Abstract
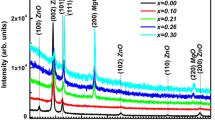
Ultrasound pyrolysis spray technique is used to prepare single-phase thin films of Zn1−xCoxO (x = 0–22 at.%). The hexagonal wurtzite structure of the films is confirmed by X-ray diffraction with an average crystallite size estimated in the range of 18–30 nm. The compound structure and stoichiometry of the films are further characterized by energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDAX). The spectrum analysis agreement great chords between the expected and measured Co atomic content in the films indicating an effective doping. The results also reveal a high solubility of Co into ZnO solid solution at about 14 at.%. For the optical proprieties, the bandgap energy decreases due to the presence of high concentrations of localized states in the thin films. The photoluminescence spectra of all the samples exhibited a broad emission in the visible range. In addition, the magnetic properties of Zn1−xCoxO thin films are found to be strongly influenced by Co doping.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Oktik, Low cost non-vacuum techniques for the preparation of thin/thick films for photovoltaic applications. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. 17, 171–240 (1988)
K. Bouzid, A. Djelloul, N. Bouzid, J. Bougdira, Electrical resistivity and photoluminescence of zinc oxide films prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Phys. Status Solid. A. 206, 106–115 (2009)
A. Janotti, ChG Van de Walle, Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys. 72, 126501 (2009)
K. Ellmer, A. Klein, B. Rech (eds.), Transparent Conductive Zinc Oxide-Basics and Applications in Thin Film Solar Cells. (Series: Springer Series in Materials Science, Berlin, 2008), p. 104
H.M. Yang, S. Nie, Preparation and characterization of Co-doped ZnO nanomaterials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 279–282 (2009)
M. Yang, Z.X. Guo, K.H. Qiu, J.P. Long, G.F. Yin, D.G. Guan, S.T. Liu, S.J. Zhou, Synthesis and characterization of Mn-doped ZnO column arrays. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 4201–4205 (2010)
H. Saal, T. Bredow, M. Binnewies, Band gap engineering of ZnO via doping with manganese: effect of Mn clustering. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 3201–3209 (2009)
G.M. Kumar, P. Ilanchezhiyan, J. Kawakita, M. Subramanian, R. Jayavel, Magnetic and optical property studies on controlled low-temperature fabricated one-dimensional Cr doped ZnO nanorods. Cryst. Eng. Commun. 12, 1887–1892 (2010)
S. Fabbiyola, L.J. Kennedy, U. Aruldoss, M. Bououdina, A.A. Dakhel, J. Judith Vijaya, Synthesis of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles via co-precipitation: structural, optical and magnetic properties. Powder Technol. 286, 757–765 (2015)
T. Dietl, H. Ohno, F. Matsukura, J. Cibert, D. Ferrand, Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 287, 1019–1022 (2000)
Y.X. Wang, X. Ding, Y. Cheng, Y.J. Zhang, L.L. Yang, H.L. Liu, H.G. Fan, Y. Liu, J.H. Yang, Properties of Co-doped ZnO films prepared by electrochemical deposition. Cryst. Res. Technol. 44(5), 517–520 (2009)
C. Song, F. Zeng, K.W. Geng, X.B. Wang, Y.X. Shen, F. Pan, The magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO diluted magnetic insulator films prepared by direct current reactive magnetron co-sputtering. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 309, 25–30 (2007)
A. Zukova, A. Teiserskis, S. van Dijken, Y.K. Gun’ko, V. Kazlauskiene, Giant moment and magnetic anisotropy in Co-doped ZnO films grown by pulse-injection metal organic chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 232503–232505 (2006)
H. Matsui, H. Tabata, Simultaneous control of growth mode and ferromagnetic ordering in Co-doped ZnO layers with Zn polarity. Phys. Rev. B. 75, 014438–014447 (2007)
A. Sivagamasundari, R. Pugaze, S. Chandrasekar, S. Rajagopan, R. Kannan, Absence of free carrier and paramagnetism in cobalt-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized at low temperature using citrate sol–gel route. Appl. Nanosci. 3, 383–388 (2013)
G. Iqbal, S. Faisal, S. Khan, D.F. Shams, A. Nadhman, Photo-inactivation and efflux pump inhibition of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus using thiolated cobalt doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 192, 141–146 (2019)
H.S. Sindhu, S. D. Kulkarni, R.J. Choudhary, P.D. Babu, B.V. Rajendra, Influence of cobalt doping on structure, optical and magnetic properties of spray pyrolysed nano structured ZnO films. Phys. B: Phys. Condens. Matter. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.07.034
M. Ivill, S.J. Pearton, S. Rawal, L. Leu, P. Sadik, R. Das, A.F. Hebard, M. Chisholm, J.D. Budai, D.P. Norton, Structure and magnetism of cobalt doped ZnO thin films. New J. Phys. 10, 065002 (2008)
N.K. Tarwal, K.V. Gurav, T. PremKumar, Y.K. Jeong, H.S. Shim, I.Y. Kim, J.H. Kim, J.H. Jang, P.S. Patil, Structure, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and photoluminescence investigations of the spray deposited cobalt doped ZnO thin films. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 106, 26–32 (2014)
S. Karamat, R.S. Rawat, T.L. Tan, P. Lee, R. Chen, H.D. Sun, W. Zhou, Ferromagnetism in ZnCoO thin films deposited by PLD. Appl. Phys. A 101, 717–722 (2010)
C.B. Fitzgerald, M. Venkatesan, J.G. Lunney, L.S. Dorneles, J.M.D. Coey, Cobalt-doped ZnO—a room temperature dilute magnetic semiconductor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 247, 493–496 (2005)
A. Dinia, G. Schmerber, C. Mény, V. Pierron-Bohnes, E. Beaurepaire, Room- temperature ferromagnetism in Zn1 − xCoxOZn1 − xCoxO magnetic semiconductors prepared by sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 123908 (2005)
G. Lawes, A.S. Risbud, A.P. Ramirez, R. Seshadri, Absence of ferromagnetism in Co and Mn substituted polycrystalline ZnO. Phys. Rev. B. 71, 045201 (2005)
J.H. Park, M.G. Kim, H.M. Jang, S. Ryu, Y.M. Kim, Co-metal clustering as the origin of ferromagnetism in Co-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1338 (2004)
J.H. Kim, H. Kim, D. Kim, Y.E. Ihm, W.K. Choo, Magnetic properties of epitaxially grown semiconducting Zn1 − xCoxOZn1 − xCoxO thin films by pulsed laser deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 6066 (2002)
Y.Z. Peng, T. Liew, W.D. Song, C.W. An, K.L. Teo, T.C. Chong, Structural and optical properties of Co-doped ZnO thin films. J. Supercond. 18, 97–103 (2005)
R. Siddheswaran, R. Medlín, C.E. Jeyanthi, S.G. Raj, R.V. Mangalaraja, Structural, morphological, optical and magnetic properties of RF sputtered Co doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductor for spintronic applications. Appl. Phys. A 9, 125 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2886-0
A. Aravind, K. Hasna, M.K. Jayaraj, M. Kumar, R. Chandra, Magnetic and Raman scattering studies of Co-doped ZnO thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Phys. A 115(3), 843–849 (2014)
S. Roguai, A. Djelloul, C. Nouveau, T. Souier, A.A. Dakhel, M. Bououdina, Structure, microstructure and determination of optical constants from transmittance data of Co-doped Zn0.90 Co0.05M 0.05 O (M = Al, Cu, Cd, Na) films. J. Alloys Compd. 599, 150–158 (2014)
M. Bouloudenine, N. Viart, S. Colis, J. Kortus, A. Dinia, Antiferromagnetism in bulk Zn1 − xCoxO Zn1 − xCoxO magnetic semiconductors prepared by the coprecipitation technique. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 052501 (2005)
X.C. Chen, J.P. Zhou, H.Y. Wang, P.S. Xu, G.Q. Pan, Chin. Phys. B. 20, 9 (2011)
D. Bao, H. Gu, A. Kuang, Sol-gel-derived c-axis oriented ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Films 312, 37–39 (1998)
S. Benramache, B. Benhaoua, Influence of substrate temperature and Cobalt concentration on structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by ultrasonic spray technique. Superlattices Microstruct. 52, 807–815 (2012)
G. Vijayaprasath, R. Murugan, G. Ravi, T. Mahalingam, Y. Hayakawa, Characterization of dilute magnetic semiconducting transition metal doped ZnO thin films by a sol-gel spin coating method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 313, 870–876 (2014)
P. Lommens, P.F. Smet, C.M. Donega, A. Meijerink, L. Piraux, S. Michotte, S.M. Tempfli, D. Poelman, Z. Hens, Photoluminescence properties of Co2+-doped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Lumin. 118, 245–250 (2006)
A.S. Pereira, A.O. Ankiewicz, W. Gehlhoff, A. Hoffmann, S. Pereira, T. Trindade, M. Jrundmann, M.C. Carmo, N.A. Sobolev, Surface modification of Co-doped ZnO nanocrystals and its effects on the magnetic properties. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 07D140 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2833300
F. Urbach, The long-wavelength edge of photographic sensitivity and electronic absorption of solids. APS J. Phys. Rev. 92, 1324–1326 (1953)
B.J. Jin, S. Im, S.Y. Lee, Violet and UV luminescence emitted from ZnO thin films grown on sapphire by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 366, 107–110 (2000)
D.H. Zhang, Z.Y. Xue, Q.P. Wang, The mechanisms of blue emission from ZnO films deposited on glass substrate by r.f. magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. D. 35, 2837 (2002)
A. Kaphle, P. Hari, Characterization of aluminium doped nanostructured ZnO/p-Si heterojunctions. Int. J. Eng. Sci. (IJES) 5, 41–51 (2016)
U. Godavarti, V.D. Mote, M.V. Ramana Reddy, P. Nagaraju, Y. VijayKumar, K. T. Dasari, M. P. Dasari, Precipitated cobalt doped ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced low temperature xylene sensing properties. Phys. B Phys. Condens. Matter. 533, 151–160 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.10.034
U. Philipose, S.V. Nair, S. Trudel, C.F. Souza, S. Aouba, R.H. Hill, H.E. Ruda, High- temperature ferromagnetism in Mn-doped ZnO nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 263101 (2006)
L. Xu, H. Zhang, K. Shen, M. Xu, Q. Xu, Room temperature ferromagnetism in Co-doped ZnO prepared by microemulsion. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 25, 1951–1956 (2012)
M. Shatnawi, A.M. Alsmadi, I. Bsoul, B. Salameh, G.A. Alna’Washi, F. Al-Dweri, F. El Akkad, Magnetic and optical properties of Co-doped ZnO nanocrystalline particles. J Alloys. Compd. 655, 244–252 (2016)
Z. Xiong, X.C. Liu, S.Y. Zhuo, J.H. Yang, E.W. Shi, W.S. Yan, Oxygen enhanced ferromagnetism in Cr-doped ZnO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 052513 (2011)
J.A. Wibowo, N.F. Djaja, R. Saleh, Cu- and Ni-doping effect on structure and magnetic properties of Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 3, 48–57 (2013)
J.R. Neal, A.J. Behan, R.M. Ibrahim, H.J. Blythe, M. Ziese, A.M. Fox, G.A. Gehring, Room-temperature magneto-optics of ferromagnetic transition-metal-doped ZnO thin films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 197208–197212 (2006)
M. R. Baklanov, K. P. Mogilnikov, V. G. Polovinkin, F. N. Dultsev, Determination of pore size distribution in thin films by ellipsometric porosimetry. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B. 18, 1385–1391(2000).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Project Research (PNR) and LASPI2A Laboratory of Khenchela University (Algeria) for their financial support of this research project. The authors thank Dr. Ali Hafs for VSM measurements, Laboratoire de Physicochimie des Matériaux (LPCM), El Tarf University, 36000 El Tarf, Algeria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roguai, S., Djelloul, A. Synthesis and evaluation of the structural, microstructural, optical and magnetic properties of Zn1−xCoxO thin films grown onto glass substrate by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Appl. Phys. A 125, 816 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3118-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3118-3