Abstract
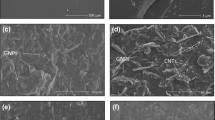
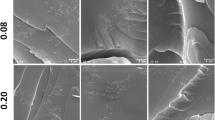
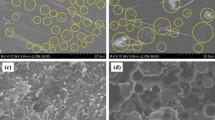
For a thermoelectric application, the thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity and figure of merit of epoxy resin-based composites incorporated with carbon nanotubes and TiO2 are investigated in this paper. First, the composite is prepared with a solution blending method. Then, the structure, thermal and electrical conductivities are characterized with experimental methods. Finally, the thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity and figure of merit are discussed. Results turn out that with an increasing content of carbon nanotube fillers, there are different changing trends of thermal and electrical conductivities because of large difference between thermal and electrical contact resistances in the composite. With the increasing filler content, the electrical conductivity increases exponentially while thermal conductivity saturates to be a constant value. Due to the large ratio of electrical to thermal conductivities, the figure of merit with 8 wt% of fillers is more than 50 times larger than that with a low content of fillers. Our results confirm that the recently proposed concept of ‘electron-percolation thermal-insulator’ is a feasible way to enhance the figure of merit of a polymer composite.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, M.Y. Tang, R.G. Yang, H. Lee, D.Z. Wang, Z.F. Ren, J.P. Fleurial, P. Gogna, Adv. Mater. 19, 1043 (2007)
D. Zhao, G. Tan, Appl. Therm. Eng. 66, 15 (2014)
R. Yang, G. Chen, Phys. Rev. B 69, 195316 (2004)
T.H. Wang, Q.H. Wang, C. Leng, X.D. Wang, Appl. Energy 154, 1 (2015)
J.H. Meng, X.X. Zhang, X.D. Wang, Energy 71, 367 (2014)
H. Lv, X.D. Wang, T.H. Wang, C.H. Cheng, Appl. Energy 164, 501 (2016)
T. Ma, J. Pandit, S.V. Ekkad, S.T. Huxtable, Q. Wang, Energy 84, 695 (2015)
G. Tan, D. Zhao, Appl. Therm. Eng. 86, 187 (2015)
G.S. Nolas, D.T. Morelli, T.M. Tritt, Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 29, 89 (1999)
T. Takabatake, K. Suekuni, T. Nakayama, E. Kaneshita, Rev. Mod. Phys. 86, 669 (2014)
R. Venkatasubramanian, E. Siivola, T. Colpitts, B. O’Quinn, Nature 413 597 (2001)
Y. Wang, J. Liu, J. Zhou, R. Yang, J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 24716 (2013)
Z.Z. Lin, C.L. Huang, Z. Huang, J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 17 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2017.14681
Z.Z. Lin, C.L. Huang, W.K. Zhen, Y.H. Feng, X.X. Zhang, G. Wang, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12, 189 (2017)
C.K. Mai, J. Liu, C.M. Evans, R.A. Segalman, M.L. Chabinyc, D.G. Cahill, G.C. Bazan, Macromolecules 49, 4957 (2016)
C.L. Huang, X. Qian, R.G. Yang, EPL 117, 24001 (2017)
B. Liu, T. Lu, B. Wang, J. Liu, T. Nakayama, J. Zhou, B. Li, Appl. Phys. Lett. 110, 113102 (2017)
M. He, W. Han, J. Ge, Y. Yang, F. Qiu, Z. Lin, Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 2894 (2011)
Z.L. Wang, Adv. Mater. 24, 280 (2012)
Z.D. Han, A. Fina, Prog. Polym. Sci. 36, 914 (2011)
A.P. Singh, B.K. Gupta, M. Mishra, A. Chandra, R. Mathur, S. Dhawan, Carbon 56, 86 (2013)
H. Xu, C. Wang, Y. Song, J. Zhu, Y. Xu, J. Yan, Y.X. Song, H.M. Li, Chem. Eng. J. 241, 35 (2014)
R.F. Zhang, D.Z. Guo, G.M. Zhang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 426, 763 (2017)
C.L. Huang, Z.Z. Lin, Y.H. Feng, X.X. Zhang, G. Wang, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 239 (2015)
D. Zhao, X. Qian, X. Gu, S.A. Jajja, R. Yang, J. Electron. Packag. 138, 040802 (2016)
Z.Z. Lin, C.L. Huang, W.K. Zhen, Z. Huang, Appl. Therm. Eng. 119, 425 (2017)
M.R. Zakaria, M.H.A. Kudus, H.M. Akil, M.Z.M. Thirmizir, Compos. B Eng. 119, 57 (2017)
J. Huang, M. Gao, T. Pan, Y. Zhang, Y. Lin, Compos. Sci. Technol. 95, 16 (2014)
C.W. Nan, R. Birringer, D.R. Clarke, H. Gleiter, J. Appl. Phys. 81, 6692 (1997)
D.J. Yang, Q. Zhang, G. Chen, S.F. Yoon, J. Ahn, S.G. Wang, Q. Zhou, Q. Wang, J.Q. Li, Phys. Rev. B 66, 165440 (2002)
D.L. Feng, Y.H. Feng, Y. Chen, W. Li, X.X. Zhang, Chin. Phys. B 22, 016501 (2013)
W. Li, Y.H. Feng, J. Peng, X.X. Zhang, ASME J. Heat Transf. 134, 092401 (2012)
W.K. Zhen, Z.Z. Lin, C.L. Huang, Modified Maxwell model for thermal conductivity. Prediction of nanocomposites with effect of aggregation. Chin. Phys. B 26, 114401 (2017)
X. Li, X. Fan, Y. Zhu, J. Li, J.M. Adams, S. Shen, H. Li, Comp. Mater. Sci. 63, 207 (2012)
C.W. Nan, G. Liu, Y. Lin, M. Li, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 3549 (2004)
Y. Hwang, M. Kim, J. Kim, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 55, 195 (2013)
M. Foygel, R.D. Morris, D. Anez, S. French, V.L. Sobolev, Phys. Rev. B 71, 104201 (2005)
T. Nakayama, K. Yakubo, R.L. Orbach, Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 381 (1994)
I. Balberg, N. Binenbaum, Phys. Rev. B 28, 3799 (1983)
R.S. Prasher, X.J. Hu, Y. Chalopin, N. Mingo, K. Lofgreen, S. Volz, F. Cleri, P. Keblinski, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 105901 (2009)
R. Martel, T. Schmidt, H.R. Shea, T. Hertel, P. Avouris, Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 2447 (1998)
A.B. Kaiser, Phys. Rev. B 40 2806 (1989)
C. Meng, C. Liu, S. Fan, Adv. Mater. 22, 535 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2015XKMS062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, C., Zhen, W., Huang, Z. et al. Thermal and electrical conductivities of epoxy resin-based composites incorporated with carbon nanotubes and TiO2 for a thermoelectric application. Appl. Phys. A 124, 38 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1467-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1467-3