Abstract
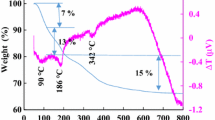
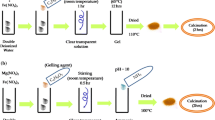
In this work, NH4MPO4.H2O (M = Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Cu2+) microstructures were synthesized by a simple precipitation method at room temperature without any templates or surfactants. The materials were characterized by means of thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), differential scanning calorimetric method (DSC), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The characterization results show that the prepared samples have an orthorhombic structure for M = Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+ samples without any impurity phase, whereas the monoclinic structure is presented in the NH4CuPO4.H2O sample. The morphology of all the obtained samples completely consists of a plate-like shape with the size of several micrometers. In addition, the microflower-like morphology with size about 10 µm was obtained when the metal was Mn. The oxidation state of P ions in all samples is 5 + which is consistent with the surface analysis using XPS. For the magnetic properties, the obtained materials show antiferromagnetic behavior with the highest magnetization value of 26.17 emu.g−1 at 10 kOe in the NH4MnPO4.H2O sample. By using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES), the ion release properties of NH4MPO4.H2O (M = Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Cu2+) microstructures show the potential application as slow-release fertilizer. This could be beneficial in order to reduce the amount of fertilizer used in plants and may be extended for the commercial.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Li, P. Gu, Y. Feng, G. Zhang, K. Huang, H. Xue, H. Pang, Ultrathin Nickel-Cobalt Phosphate 2D Nanosheets for electrochemical energy storage under Aqueous/Solid-State Electrolyte. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27(12), 1605784 (2017)
X. Guo, N. Li, Y. Cheng, G. Wang, Y. Zhang, H. Pang, General synthesis of nitrogen-doped metal (M = Co2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, or Cu2+) phosphates. Chem. Eng. J. 411, 128544 (2021)
A. Yuan, J. Wu, L. Bai, S. Ma, Z. Huang, Z. Tong, Standard molar enthalpies of formation for ammonium/3d-transition metal phosphates NH4MPO4·H2O (M = Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+). J. Chem. Eng. Data 53(5), 1066–1070 (2008)
M. Debray, C. R. Acad. Sci. 59(4), 40 (1864)
A. Pujana, J. Luis Pizarro, L. Lezama, A. Goñi, M. Isabel Arriortua, T. Rojo, Synthesis, crystal structure, and magnetic properties of NH4CuPO4·H2O. J. Mater. Chem. 8(4), 1055–1060 (1998)
S. Wang, H. Pang, S. Zhao, W. Shao, N. Zhang, J. Zhang, J. Chen, S. Li, NH4CoPO4·H2O microbundles consisting of one-dimensional layered microrods for high performance supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 4(1), 340–347 (2014)
G.L. Bridger, M.L. Salutsky, R.W. Starostka, Micronutrient sources, metal ammonium phosphates as fertilizers. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 10(3), 181–188 (1962)
V. Römheld, H. Marschner, Function of micronutrients in plants, in Micronutrients in Agriculture. ed. by J.J. Mortvedt (Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, USA, 1991), pp. 297–328
L.M. Lapina, Metal ammonium phosphates and their new applications. Russ. Chem. Rev. 37(9), 693 (1968)
H. Wu, S. Liao, W. Wu, M. Liao, H. Cao, Synthesis and characterization of multi-micronutrient fertilizer ammonium cupric phosphate via solid state reaction. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 58(5), 1215–1219 (2007)
V.G. Koleva, Metal-water interactions and hydrogen bonding in dittmarite-type compounds M’M’’PO4.H2O (M’=K+, NH4+; M’’=Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+).Correlations of IR spectroscopic and structural data. Spectrochim. Acta A. 62(4–5), 1196–1202 (2005)
A. Karaphun, P. Chirawatkul, S. Maensiri, E. Swatsitang, Influence of calcination temperature on the structural, morphological, optical, magnetic and electrochemical properties of Cu2P2O7 nanocrystals. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 88(2), 407–421 (2018)
A. Karaphun, S. Maensiri, E. Swatsitang, Effect of calcination on structural, morphological, magnetic and electrochemical properties of mesoporous Ni2P2O7 microplates. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30(3), 3019–3031 (2019)
H. Pang, Z. Yan, W. Wang, J. Chen, J. Zhang, H. Zheng, Facile fabrication of NH4CoPO4.H2O nano/microstructures and their primarily application as electrochemical supercapacitor. Nanoscale. 4(19), 5946–5953 (2012)
X. Wang, Z. Yan, H. Pang, W. Wang, G. Li, Y. Ma, H. Zhang, X. Li, J. Chen, NH4CoPO4· H2O microflowers and porous Co2P2O7 microflowers: effective electrochemical supercapacitor behavior in different alkaline electrolytes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 8, 3768–3785 (2013)
T. Yokoyama, H. Masuda, M. Suzuki, K. Ehara, K. Nogi, M. Fuji, T. Fukui, H. Suzuki, J. Tatami, K. Hayashi, K. Toda (2008) Basic Properties and Measuring Methods of Nanoparticles. In: Masuo, H., Kiyoshi, N., Mario, N., ToyokazU YokoyamaA2 - Masuo Hosokawa, K.N.M.N., Toyokaz, U.Y. (eds.) Nanoparticle Technology Handbook. (Elsevier, Amsterdam), pp. 3–48
L. Wannasen, N. Chanlek, S. Maensiri, E. Swatsitang, Composition effect of Co/Ni on the morphology and electrochemical properties of NH4Co1-xNixPO4.H2O nanocrystallites prepared by a facile hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30(8), 7794–7807 (2019)
Z. Huang, Z. Wang, X. Zheng, H. Guo, X. Li, Q. Jing, Z. Yang, Structural and electrochemical properties of Mg-doped nickel based cathode materials LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2−xMgxO2 for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv. 5(108), 88773–88779 (2015)
B. Ravel, M. Newville, ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 12(4), 537–541 (2005)
C.-C. Xu, Y. Wang, L. Li, Y.-J. Wang, L.-F. Jiao, H.-T. Yuan, Hydrothermal synthesis mechanism and electrochemical performance of LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4 cathode material. Rare Metals 38(1), 29–34 (2019)
N.V. Kosova, E.T. Devyatkina, V.V. Kaichev, Mixed layered Ni–Mn–Co hydroxides: crystal structure, electronic state of ions, and thermal decomposition. J. Power Sources 174(2), 735–740 (2007)
P. Xu, J. Liu, T. Liu, K. Ye, K. Cheng, J. Yin, D. Cao, G. Wang, Q. Li, Preparation of binder-free CuO/Cu2O/Cu composites: a novel electrode material for supercapacitor applications. RSC Adv. 6(34), 28270–28278 (2016)
E. Swatsitang, A. Karaphun, S. Phokha, S. Hunpratub, T. Putjuso, Magnetic and optical properties of Cu1−xFexO nanosheets prepared by the hydrothermal method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 83(2), 382–393 (2017)
A. Gaur, B.D. Shrivastava, S.K. Joshi, Copper K-edge XANES of Cu(I) and Cu(II) oxide mixtures. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 190, 012084 (2009)
W.E. Morgan, J.R. Van Wazer, W.J. Stec, Inner-orbital photoelectron spectroscopy of the alkali metal halides, perchlorates, phosphates, and pyrophosphates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 95(3), 751–755 (1973)
Q.-Z. Ou, Y. Tang, Y.-J. Zhong, X.-D. Guo, B.-H. Zhong, L. Heng, M.-Z. Chen, Submicrometer porous Li3V2(PO4)3/C composites with high rate electrochemical performance prepared by sol-gel combustion method. Electrochim. Acta 137, 489–496 (2014)
I. Bica, Nanoparticle production by plasma. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 68(1), 5–9 (1999)
M.A. López-Quintela, J. Rivas, Chemical reactions in microemulsions: a powerful method to obtain ultrafine particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 158(2), 446–451 (1993)
L. Rezlescu, E. Rezlescu, P.D. Popa, N. Rezlescu, Fine barium hexaferrite powder prepared by the crystallisation of glass. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 193(1–3), 288–290 (1999)
H.-J. Koo, M.-H. Whangbo, On the correct spin lattice for the spin-gapped magnetic solid NH4CuPO4·H2O. J. Solid State Chem. 181(2), 276–281 (2008)
M. Touaiher, M. Bettach, K. Benkhouja, M. Zahir, M.A.G. Aranda, S. Bruque, Synthesis and structure of NH4CoPO46H2O. Ann. Chim. - Sci. Mat. 26(3), 49–54 (2001)
M.E. Trenkel, Slow- and Controlled-release and Stabilized Fertilizers: An Option for Enhancing Nutrient Use Efficiency in Agriculture. International fertilizer industry Association, (2010)
V. Römheld, H. Marschner, Function of micronutrients in plants, in Micronutrients in agriculture. ed. by J.J. Mortvedt (Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, USA, 1991), pp. 297–328
P. Li, Y. Du, L. Li, L. Huang, V. Rudolph, A.V. Nguyen, Z.P. Xu, Preparation and characterisation of manganese and iron compounds as potential control-release foliar fertilisers. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 4(3), 746–753 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Suranaree University of Technology (SUT) and the SUT-NANOTEC RNN on Nanomaterials and Advanced Characterizations and the SUT Center of Excellence on Advanced Functional Materials, Suranaree University of Technology, Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand, for providing XRD, TEM facilities, and financial support. S. Phumying is supported by SUT-PhD Fund. The authors would like to thank Synchrotron Light Research Institute (Public Organization), Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand, for XANES and XPS facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phumying, S., Sichumsaeng, T., Sonsupap, S. et al. Synthesis, characterization, magnetic and ion release properties of NH4MPO4.H2O (M = Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Cu2+) prepared by a simple precipitation method in water solution. Appl. Phys. A 127, 352 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04492-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04492-y