Abstract
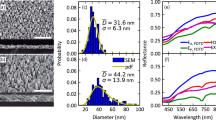
The particle size limit for enhanced infrared absorption on metal nanostructures was identified using an infrared spectrometer and microscope accessory for well-defined periodic gold square column (SC) arrays with various nanoparticle sizes on silicon wafers fabricated by electron beam lithography. The sizes of SC arrays are compatible with those of vacuum evaporated thin metal films, which are used conventionally for surface-enhanced infrared absorption. The experimental results revealed that the particle size limit for the enhancement was about one-tenth of wavelength of infrared radiation. It indicates that this ratio limits the applicability of effective medium approximation in the SC model.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Hartstein, J.R. Kirtley, J.C. Tsang, Enhancement of the infrared absorption from molecular monolayers with thin metal overlayers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 201–203 (1980)
A. Hatta, Y. Suzuki, W. Suëtaka, Infrared absorption enhancement of monolayer species on thin evaporated Ag films by use of a Kretschmann configuration: evidence for two types of enhanced surface electric fields. Appl. Phys. A Solids Surf. 35, 135–140 (1984)
Y. Suzuki, K. Kita, N. Matsumoto, Local enhanced site in enhanced infrared absorption. Phys. Low Dimens. Struct. 1, 1–8 (2001)
Y. Suzuki, Y. Ojima, Y. Fukui, H. Fazyia, K. Sagisaka, Post-annealing temperature dependence of infrared absorption enhancement of polymer on evaporated silver films. Thin Solid Films 515, 3073–3078 (2007)
Y. Suzuki, H. Nakashima, Verifying electromagnetic first layer effect on surface enhanced infrared absorption with evaporated gold nano island film. Mater. Res. Express 6, 085038 (2019)
Y. Suzuki, K. Kita, N. Matsumoto, The square columnar model in enhancement of an electromagnetic field. Appl. Phys. A Solids Surf. 77, 613–617 (2003)
T. Shimada, H. Nakashima, Y. Kumagai, Y. Ishigo, M. Tsushima, A. Ikari, Y. Suzuki, What is the key structural parameter for infrared absorption enhancement on nanostructures? J. Phys. Chem. C 120(1), 534–541 (2016)
N.A.F. Al-Rawashdeh, M.L. Sandrock, C.J. Seugling, C.A. Foss, Visible region polarization spectroscopic studies of template-synthesized gold nanoparticles oriented in polyethylene. J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 361–371 (1998)
J.C. Maxwell-Garnett, Colours in metal glasses and in metallic films. Philos. Trans. R. Soc A 203, 385–420 (1904)
M.G. Moharam, E.B. Grann, D.A. Pommet, Formulation for stable and efficient implementation of the rigorous coupled-wave analysis of binary gratings. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 12(5), 1068–1076 (1995)
V. Liu, S. Fan, S4: A free electromagnetic solver for layered periodic structures. Comput. Phys. Commun. 183, 2233–2244 (2012)
T.R. Jensen, R.P. Van Duyne, S.A. Johnson, V.A. Maroni, Surface-enhanced infrared spectroscopy: a comparison of metal island films with discrete and nondiscrete surface plasmons. Appl. Spectrosc. 54(3), 371–377 (2000)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research, JSPS KAKENHI Grant numbers 16H03820 and 18H01998. A part of this work was conducted at the Center for Nano Lithography & Analysis at The University of Tokyo supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan and at the Shared Facility Center for Science and Technology (SFCST) at Hirosaki University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishigo, Y., Nakashima, H., Tsushima, M. et al. Maximum size limit of Au nanoparticle applicable for surface enhanced infrared absorption. Appl. Phys. A 125, 863 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3140-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3140-5