antibacterial properties. Toxicol. Rep. 6, 176–185 (2019)
O. Akhavan, The effect of heat treatment on formation of graphene thin films from graphene oxide nanosheets. Carbon 48, 509–19 (2010)
C.Q. Song, X.W. Yin, M.K. Han, X.L. Li, Z.X. Hou, L.T. Zhang et al., Three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide foam modified with ZnO nanowires for enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 116, 50–58 (2017)
X. Liu, L.-S. Wang, Y. Ma, Y. Qiu, Q. Xie, Y. Chen et al., Facile synthesis and microwave absorption properties of yolk-shell ZnO-Ni-C/RGO composite materials. Chem. Eng. J. 333, 92–100 (2018)
A. Manikandan, J. Judith Vijaya, L. John Kennedy, M. Bououdina, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Zn1−xCuxFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by microwave combustion method. J. Mol. Struct. 1035, 332–340 (2013)
L. Wang, X.F. Yu, X. Li, J. Zhang, M. Wang, R.C. Che, MOF-derived yolk-shell Ni@C@ZnO Schottky contact structure for enhanced microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 383, 123099 (2020)
L. Wang, B. Wen, T. Zhao, Y. Lin, Facile synthesis of N, S-codoped honeycomb-like C/Ni3S2 composites for broadband microwave absorption with low filler mass loading. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 580, 126–134 (2020)
L. Wang, Z. Du, L. Xiang, D. Hou, S. Zhu, J. Zhu et al., The ordered mesoporous carbon coated graphene as a high-performance broadband microwave absorbent. Carbon 179, 435–444 (2021)
J. Qiao, D. Xu, L. Lv, X. Zhang, F. Wang, W. Liu et al., Self-Assembled ZnO/Co Hybrid Nanotubes Prepared by Electrospinning for Lightweight and High-Performance Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 1(9), 5297–5306 (2018)
L. Wang, Z. Du, X. Bai, Y. Lin, Constructing macroporous C/Co composites with tunable interfacial polarization toward ultra-broadband microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 591, 76–84 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Key R&D Project of Science and Technology Department of Henan Province (Key Science and Technology Tackling Project, Grant No. 212102210584), Cultivation Project of “Young Key Teachers in Universities of Henan Province, Funded by Young Key Teachers of Zhongyuan Institute of Technology” in 2019 (Jiaogao [2019] No. 350, Zhong Gongong [2018] No. 60) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11901162).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, J., Cheng, L. & Zhuang, X. Three-dimensional hierarchical structured Fe3O4/rGO/ZnO composite for effective electromagnetic wave absorption. Appl. Phys. A 127, 470 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04625-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04625-3