Abstract
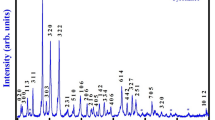
In this communication, the effect of gadolinium (Gd) substitution on structural, microstructural, electrical and dielectric properties of bismuth ferrite BiFeO3 (i.e. Bi(Fe0.95Gd0.05)O3 abbreviated as BFGO5) has been reported. The development of an environment-friendly lead-free multiferroic material by substituting a rare earth element at the uncommon site of BiFeO3 (BFO) (i.e. Gd at the Fe site rather than commonly preferred Bi site) for the tailoring of its multiferroic properties has been attempted in this study. The present studied material has been fabricated through a conventional standard solid-state reaction (SSR) method using carbonates and high-quality oxides in a stoichiometric amount. The phase formation and basic crystal data were analysed by X-ray diffraction technique which shows a single-phase formation of BFGO5 material in orthorhombic symmetry. The average crystallite size was calculated using Scherrer’s formula and found to be 84 nm. The surface morphology and compositions examined by FE-SEM, EDX, FT-IR and TEM show the formation of highly compact sample with uniform distribution of grains. Detailed studies of dielectric parameters (dielectric constant and tangent loss) in a selected frequency range (1–1000 kHz) at different temperatures (273–773 K) clearly exhibit enhancement on dielectric properties of BFO. Studies of its impedance spectroscopy, electrical modulus and electrical conductivity confirm the semiconductor behaviour [negative temperature coefficient of resistance (NTCR)] and non-Debye type relaxation process of the material. The polarization versus electric field (P–E) analysis of BFGO5 shows an improvement in remnant polarization as compared to the parent compound BFO. Therefore, based on the several investigations of results, the BFGO5 material could be considered as a favourable candidate for electronic device applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 September 2021
Editor's Note: Readers are alerted that the reliability of the data presented in this article is subject to criticism that is being considered by the editors. We will update readers once we have further information and all parties have been given an opportunity to respond in full.
19 May 2022
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05625-7
References
S.W. Cheong, M. Mostovoy, Multiferroics: a magnetic twist for ferroelectricity. Nat. Mater. 6, 13–20 (2007)
W. Prellier, M. Singh, P. Murugavel, The single-phase multiferroic oxides: from bulk to thin film. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 17, R803 (2005)
N. Kumar, A. Shukla, N. Kumar, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of eco-friendly complex multiferroic material: Bi(Co0.35Ti0.35Fe0.30)O3. Ceram. Int. 45, 822–831 (2019)
N. Kumar, A. Shukla, C. Behera, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Bi(Ni0.45Ti0.45Fe0.1)O3. J Alloy Compd. 688, 858–869 (2016)
N.A. Spaldin, S. Cheong, R. Ramesh, Multiferroics: past, present, and future. Phys. Today 63, 38 (2010)
E.A.V. Ferri, I.A. Santos, E. Radovanovic, R. Bonzanini, E.M. Girotto, Chemical characterization of BiFeO3 obtained by Pechini method. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 19, 1153–1157 (2008)
S.K. Pradhan, J. Das, P.P. Rout, S.K. Das, D.K. Mishra, D.R. Sahu, A.K. Pradhan, V.V. Srinivasu, B.B. Nayak, S. Verma, B.K. Roul, Defect driven multiferroicity in Gd doped BiFeO3 at room temperature. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 3614–3622 (2010)
A.K. Pradhan, K. Zhang, D. Hunter, J.B. Dadson, G.B. Louts, Magnetic and electrical properties of single-phase multiferroic BiFeO3. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 093903 (2005)
Y.P. Wang, L. Zhou, M.F. Zhang, X.Y. Chen, J.M. Liu, Z.G. Liu, Room-temperature saturated ferroelectric polarization in BiFeO3 ceramics synthesized by rapid liquid phase sintering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1731–1733 (2004)
J. Wei, R. Haumont, R. Jarrier, P. Berhtet, B. Dkhi, Nonmagnetic Fe-site doping of BiFeO3 multiferroic ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 102509 (2010)
N. Kumar, A. Shukla, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural electrical and magnetic properties of (Cd, Ti) modified BiFeO3. Phys. Lett. A 381, 2721–2730 (2017)
A. Shukla, N. Kumar, C. Behera, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural and electrical characteristics of (Co, Ti) modified BiFeO3. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 7115–7123 (2016)
A. Mukherjee, S. Basu, G. Chakraborty, M. Pal, Effect of Y-doping on the electrical transport properties of nanocrystalline BiFeO3. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 014321–014328 (2012)
V.V. Lazenka, A.F. Ravinski, I.I. Makoed, J. Vanacken, G. Zhang, V.V. Moshchalkov, Weak ferromagnetism in La-doped BiFeO3 multiferroic thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 123916 (2012)
H. Uchida, R. Ueno, H. Funakubo, S. Koda, Crystal structure and ferroelectric properties of rare-earth substituted BiFeO3 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 014106 (2006)
Z.X. Cheng, X.L. Wang, S.X. Dou, H. Kimura, K. Ozawa, Enhancement of ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism in rare earth element doped BiFeO3. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 116109 (2008)
A. Mukherjee, S. Basu, P.K. Manna, S.M. Yusuf, M. Pal, Enhancement of multiferroic properties of nanocrystalline BiFeO3 powder by Gd-doping. J. Alloy Comp. 598, 142–150 (2014)
D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, M. Ghasemi-Kooch, A sonochemical method for synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and thermal stable PVA-based magnetic nanocomposite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20(6), 3970–3974 (2014)
A. Abbasi, D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, M. Hamadanian, Photo-degradation of methylene blue: photocatalyst and magnetic investigation of Fe2O3–TiO2 nanoparticles and nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 4800–4809 (2016)
D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, Synthesis of urchin-like CdS-Fe3O4 nanocomposite and its application in flame retardancy of magnetic cellulose acetate. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 24, 284–292 (2015)
A. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, Synthesis and characterization of FeSe2 nanoparticles and FeSe2/FeO(OH) nanocomposites by hydrothermal method. J. Alloy Compd. 625, 26–33 (2015)
G.S. Lotey, N.K. Verma, Structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of Gd-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles with reduced particle size. J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 742 (2012)
F. Chang, S. Guilin, F. Kun, Q. Ping, Z. Qijun, Effect of gadolinium substitution on dielectric properties of bismuth ferrite. J. Rare Earth 24, 273–276 (2006)
D.V. Vassallo, M.R. Simões, L.B. Furieri, M. Fioresi, J. Fiorim, E.A.S. Almeida, J.K. Angeli, G.A. Wiggers, F.M. Peçanha, M. Salaices, Toxic effects of mercury, lead and gadolinium on vascular reactivity. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 44, 939–946 (2011)
T.W. Clarkson, L. Magos, G.J. Myers, The toxicology of mercury-current exposures and clinical manifestations. N. Engl. J. Med. 349, 1731–1737 (2003)
W. Zhou, H. Deng, H. Cao, J. He, J. Liu, P. Yang, J. Chu, Effects of Sm and Mn co-doping on structural, optical and magnetic properties of BiFeO3 films prepared by a sol–gel technique. Mater. Lett. 144, 93–96 (2015)
R. Guo, L. Fang, W. Dong, F. Zheng, M. Shen, Enhanced photocatalytic activity and ferromagnetism in Gd doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J Phys. Chem. C 114, 21390–21396 (2010)
D. Kuang, P. Tang, X. Wu, S. Yang, X. Ding, Y. Zhang, Structural, optical and magnetic studies of (Y, Co) co-substituted BiFeO3 thin films. J. Alloy. Compd. 671, 192–199 (2016)
S. Chauhan, M. Kumar, S. Chhoker, S.C. Katyal, H. Singh, M. Jewariya, K.L. Yadav, Multiferroic, magnetoelectric and optical properties of Mn doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 152, 525–529 (2012)
S. Irfan, S. Rizwan, Y. Shen, L. Li, S. Butt, C.W. Nan, The gadolinium (Gd3+) and tin (Sn4+) co-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles as new solar light active photocatalyst. Sci. Rep. 7, 42493 (2017)
M. Esmaeili-Zare, M. Salavati-Niasari, A. Sobhani, Simple sonochemical synthesis and characterization of HgSe nanoparticles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 19, 1079–1086 (2012)
S. Moshtaghia, D. Ghanbarib, M. Salavati-Niasari, Characterization of CaSn(OH)6 and CaSnO3 nanostructures synthesized by a new precursor. J. Nanostruct. 5, 169–174 (2015)
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M.S. Morassaei, M. Salavati-Niasari, Facile fabrication of Dy2Sn2O7–SnO2 nanocomposites as an effective photocatalyst for degradation and removal of organic contaminants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 497, 298–308 (2017)
B. Park, An interactive powder diffraction data interpretations and indexing program version 2.1 (E. WU School of Physical Sciences, Flinders University of South Australia, Bedford Park, 1989), p. 5042
N. Kumar, A. Shukla, N. Kumar, S. Sahoo, S. Hajra, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, bulk permittivity and impedance spectra of electronic material: Bi(Fe0.5La0.5)O3. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 1919–1926 (2019)
N. Kumar, A. Shukla, N. Kumar, S. Sahoo, S. Hajra, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, electrical and ferroelectric characteristics of Bi(Fe0.9La0.1)O3. Ceram. Int. 44, 21330–21337 (2018)
A. Shukla, N. Kumar, C. Behera, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, dielectric and magnetic characteristics of Bi(Ni0.25Ti0.25Fe0.50)O3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 1209–1216 (2016)
N. Kumar, A. Shukla, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, dielectric, electrical and magnetic characteristics of lead-free multiferroic, Bi(Cd0.5Ti0.5)O3–BiFeO3 solid solution. J Alloy. Compd. 747, 895–904 (2018)
A.V. Zalesskii, A.A. Frolov, T.A. Khimich, A.A. Bush, Composition-induced transition of spin-modulated structure into a uniform antiferromagnetic state in a Bi1−xLaxFeO3 system studied using 57Fe NMR. Phys. Solid State 45(1), 141–145 (2003)
I.O. Troyanchuk, A.N. Chobot, O.S. Mantytskaya, N.V. Tereshko, Magnetic properties of Bi(Fe1−xMx)O3 (M = Mn, Ti). Inorg. Mater. 46, 424–428 (2010)
N. Kumar, A. Shukla, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, electrical and magnetic characteristics of Ni/Ti modified BiFeO3 lead free multiferroic material. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 6673–6684 (2017)
J.R. Macdonald, W.B. Johnson, Impedance spectroscopy theory, experiments and applications (Wiley, Hoboken, 2005)
A.K. Jonscher, The ‘universal’ dielectric response. Nature 267, 673–679 (1977)
S. Dash, R.N.P. Choudhary, A. Kumar, Impedance spectroscopy and conduction mechanism of multiferroic (Bi0.6K0.4)(Fe0.6Nb0.4)O3. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 75, 1376–1382 (2014)
N. Hirose, A.R. West, Impedance spectroscopy of undoped BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 1633 (1996)
A. Sinha, A. Dutta, Microstructure evolution, dielectric relaxation and scaling behaviour of Dy for-Fe substituted Ni-nanoferrites. RSC Adv. 5, 100330–100338 (2015)
G. Singh, V.S. Tiwari, P.K. Gupta, Role of oxygen vacancies on relaxation and conduction behaviour of KNbO3 ceramic. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 064103 (2010)
N.K. Karan, D.K. Pradhan, R. Thomas, B. Natesan, R.S. Katiyar, Solid polymer electrolytes based on polyethylene oxide and lithium trifluoro-methane sulfonate (PEO–LiCF3SO3): ionic conductivity and dielectric relaxation. Solid State Ion. 179, 689 (2008)
A.K. Jonscher, Universal relaxation law (Chelsea Dielectrics Press, London, 1996)
B. Dhanalakshmi, P. Kollu, B. Chandra Sekhar, B. Parvatheeswara Rao, P.S.V. Subba Rao, Enhanced magnetic and magneto-electric properties of Mn doped multiferroic ceramics. Ceram. Int. 43, 9272–9275 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to National Physical Laboratory, New Delhi, for providing some TEM characterization facility. Author Alok Shukla gratefully acknowledges the financial support received from SERB-DST, Government of India, New Delhi, in the form of Research Project no. EMR/2015/002420.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Thansanga, L., Shukla, A., Kumar, N. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Study of effect of Gd substitution at the Fe site on structural, dielectric and electrical characteristics of BiFeO3. Appl. Phys. A 125, 764 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3058-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3058-y