Abstract
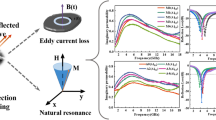
Soft magnetic alloy powder NdNi5-xFex (x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.4) was prepared by vacuum arc melting, homogenization annealing and ball milling methods. The reflection loss of NdNi5-xFex powders were discussed based on the structural morphology, measured hysteresis loops and electromagnetic parameters. The lattice distortion and the saturation magnetization of NdNi5-xFex powders increase and the formant of the electromagnetic parameter moves toward the low frequency. The absorption peak of reflection loss also moves toward low frequency. In addition, the Nd–Ni–Fe alloy powder can achieve the best absorption bandwidth, and the minimum reflection loss value of 1.29 GHz and − 29.29 dB, respectively, with the addition of Fe content is 0.1. Add Fe content appropriately, and adjusting the thickness can effectively improve the absorbing performance of the material in c-band, so the powder has a good application prospect in c-band.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Wang, J.I. Chang-Song, J.L. Yue, X.Z. Huang, D.U. Zuo-Juan, X.Z. Tang, University, C.S., Soft magnetic properties and electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of magnetic FeNi coated carbon fibers. Surf. Technol. 47(6), 174–180 (2018)
L.-J. Wang, J. Li, Y.-X. Liu, Preparation of electromagnetic shielding wood-metal composite by electroless nickel plating. J. For. Res. 17(1), 53–56 (2006)
W. Feng-de, X. Peng, Y. Jing, H. Xin-quan, G. Qiang, W. Jian-qiang, L. Xiao-feng, Y. Shao-hua, Distribution of electromagnetic pollution in driver compartment of electric locomotive after rail speed elevated. J. Environ. Occup. Med. 31(1), 30–32 (2014)
G. Ganapathi Rao, B. Lakshmi Rekha, Structural, ferroelectric, dielectric, impedance and magnetic properties of Gd and Nb doped barium titanate–lithium ferrite solid solutions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 494(15), 165822 (2020)
G. Ganapathi Rao, B. Lakshmi Rekha, C. Arun Kumar, K.N. Chidambara Kumar, N. Gnana Praveena, D. Madhvaprasad, Studies on structural dielectric conductivity magnetic and magneto-electric properties of barium titanate doped with lithium ferrite. Phys. B Condens. Matter 543(15), 38–45 (2018)
G. Ganapathi Rao, B. Lakshmi Rekha, K.N. Chidambara Kumar, C. Arun Kumar, K. Samatha, D. Madhava Prasad, Investigations on multiferroic properties of BaTi0.9Zr0.1O3 substituted with Li0.5Fe2.5O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 444(15), 444–450 (2017)
G. Ganapathi Rao, B. Lakshmi Rekha, D. Madhav Prasad, C. Arun Kumar, K. Jayant, K. Samatha, Structural and magnetic properties of lithium ferrite substituted BaTi0.9Zr0.1O3 composite ceramics. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 5(2), 109–112 (2017)
T.A. Elwi, D.G. Rucker, H.M. Al-Rizzo, H.R. Khaleel, E. Dervishi, A.S. Biris, A dual frequency wearable MWCNT ink based spiral microstrip antenna. In NSTI Nanotech 2010 conference and Expo. pp 266–269 (2010).
M.A. Jawad, M.A. Elwi, E.Y. Salih, T.A. Elwi, A. Zulkifly, Monitoring the dielectric properties and propagation conditions of mortar for modern wireless mobile networks. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 89, 91–97 (2020)
T.A. Elwi, Z.A. Al-Hussain, O. Tawfeeq, Hilbert metamaterial printed antenna based on organic substrates for energy harvesting. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 12(4), 1–8 (2019)
T.A. Elwi, Printed microwave metamaterial-antenna circuitries on nickel oxide polymerized palm fiber substrates. Nat. Sci. Rep. 9(2174), 1–14 (2019)
T.A. Elwi, Novel UWB printed metamaterial microstrip antenna based organic substrates for RF-energy harvesting applications. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 101, 1–10 (2019)
T.A. Elwi, B.A. Ahmed, A Fractal metamaterial based printed dipoles on a nickel oxide polymer palm fiber substrate for Wi-Fi applications. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 96, 122–129 (2018)
T.A. Elwi, A miniaturized folded antenna array for MIMO applications. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 98(2), 1871–1883 (2018)
Y. Al-Naiemy, T.A. Elwi, H.R. Khaleel, H.M. Al-Rizzo, A systematic approach for the design, fabrication and testing of microstrip antennas using ink-jet printing technology. ISRN Commun. Netw. 132465, 1–11 (2012)
T.A. Elwi, H.M. Al-Rizzo, D.G. Rucker, E. Dervishi, Z. Li, A.S. Biris, Multi-walled carbon nanotube-based RF antennas. Inst. Phys. 2010 Nanotechnol. 21(4), 1–10 (2010)
W. Chu, Y. Wang, Y. Du, R. Qiang, C. Tian, X. Han, FeCo alloy nanoparticles supported on ordered mesoporous carbon for enhanced microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. 52(23), 13636–13649 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1439-1
M. Qiao, X. Lei, Y. Ma, L. Tian, K. Su, Q. Zhang, Dependency of tunable microwave absorption performance on morphology-controlled hierarchical shells for core-shell Fe 3 O 4 @MnO 2 composite microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 304, 552–562 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.094
H.S. Ji, H.Y. Ryu, S.M. Jeong, S.W. Cho, Fast electrochemical synthesis of NdNi5 hydrogen storage alloy in molten salt. Chem. Lett. 42(10), 1182–1184 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.130538
J.-L. Bobet, S. Pechev, B. Chevalier, B. Darriet, Structural and hydrogen sorption studies of NdNi5–xAlx and GdNi5–xAlx. J. Alloys Compd. 267(1), 136–141 (1998)
Z. Guo, F. Sun, Y. Chen, Y. Mao, L. Wan, X. Yan, Y. Yang, W. Yuan, Synthesis, structure and superconductivity of FeS1–xSex (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) solid solution crystals. CrystEngComm 21(19), 2994–2999 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ce00038k
Y. Li, H. Cheng, N. Wang, S. Zhou, D. Xie, T. Li, Annealing effects on the microstructure, magnetism and microwave-absorption properties of Fe/TiO2 nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 471, 346–354 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.09.101
G. Ganapathi Rao, B. Lakshmi Rekha, K.N. Chidambara Kumar, D. Madhavaprasad, Influence of Sm and Nb on the structural, electric, magnetic and magneto-electric properties of BaTiO3–Li0.5Fe2.5O4 composite ceramics grown by the conventional solid state technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 1262–1274 (2019)
P.N. Gnana, T. Ravindar, G. Ganapathi Rao, P.V. PrakashMadduri, A.V. Anupama, V. Veeraiah, Influence of Cr on structural, spectroscopic and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 grown by the wet chemical method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 238(1), 121903 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121903
N. Song, Y. Ke, H. Yang, H. Zhang, X.Q. Zhang, B. Shen, Z. Cheng, Integrating giant microwave absorption with magnetic refrigeration in one multifunctional intermetallic compound of LaFe11.6Si1.4C0.2H1.7. Sci. Rep. 3(1), 2045–2322 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02291
J. Yan, Y. Huang, P.B. Liu, C. Wei, Large-scale controlled synthesis of magnetic FeCo alloy with different morphologies and their high performance of electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28(4), 3159–3167 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5904-4
H. Li, Y. Huang, G. Sun, X. Yan, Y. Yang, W. Jian, Z. Yue, Directed growth and microwave absorption property of crossed ZnO netlike micro-/nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(22), 10088–10091 (2010)
X. Huang, J. Zhang, W. Wang, T. Sang, B. Song, H. Zhu, W. Rao, C. Wong, Effect of pH value on electromagnetic loss properties of Co–Zn ferrite prepared via coprecipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 405, 36–41 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.12.051
Y. Yang, C. Xu, Y. Xia, T. Wang, F. Li, Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of FeCo nanoplates. J. Alloy. Compd. 493(1–2), 549–552 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.12.153
H. Xu, W. Sun, Y. Gui, L. Wang, M. Yu, Q. Zhang, Electromagnetic loss properties of ZnO nanofibers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(12), 12846–12851 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5419-z
Z. Ma, Y. Zhang, C. Cao, J. Yuan, Q. Liu, J. Wang, Attractive microwave absorption and the impedance match effect in zinc oxide and carbonyl iron composite. Phys. B 406(24), 4620–4624 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2011.09.039
A. Arora, S.B. Narang, Effect of La–Na Doping in Co–Ti substituted barium hexaferrite on electrical and X-Band microwave absorption properties. J. Electron. Mater. 47(8), 4919–4928 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6349-8
S. Waseem, S. Anjum, L. Mustafa, T. Zeeshan, Zohra N. Kayani, K. Javed, Structural, magnetic and optical investigations of Fe and Ni co-doped TiO2 dilute magnetic semiconductors. Ceram. Int. 44(15), 17767–17774 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.06.244
Yuriy A. Zaharov, Valeriy M. Pugachev, Victor I. Ovcharenko, Kseniya A. Datiy, Anna N. Popova, Artem S. Bogomyakov, Phase composition and magnetic properties of nanostructured Fe–Co–Ni powders. Phys. Stat. Solidi B Basic Solid State Phys. 255(3), 0370–1972 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.201700175
H.Y. Liu, Y.S. Li, Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of Cobalt ferrite. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 292(1), 012062 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/292/1/012062
J.I.A.O. Qingze, W.A.N.G. Yanfeng, H.A.O. Liang, L.I. Hansheng, Z.H.A.O. Yun, Synthesis of magnetic nickel ferrite microspheres and their microwave absorbing properties. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 32(4), 678–681 (2016)
X. Guo, Z. Yao, H. Lin, J. Zhou, Y. Zuo, X. Xu, B. Wei, W. Chen, K. Qian, Epoxy resin addition on the microstructure, thermal stability and microwave absorption properties of core-shell carbonyl iron@epoxy composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 485, 244–250 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.04.059
Acknowledgment
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51361007), 2017 director fund of Guangxi Key Laboratory of wireless wideband communication and signal processing (GXKL06170107), Guangxi Key Laboratory of information materials (171016-Z, 191016-K and 191010-Z), Guangxi Key Laboratory of Information Materials (171016-Z), Innovation Project of GUET Graduate Education (2018YJCX87, 2019YCXS116) and the Talents Project of Guilin University of Electronic Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Jj., Pan, Sk., Cheng, Lc. et al. Effect of Fe doping on microwave absorption performance of magnetic powder NdNi5. Appl. Phys. A 126, 348 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03521-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03521-6