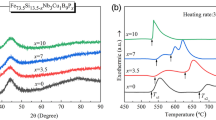
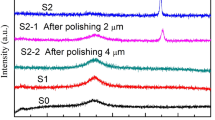
Abstract
We report on systematic structural and magnetic characteristics’ evolution studies of (Fe1−xCox)81Zr9B10 (x = 0, 1/6, 1/3, 1/2) amorphous alloys prepared by a single roller melt spinning with post-annealing treatments under a vacuum condition. With representative chemical composition, the crystallization processes of the above four typical amorphous alloys are complicated under the dedicated experimental investigations and interpretation. The α-Mn-type phase is detected in Fe81Zr9B10 alloy, while the β-Mn-type phase is observed for high Co concentration alloys. Both α-Mn-type phase and β-Mn-type phase are the transitional metastable phases formed during the dynamic crystallization. Importantly, the precipitations of metastable α-Mn- and β-Mn-type phases boost up corresponding coercivity (Hc). Along with the transformation of metastable phases, Hc decreases considerably. The precipitation of certain of β-Mn-type phase in the primary crystallization stage facilitates gaining low Hc in the second stage of crystallization. Our work paves a new path to tailor the magnetic characteristics in Fe(Co)-based nanocrystalline alloys by engineering the microstructure of metastable phase(s).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.R. Lashgari, D. Chu, S. Xie, H. Sun, M. Ferry, S. Li, Composition dependence of the microstructure and soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys: a review study. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 391, 61–82 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2014.03.010
Adrian Radoń, Patryk Włodarczyk, Łukasz Hawełek, Mariola Kądziołka-Gaweł, Piotr Gębara, Ryszard Nowosielski, Rafał Babilas, Thermodynamic approach for determining chemical composition of Fe–Co based amorphous alloys with high thermal stability and glass forming ability. J. Alloy Compd. 763, 141–152 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.242
I. Solomon, N. Solomon, Effect of cobalt on the corrosion behaviour of amorphous Fe–Co–Cr–B–Si alloys in dilute mineral acids. Can. Metall. Q 49, 319–324 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1179/cmq.2010.49.3.319
T. Kaňčuch, M. Miglierini, A. Lancok, P. Švec, E. Illeková, Influence of cobalt substitution on hyperfine interactions in (Fe1-xCox)76Mo8Cu1B15 alloys. Acta Phys. Pol. 113, 63–66 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/112/3/032055
L. Xue, W.M. Yang, H.S. Liu, H. Men, A.D. Wang, C.T. Chang, B.L. Shen, Effect of Co addition on the magnetic properties and microstructure of FeNbBCu nanocrystalline alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 198–201 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.06.020
J. Wang, Z. Wang, Y.Y. Jia, R.M. Shi, Z.P. Wen, High temperature soft magnetic properties of (FexCo1−x)73.5Cu1Mo3Si13.5B9 (x=0.5, 1) alloys. J Magn Magn Mater 328, 62–65 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.09.068
B. Kunca, J. Marcin, P. Švec, J. Kováč, P. Švec Sr., I. Škorvánek, Influence of Co doping on induced anisotropy and domain structure in magnetic field annealed (Fe1−xCox)79Mo8Cu1B12. Acta Phys. Pol. A 131, 759–761 (2017). https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.131.759
G. Herzer, Grain structure and magnetism of nanocrystalline ferromagnets. IEEE Trans. Mag. 25, 3327–3329 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1109/20.42292
K. Suzuki, J.M. Cadogan, Random magnetocrystalline anisotropy in two-phase nanocrystalline systems. Phys. Rev. B 58, 2730–2739 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.58.2730
I.V. Lyasotsky, N.B. Dyakonova, D.L. Dyakonov, Metastable primary precipitation phases in multicomponent glass forming Fe-base alloys with metalloids. J. Alloy Compd. 586, S20–S23 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.03.112
T. Nagase, Y. Umakoshi, Phase transformation in Fe81.0Zr9.0B10.0 metallic glass during thermal annealing and electron irradiation. ISIJ Int. 46, 1371–1380 (2006)
Y.M. Sun, B. Li, Z. Hua, The crystallization process and magnetic property of Fe81Zr3Nb6B10 alloy. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 29, 1550196-1-1550206 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984915501961
M. Imafuku, S. Sato, H. Koshiba, E. Matsubara, A. Inoue, Structural variation of Fe–Nb–B metallic glasses during crystallization process. Scr. Mater. 44, 2369–2372 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(01)00776-X
A. Hirata, Y. Hirotsu, K. Amiya, N. Nishiyama, A. Inoue, Fe23B6-type quasicrystal-like structures without icosahedral atomic arrangement in an Fe-based metallic glass. Phys. Rev. B 80, 140201-1-140204 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.80.140201
J. Jahng, H. Yang, E.S. Lee, Substructure imaging of heterogeneous nanomaterials with enhanced refractive index contrast by using a functionalized tip in photoinduced force microscopy. Light Sci. Appl. 7, 73-1-9 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-018-0069-y
G.Z. Xing, D.D. Wang, C.-J. Cheng, M. He, S. Li, T. Wu, Emergent ferromagnetism in ZnO/Al2O3 core-shell nanowires: towards oxide spinterfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 022402-1-22405 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4813217
X.Y. Chen, Z. Tian, Recent progress in terahertz dynamic modulation based on graphene. Chin. Opt. 10, 86–97 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3788/CO.20171001.0086
X. Zhang, L. Song, L. Cai, X.Z. Tian, Q. Zhang, X.Y. Qi, W.B. Zhou, N. Zhang, F. Yang, Q.X. Fan, Y.C. Wang, H.P. Liu, X.D. Bai, W.Y. Zhou, S.S. Xie, Optical visualization and polarized light absorption of the single-wall carbon nanotube to verify intrinsic thermal applications. Light Sci. Appl. 4, e318(1–8) (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2015.91
J.F. Wu, H.T. Wang, Z.W. Su, M.H. Zhang, X.D. Hu, Y.J. Wang, Z. Wang, B. Zhong, W.W. Zhou, J.P. Liu, G.Z. Xing, Highly flexible and sensitive wearable E-skin based on graphite nanoplatelet and polyurethane nanocomposite films in mass industry production available. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 38745–38754 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b10316
X. Bao, Y. Yuan, J.Q. Chen, B.H. Zhang, L. Song, C.B. Liu, R. Zbořil, S.N. Qu, In vivo theranostics with near-infrared-emitting carbon dots—highly efficient photothermal therapy based on passive targeting after intravenous administration. Light Sci. Appl. 7, 91 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-018-0090-1
T. Li, M.L. Zhang, F. Wang, D.M. Zhang, G.P. Wang, Fabrication of optical waveguide amplifiers based on bonding-type NaYF4: Er nanoparticles-polymer. Chin. Opt. 10, 219–225 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3788/CO.20171002.0219
D. Qu, M. Zheng, J. Li, Z.G. Xie, Z.C. Sun, Tailoring color emissions from N-doped graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Light: Sci. Appl. 4, 364 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2015.137
D.D. Wang, Q. Chen, G.Z. Xing, J.B. Yi, S.R. Bakaul, J. Ding, J.L. Wang, T. Wu, Robust room-temperature ferromagnetism with giant anisotropy in Nd-doped ZnO nanowire arrays. Nano Lett. 12, 3994–4000 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl301226k
Y.C. Li, H.B. Xin, H.X. Lei, L.L. Liu, Y.Z. Li, Y. Zhang, B.J. Li, Manipulation and detection of single nanoparticles and biomolecules by a photonic nanojet. Light Sci. Appl. 5, e16176-1-9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2016.176
D.D. Wang, G.Z. Xing, F. Yan, Y.S. Yan, S. Li, Ferromagnetic (Mn, N)-codoped ZnO nanopillars array: experimental and computational insights. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 022412-1-5 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4861936
J.F. Wu, Z.Y. Ma, Z. Hao, J.T. Zhang, P.F. Sun, Sheath-core fiber strain sensors driven by in-situ crack and elastic effects in graphite nanoplate composites. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2, 750–759 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.8b01926
A. Takeuchi, A. Inoue, Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 46, 2817–2829 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.46.2817
L. Wang, X.-W. Lin, W. Hu, G.-H. Shao, P. Chen, L.-J. Liang, B.-B. Jin, P.-H. Wu, H. Qian, Y.-N. Lu, X. Liang, Z.-G. Zheng, Y.-Q. Lu, Broadband tunable liquid crystal terahertz waveplates driven with porous graphene electrodes. Light Sci. Appl. 4, e253-1-6 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2015.26
D.D. Wang, W.L. Wang, M.Y. Huang, A. Lek, J. Lam, Z.H. Mai, Failure mechanism analysis and process improvement on time-dependent dielectric breakdown of Cu/ultra-low-k dielectric based on complementary Raman and FTIR spectroscopy study. AIP Adv. 4, 077124-1-9 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4890960
L. Li, W. Guo, Y.Z. Yan, S. Lee, T. Wang, Label-free super-resolution imaging of adenoviruses by submerged microsphere optical nanoscopy. Light Sci. Appl. 2, e104-1-8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2013.60
X.B. Cheng, J.L. Zhang, T. Ding, Z.Y. Wei, H.Q. Li, Z.S. Wang, The effect of an electric field on the thermomechanical damage of nodular defects in dielectric multilayer coatings irradiated by nanosecond laser pulses. Light Sci. Appl. 2, e80-1-8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2013.36
G.Z. Xing, J. Yi, L.M. Wong, J. Ding, T.C. Sum, C.H.A. Huan, T. Wu, Comparative study of room-temperature ferromagnetism in Cu-doped ZnO nanowires enhanced by structural inhomogeneity. Adv. Mater. 20, 3521–3527 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200703149
P. Wang, Y.P. Wang, L.M. Tong, Functionalized polymer nanofibers: a versatile platform for manipulating light at the nanoscale. Light Sci. Appl. 2, e102-1-10 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2013.58
G.Z. Xing, J. Yi, D.D. Wang, L. Liao, Z.X. Shen, J. Ding, T. Wu, Strong correlation between ferromagnetism and oxygen deficiency in Cr-doped In2O3−δ nanostructures. Phys. Rev. B 76, 174406-1-9 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.79.174406
E. Matioli, S. Brinkley, K.M. Kelchner, Y.-L. Hu, S. Nakamura, S. DenBaars, J. Speck, C. Weisbuch, High-brightness polarized light-emitting diodes. Light. Sci. Appl. 1, e22-1-7 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2012.22
W.Q. Yu, Q.L. Zhou, Z.S. Liu, H.Q. Zeng, Z.Q. Wang, Z. Hua, Effect of Cu and Mo additions on the crystallization behavior and magnetic properties of Fe80Zr10B10 alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 26, 4807–4812 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2950-x
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 51301075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, W., Lu, L., Zuo, B. et al. Tailoring magnetic characteristics of (Fe1−xCox)81Zr9B10 amorphous alloys via engineering crystallization processes. Appl. Phys. A 125, 636 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2935-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2935-8