Abstract
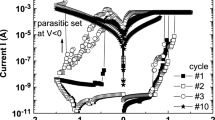
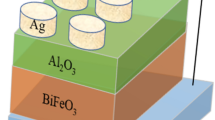
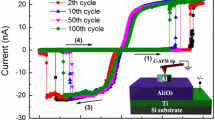
In this work, a resistive switching memory device with Ag/(NiO/Al2O3)3/fluorine-doped SnO2 structure was fabricated with solution-based process including spin-coating of triple-layered NiO/Al2O3 films and ink-jet printing of Ag electrodes. Bipolar resistive switching characteristic was observed in such a structure, with the resistance ratio between high and low resistance states over two orders and good cycling stability in voltage sweeping measurements. More importantly, the SET/RESET voltages, which were in the range of 0.8‒2.4 V and − 0.7 to − 2.8 V, respectively, showed significant improvement in voltage distribution (78.4% and 71.2% narrower) as compared to devices solely based on Al2O3 film. It is believed that the narrow distribution of SET and RESET voltages results from the reduced randomness of the formation and rupture of conductive filaments under applied voltages, since NiO and Al2O3 have different dielectric constants and the distribution of electric field in the multilayers can be varied to facilitate the formation and rupture of conductive filaments. Moreover, electroforming process was not required to activate the device based on triple-layered NiO/Al2O3 films. The characterization results especially the narrow SET/RESET voltage distribution and forming-free property make devices based on multilayered NiO/Al2O3 thin films promising for thin film-based nonvolatile memory applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.J. Yang, D.B. Strukov, D.R. Stewart, Memristive devices for computing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 13–24 (2013)
T.C. Chang, K.C. Chang, T.M. Tsai, T.J. Chu, S.M. Sze, Resistance random access memory. Mater. Today 19, 254–264 (2016)
A. Chen, A review of emerging non-volatile memory (NVM) technologies and applications. Solid-State Electron. 125, 25–38 (2016)
D. Ielmini, Resistive switching memories based on metal oxides: mechanisms, reliability and scaling. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 31, 063002 (2016)
Y. Liu, T.P. Chen, Z. Liu, Y.F. Yu, Q. Yu, P. Li, S. Fung, Self-learning ability realized with a resistive switching device based on a Ni-rich nickel oxide thin film. Appl. Phys. A 105, 855–860 (2011)
Z. Liu, T.P. Chen, Y. Liu, S. Zhang, Magnetron Sputtered Ni-rich Nickel Oxide Nano-Films for resistive switching memory applications. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 10, 20–25 (2013)
E.J. Yoo, M. Lyu, J.H. Yun, C.J. Kang, Y.J. Choi, L.Z. Wang, Resistive switching behavior in organic-inorganic hybrid CH3NH3PbI3- xClx perovskite for resistive random access memory devices. Adv. Mater. 27, 6170–6175 (2015)
Y. Ji, B. Cho, S. Song, T.W. Kim, M. Choe, Y.H. Kahng, T. Lee, stable switching characteristics of organic nonvolatile memory on a bent flexible substrate. Adv. Mater. 22, 3071–3075 (2010)
C.L. He, F. Zhuge, X.F. Zhou, M. Li, G.C. Zhou, Y.W. Liu, J.Z. Wang, B. Chen, W.J. Su, Z.P. Liu, Y.H. Wu, P. Cui, R.W. Li, Nonvolatile resistive switching in graphene oxide thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 232101 (2009)
W.A. Hubbard, A. Kerelsky, G. Jasmin, E.R. White, J. Lodico, M. Mecklenburg, B.C. Regan, Nanofilament formation and regeneration during Cu/Al2O3 resistive memory switching. Nano Lett. 15, 3983–3987 (2015)
U. Celano, L. Goux, R. Degraeve, A. Fantini, O. Richard, H. Bender, M. Jurczak, W. Vandervorst, Imaging the three-dimensional conductive channel in filamentary-based oxide resistive switching memory. Nano Lett. 15, 7970–7975 (2015)
Z.H. Chen, Z. Liu, W.K. Ma, Y.K. Shen, H.Y. Zhang, T.P. Chen, International Nanoelectronics Conference 1–2 (2016)
P. Zhou, H. Shen, J. Li, L.Y. Chen, C. Gao, Y. Lin, T.A. Tang, Resistance switching study of stoichiometric ZrO2 films for non-volatile memory application. Thin Solid Films 518, 5652–5655 (2010)
S.A. Hadi, K.M. Humood, M.A. Jaoude, H. Abunahla, H.F.A. Shehhi, B. Mohammad, Bipolar Cu/HfO2/p2+ Si memristors by sol-gel spin-coating method and their application to environmental sensing. Sci. Rep. 9, 9983 (2019)
D. Conti, M. Laurenti, S. Porro, C. Giovinazzo, S. Bianco, V. Fra, A. Chiolerio, C.F. Pirri, G. Milano, C. Ricciardi, Resistive switching in sub-micrometric ZnO polycrystalline films. Nanotechnology 30, 065707 (2019)
T. You, Y. Shuai, W. Luo, N. Du, D. Burger, I. Skorupa, R. Hubner, S. Henker, C. Mayr, R. Schuffny, T. Mikolajick, O.G. Schmidt, H. Schmidt, Exploiting memristive BiFeO3 bilayer structures for compact sequential logics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 3357–3365 (2014)
Y. Yang, P. Gao, S. Gaba, T. Chang, X. Pan, W. Lu, Observation of conducting filament growth in nanoscale resistive memories. Nat. Commun. 3, 732 (2012)
K.C. Chang, T.C. Chang, T.M. Tsai, R. Zhang, Y.C. Hung, Y.E. Syu, Y.F. Chang, M.C. Chen, T.J. Chu, H.L. Chen, C.H. Pan, C.C. Shih, J.C. Zheng, S.M. Sze, Physical and chemical mechanisms in oxide-based resistance random access memory. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10, 1–27 (2015)
electrochemical systems at the atomic scale, Valov, Redox-based resistive switching memories (ReRAMs). Chemelectrochem 1, 26–36 (2014)
Z. Liu, T.P. Chen, Y. Liu, M. Yang, J.I. Wong, Z.H. Cen, Static dielectric constant of Al nanocrystal/Al2O3 nanocomposite thin films determined by the capacitance-voltage reconstruction technique. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 173110 (2010)
R.L. Nigro, G. Fisichella, S. Battiato, G. Greco, P. Fiorenza, F. Roccaforte, G. Malandrino, An insight into the epitaxial nanostructures of NiO and CeO2 thin film dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN heterostructures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 162, 461–468 (2015)
G.D. Wilk, R.M. Wallace, J.M. Anthony, High-K gate dielectrics: current status and materials properties considerations. J. Appl. Phys. 89, 5243–5275 (2001)
S.B. Chen, C.H. Lai, A. Chin, J.C. Hsieh, J. Liu, High-density MIM capacitors using Al2O3 and AlTiOx dielectrics. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 23, 185–187 (2002)
R. Ravindran, K. Gangopadhyay, S. Gangopadhyay, N. Mehta, N. Biswas, Permittivity enhancement of aluminum oxide thin films with the addition of silver nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 263511 (2006)
K.M. Kim, D.S. Jeong, C.S. Hwang, Nanofilamentary resistive switching in binary oxide system; a review on the present status and outlook. Nanotechnology 22, 254002 (2011)
C.Y. Huang, C.Y. Huang, T.L. Tsai, C.A. Lin, T.Y. Tseng, Switching mechanism of double forming process phenomenon in ZrOx/HfOy bilayer resistive switching memory structure with large endurance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 062901 (2014)
Q.Q. Sun, J.J. Gu, L. Chen, P. Zhou, P.F. Wang, S.J. Ding, D.W. Zhang, Controllable filament with electric field engineering for resistive switching uniformity. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 32, 1167–1169 (2011)
K. Kim, E. Kim, Y. Kim, J.H. Sok, K. Park, Characteristics of resistive switching in ZnO/SiOx multi-layers for transparent nonvolatile memory devices. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 69, 1798–1804 (2016)
Z. Fang, H.Y. Yu, X. Li, N. Singh, G.Q. Lo, D.L. Kwong, HfOx/TiOx/HfOx/TiOx multilayer-based forming-free RRAM devices with excellent uniformity. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 32, 566–568 (2011)
Y.-T. Wu, S. Jou, P.-J. Yang, Resistance switching of thin AlOx and Cu-doped-AlOx films. Thin Solid Films 544, 24–27 (2013)
P.S. Chen, Y.S. Chen, H.Y. Lee, W. Liu, P.Y. Gu, F. Chen, M.J. Tsai, Improved endurance in ultrathin Al2O3 film with a reactive Ti layer based resistive memory. Solid State Electron 77, 41–45 (2012)
M.S. Kim, Y.H. Hwang, S. Kim, Z. Guo, D.I. Moon, J.M. Choi, M.L. Seol, S.S. Bae, Y.K. Choi, Effects of the oxygen vacancy concentration in InGaZnO-based resistance random access memory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 243503 (2012)
S. Kim, Y.K. Choi, Resistive switching of aluminum oxide for flexible memory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 223508 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under project No. 61404031, the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province of China under Project No. 2016A050502058, and the Department of Education of Guangdong Province under Project No. 2014KTSCX054.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X.L., Wen, C., Liu, Y. et al. Uniform and electroforming-free resistive memory devices based on solution-processed triple-layered NiO/Al2O3 thin films. Appl. Phys. A 125, 666 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2960-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2960-7