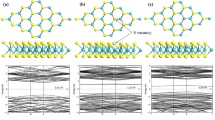
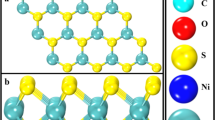
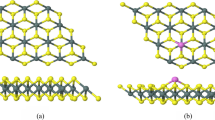
Abstract
Lung cancer prognosis in its early stage has received considerable attention due to its high incidence and mortality rates. This work proposed a novel candidate, Ni-doped MoS2, as a promising biosensor for lung cancer prognosis through exhaled breathe analysis, based on density functional theory (DFT) method. Calculated results indicated that Ni-MoS2 would have desirable adsorption performance towards three typical (volatile organic compounds) VOCs of lung cancer patients, leading to dramatic change in geometric and electronic property of Ni-doped monolayer. These subsequently could cause visible change in conductivity for Ni-MoS2 based bio-devices, giving rise to the sensing mechanism for its real application. In addition, desorption of these gas molecules from the Ni-MoS2 surface could be fulfilled through heating process, due to the determined physisorption in these adsorbing systems, which allows the recyclable use of the biosensors. Our calculations aim at proposing advanced sensing material for experimentalists to exploit potential progress in lung cancer prognosis through exhaled air detection.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Altintas, I. Tothill, Biomarkers and biosensors for the early diagnosis of lung cancer[J]. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 188(188), 988–998 (2013)
D. Huo, Y. Xu, C. Hou, M. Yang, H. Fa, A novel optical chemical sensor based AuNR-MTPP and dyes for lung cancer biomarkers in exhaled breath identification[J]. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 199(6), 446–456 (2014)
M. Varellagarcia, J. Kittelson, A.P. Schulte, K.O. Vu, H.J. Wolf, C. Zeng, F.R. Hirsch, T. Byers, T. Kennedy, Y.E. Miller, Multi-target interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization assay increases sensitivity of sputum cytology as a predictor of lung cancer[J]. Cancer Detect. Prev. 28(4), 244–251 (2004)
T. Kikuchi, D.P. Carbone, Proteomics analysis in lung cancer: challenges and opportunities[J]. Respirology 12(1), 22–28 (2007)
M. Lichy, P. Aschoff, C.A. Stemmer, W. Horger, C. Mueller-Horvat, G. Steidle, M. Horger, J. Schafer, S. Eschmann, B. Kiefer, Tumor detection by diffusion-weighted MRI and ADC-mapping-initial clinical experiences in comparison to PET-CT[J]. Invest. Radiol. 42(9), 605 (2007)
C.I. Henschke, F. David, Yankelevitz. CT screening for lung cancer[J]. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 49(4), 477–490 (2009)
V.H. Tran, H.P. Chan, M. Thurston, P. Jackson, C. Lewis, D. Yates, G. Bell, S. Paul, Thomas, Breath analysis of lung cancer patients using an electronic nose detection system[J]. IEEE Sens. J. 10(9), 1514–1518 (2010)
L. Pauling, A.B. Robinson, R. Teranishi, P. Cary, Quantitative Analysis of urine vapor and breath by gas-liquid partition chromatography[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69(4), 2374–2376 (1971)
M. Phillips, Breath tests in medicine[J]. Sci. Am. 267(1), 74–79 (1992)
C. Xing, B.S. Ms, W.M. Fengjuan Xu, M.S. Yue, B.S. Yuefeng Pan, W. Deji Lu, M.D. Ping, M.D. Kejing Ying, M.S. Enguo Chen, W. Zhang, A study of the volatile organic compounds exhaled by lung cancer cells in vitro for breath diagnosis[J]. Cancer 110(4), 835–844 (2007)
T. Itoh, T. Nakashima, T. Akamatsu, N. Izu, W. Shin, Nonanal gas sensing properties of platinum, palladium, and gold-loaded tin oxide VOCs sensors[J]. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 187(1), 135–141 (2013)
W. Miekisch, J.K. Schubert, F.E. Gabriele, Noeldge-Schomburg, Diagnostic potential of breath analysis—focus on volatile organic compounds[J]. Clin. Chim. Acta. 347(1), 25–39 (2004)
K. Jun. YuH. Young, Young, Baek. Inbok, Ahn. Changgeun, Lee. Bong Kuk, Kim. Yarkyeon, Yoon. Yong Sun, Lim. Ji Eun, Lee. Byeongjun, Jang. Won Ik. Use of Gas-Sensor Array Technology in Lung Cancer Diagnosis[J]. Journal of Sensor Science & Technology, 2013, 22 (4), 249–255
Q. Wan, X. Zhang, Y. Gui, Theoretical study on Pt-doped carbon nanotubes used to detect typical exhaled gases of lung cancer[J]. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 12(10), 3412–3417 (2015)
B. Bogusław, L. Tomasz, J. Tadeusz, W.-P. Anna, W. Marta, R. Joanna. Identification of volatile lung cancer markers by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry: comparison with discrimination by canines[J]. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 404(1), 141–146 (2012)
Y. Wang, Y. Hu, D. Wang, K. Yu, L. Wang, Y. Zou, C. Zhao, X. Zhang, P. Wang, K. Ying, The analysis of volatile organic compounds biomarkers for lung cancer in exhaled breath, tissues and cell lines[J]. Cancer Biomarkers 11(4), 129 (2012)
Q. Wan, Y. Xu, X. Chen, H. Xiao, Exhaled gas detection by a novel Rh-doped CNT biosensor for prediagnosis of lung cancer: a DFT study[J]. Mol. Phys. 116(17), 2205–2212 (2018)
K. Xu, H.Yan,C.Fu Tan, Y. Lu, Y. Li, G.W. Ho, R. Ji, M. Hong, Hedgehog inspired CuO nanowires/Cu2O composites for broadband visible-light-driven recyclable surface enhanced Raman scattering[J]. Adv. Opt. Mater. 5, 1701167 (2018)
Z. Zhen, Yu Wei, W. Jing, L. Dan, X. Qiao, X. Qin, T. Wang, Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensor of gaseous aldehydes as biomarkers of lung cancer on dendritic Ag nanocrystals[J]. Anal. Chem. 89(3), 1416 (2017)
M. Hakim, Y.Y. Broza, O. Barash, N. Peled, M. Phillips, A. Amann, H. Haick, Volatile organic compounds of lung cancer and possible biochemical pathways[J]. Chem. Rev. 112(11), 5949–5966 (2012)
T. Itoh, T. Miwa, A. Tsuruta, T. Akamatsu, N. Izu, W. Shin, J. Park, T. Hida, T. Eda, Y. Setoguchi, Development of an exhaled breath monitoring system with semiconductive gas sensors, a gas condenser unit, and gas chromatograph columns[J]. Sensors 16(11), 1891 (2016)
M. Phillips, N. Altorki, J.H. Austin, R.B. Cameron, R.N. Cataneo, J. Greenberg, R. Kloss, R.A. Maxfield, M.I. Munawar, H.I. Pass, Prediction of lung cancer using volatile biomarkers in breath[J]. Cancer Biomarkers 3(2), 95 (2007)
G. Peng, U. Tisch, O. Adams, M. Hakim, N. Shehada, Y.Y. Broza, S. Billan, R. Abdah-Bortnyak, A. Kuten, H. Haick, Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles[J]. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4(10), 669–673 (2009)
A. Sharma, M.Shahid Anu, M. Khan, Husain, S. Khan, A. Srivastava. Sensing of CO and NO on Cu-doped MoS2 monolayer based single electron transistor: a first principles study[J]. IEEE Sens. J. 99:1–1 (2018)
M. Donarelli, S. Prezioso, F. Perrozzi, F. Bisti, M. Nardone, L. Giancaterini, C. Cantalini, L. Ottaviano. Response to NO2 and other gases of resistive chemically exfoliated MoS2-based gas sensors[J]. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 207, 602–613 (2015)
D. Zhang, J. Wu, P. Li, Y. Cao, Room-temperature SO2 gas-sensing properties based on a metal-doped MoS2 nanoflower: an experimental and density functional theory investigation[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 39 (2017)
L. Kou, Tuning magnetism and electronic phase transitions by strain and electric field in zigzag MoS2 nanoribbons[J]. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3(20), 2934 (2012)
P. Wu, N. Yin, P. Li, W. Cheng, M. Huang, The adsorption and diffusion behavior of noble metal adatoms (Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag and Au) on a MoS2 monolayer: a first-principles study[J]. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, (31) (2017)
Y. Fan, J. Zhang, Y. Qiu, J. Zhu, Y. Zhang, G. Hu, A DFT study of transition metal (Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Ag, Au, Rh, Pd, Pt and Ir)-embedded monolayer MoS2 for gas adsorption[J]. Comput. Mater. Sci. 138, 255–266 (2017)
Y. Li, X. Zhang, D. Chen, S. Xiao, J. Tang, Adsorption behavior of COF2 and CF4 gas on the MoS2 monolayer doped with Ni: a first-principles study[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. 5, 443 (2018)
X. Zhangab, Y. Guiac, H. Xiaoa, Y. Zhang, Analysis of adsorption properties of typical partial discharge gases on Ni-SWCNTs using density functional theory[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. 9, 47–54 (2016)
B. Delley, From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach[J]. J. Chem. Phys. 113(18), 7756–7764 (2000)
H. Cui, X. Zhang, D. Chen, Ju Tang, Adsorption mechanism of SF6 decomposed species on pyridine-like PtN3 embedded CNT: A DFT study[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. 32, 447 (2018)
B. Delley, Hardness conserving semilocal pseudopotentials[J]. Phys. Rev. B Condensed Matter 66(15), 155125 (2002)
A. Tkatchenko, R.A. Stasio, M. Head-Gordon, M. Scheffler, Dispersion-corrected Møller-Plesset second-order perturbation theory[J]. J Chem Phys 131(9), 171–171 (2009)
D. Chen, X. Zhang, J.U. Tang, H. Cui, Y. Li. Noble metal (Pt or Au)-doped monolayer MoS2 as a promising adsorbent and gas-sensing material to SO2, SOF2 and SO2F2 : a DFT study[J]. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 124(2):194 (2018)
H. Cui, X. Zhang, J. Zhang, Ju Tang, Adsorption behaviour of SF6 decomposed species onto Pd4-decorated single-walled CNT: a DFT study[J]. Mol. Phys. 53, 1–7 (2018)
W. Ju, T. Li, X. Su, H. Li, X. Li, D. Ma, Au cluster adsorption on perfect and defective MoS2 monolayers: structural and electronic properties[J]. Phys. Chem Chem. Phys. 51:19 (2017)
R. Kronberg, M. Hakala, N. Holmberg, K. Laasonen, Hydrogen adsorption on MoS2-surfaces: a DFT study on preferential sites and the effect of sulfur and hydrogen coverage[J]. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 24 (2017)
D. Yang, S.J. Sandoval, W.M. Divigalpitiya, J.C. Irwin, Structure of single-molecular-layer MoS2[J]. Phys.Rev.B 43(14), 12053–12056 (1991)
A. Shokri, N. Salami, Gas sensor based on MoS2 monolayer[J]. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 236, 378–385 (2016)
L. Yuwen, F. Xu, B. Xue, Z. Luo, Q. Zhang, B. Bao, S. Su, L. Weng, W. Huang, L. Wang, General synthesis of noble metal (Au, Ag, Pd, Pt) nanocrystal modified MoS2 nanosheets and the enhanced catalytic activity of Pd-MoS2 for methanol oxidation[J]. Nanoscale 6(11), 5762–5769 (2014)
D. Ma, W. Ju, T. Li, X. Zhang, C. He, B. Ma, Z. Lu, The adsorption of CO and NO on the MoS2 monolayer doped with Au, Pt, Pd, or Ni: A first-principles study[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. 383, 98–105 (2016)
B. Zhao, C.Y. Li, L.L. Liu, B. Zhou, Q.K. Zhang, Z.Q. Chen, Z. Tang, Adsorption of gas molecules on Cu impurities embedded monolayer MoS2: A first-principles study[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. 382, 280–287 (2016)
S. Zhao, J. Xue, K. Wei, Gas adsorption on MoS2 monolayer from first-principles calculations[J]. Chem. Phys. Lett. 595–596(3). 35–42 (2014)
X. Zhang, H. Cui, D. Chen, X. Dong, Ju Tang, Electronic structure and H2S adsorption property of Pt3 cluster decorated (8, 0) SWCNT[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2, 428 (2018)
A. De Jong, Sijbrand, J. Haas, G. Qian, D. Blazey, A. Hedin, Sanchezhernandez, Ann Heinson, Jose Guilherme Lima, Ronald Madaras, Arnaud Duperrin. Atomically thin MoS2: A new direct-gap semiconductor[J]. 2010
A.S. Rad, S.S. Shabestari, S. Mohseni, Samaneh Alijantabar Aghouzi. Study on the adsorption properties of O3, SO2, and SO3 on B-doped graphene using DFT calculations[J]. J. Solid State Chem. 237, 204–210 (2016)
P. Pyykkö, M. Atsumi, Molecular single-bond covalent radii for elements 1-118[J]. Chemistry 15(1), 186–197 (2009)
S.W. Han, G.B. Cha, Y. Park, S.C. Hong, Hydrogen physisorption based on the dissociative hydrogen chemisorption at the sulphur vacancy of MoS2 surface[J]. Sci Rep 7, 1 (2017)
A.J. Yang, D.W. Wang, X.H. Wang, J.F. Chu, P.L. Lv, Y. Liu, Phosphorene: A promising candidate for highly sensitive and selective SF6 decomposition gas sensors[J]. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 38(7), 963–966 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Li, M. Ni-doped MoS2 biosensor: a promising candidate for early diagnosis of lung cancer by exhaled breathe analysis. Appl. Phys. A 124, 751 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2185-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2185-1