Abstract
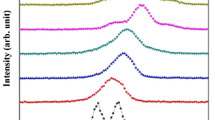
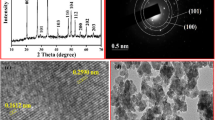
In this work, we report the effect of doping with yttrium ions (Y3+) on the magnetic and optical properties of KBiFe2O5 (KBFO). Y doped KBFO with different mole percentage (KBi1−xYxFe2O5 with x = 0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15) were synthesized by citrate assisted sol–gel route. Samples thus obtained were characterized by X-ray diffraction to establish their phase purity. Microstructural and compositional analyses were carried out using scanning electron microscope. Absorption spectra of the samples indicated a blue shift in the absorption spectra with Y doping and an increase in the energy band gap values. Y doped KBFO showed enhanced magnetic properties. Maximum magnetization at an applied field of 1.5 T showed steady increase with increase in the doping concentration. The values of magnetic moment at 1.5 T are 0.11 emu/g for x = 0, 0.16 emu/g for x = 0.05, 0.34 emu/g for x = 0.10 and 0.66 emu/g for x = 0.15. The remanent magnetization increased with increase in the Y content whereas coercivity decreased. Photoluminescence property of the samples was also evaluated. For an excitation wavelength of 450 nm, broadband emission spectra in the range 600–650 nm were observed for all samples. The evaluation of the photocatalytic activity of Y doped KBFO were also carried out by the degradation of methylene blue. Y doped KBFO showed enhanced photocatalytic efficiency which is attributed to an increase in the adsorption rate of the samples with Y doping.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Zhang et al., Sci Rep 3, 1265 (2013)
P. Boullay et al., Phys Rev B 79, 184108 (2009)
A.M. Abakumov et al., J Solid State Chem 174, 319 (2003)
S. Shin et al., Mater Res. Bull 13, 1017 (1978)
J.B. Goodenough et al., Solid State Ion 44, 21 (1990)
Y. Yang et al., Mater. Sci. Eng B 132, 311 (2006)
Ilya Grinberg et al., Nature 503, 509 (2013)
W.S. Choi et al., Nat Commun 3, 689 (2012)
X.Z. Zhai et al., RSC Adv 5, 82351 (2015)
M.A. Jalaja et al., Mater Res. Expr 4, 016401 (2017)
X. Zhai et al., Mater Lett 161, 423 (2015)
M.A. Jalaja et al., Mater Res Bull 88, 9 (2017)
R. Rai, M. Molli, J Mater Sci 30, 4318 (2019)
J. LI et al., J Inorg Mater 33, 0805 (2018)
D.S. Vavilapalli et al., ACS Omega 3, 16643 (2018)
S.M. Lam et al., Mater Res Bull 90, 15 (2017)
N. Zhang et al., Sci Rep 6, 26467 (2016)
A. Zhang et al., J Hazard Mater 173, 265 (2010)
R. Guo et al., J Phys Chem C 114, 21390 (2010)
Z. Min et al., J Mater Chem Phys 173, 126 (2016)
M.H. Ehsani et al., J Magn Magn. Mater 475, 484 (2019)
H. Zhi-Ling et al., Chin Phys Lett 28, 037702 (2011)
Ö. Özdemir et al., J. Geophys Res 119, 2582 (2014)
C. Anthonyraj et al., J Mater Sci 26, 49 (2015)
D.P. Das et al., J Mol Catal A 349, 36 (2011)
J. Zhao et al., Build Environ 38, 645 (2003)
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to Bhagawan Sri Sathya Sai Baba, the founder chancellor of SSSIHL, for his constant guidance and inspiration. We are grateful to our university, SSSIHL, for providing constant support and Central Research Instruments Facility. We also acknowledge the financial support from DST-FIST (Sanction No. SR/FST/PSI-172/2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rai, R., Molli, M. Magnetic, optical and photocatalytic properties of yttrium doped KBiFe2O5. Appl. Phys. A 125, 878 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3175-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3175-7