Abstract
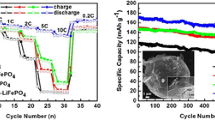
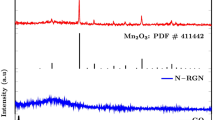
Manganese-doped lithium iron phosphate (LFMP), coated with reduced graphene oxide (RGO), has been prepared by a microwave-assisted solvothermal technique. The un-doped lithium iron phosphate material with RGO (i.e., LFP/RGO) gave a rod-like morphology (> 200 nm in length), while the LFMP/RGO gave a sponge-like spherical morphology (≥ 100 nm diameter). This dramatic change in morphology upon doping with Mn from α-MnO2 resulted in improved coin cell performance in terms of capacity, coulombic efficiency and charge-transfer properties. The increased performance can be attributed to improved particle size and higher surface area owing to the partial substitution of Mn ions for Fe ions. LiFe0.8Mn0.2PO4 synthesised using microwaves provides a quicker method of synthesis while providing a cathode material with a promising capacity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Song, Y. Kang, J. Kim et al., Simple and fast synthesis of LiFePO4-C composite for lithium rechargeable batteries by ball-milling and microwave heating. J. Power Sourc. 166(1), 260–265 (2007)
Z. Chen, M. Xu, B. Du, H. Zhu, T. Xie, W. Wang, Morphology control of lithium iron phosphate nanoparticles by soluble starch-assisted hydrothermal synthesis. J. Power Source 272, 837–844 (2014)
C.J. Jafta, M.K. Mathe, N. Manyala, W.D. Roos, K.I. Ozoemena, Microwave-assisted synthesis of high-voltage nanostructured LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 spinel: tuning the Mn3 content and electrochemical performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5(15), 7592–7598 (2013)
F.P. Nkosi, C.J. Jafta, M. Kebede, L. le Roux, M.K. Mathe, K.I. Ozoemena, Microwave-assisted optimization of the manganese redox states for enhanced capacity and capacity retention of LiAlxMn2−xO4 (x = 0 and 0.3) spinel materials. RSC Adv. 5(41), 32256–32262 (2015)
K. Raju, F.P. Nkosi, E. Viswanathan, M.K. Mathe, K. Damodaran, K.I. Ozoemena, Microwave-enhanced electrochemical cycling performance of the LiNi0.2Mn1.8O4 spinel cathode material at elevated temperature. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18(18), 13074–13083 (2016)
T. Muraliganth, A.V. Murugan, A. Manthiram, Nanoscale networking of LiFePO4 nanorods synthesized by a microwave-solvothermal route with carbon nanotubes for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 18(46), 5661–5668 (2008)
Y. Zhang, W. Wang, P. Li, Y. Fu, X. Ma, A simple solvothermal route to synthesize graphene-modified LiFePO4 cathode for high power lithium ion batteries. J. Power Source 210, 47–53 (2012)
S.W. Oh, Z. Huang, B. Zhang, Y. Yu, Y. He, J. Kim, Low temperature synthesis of graphene-wrapped LiFePO 4 nanorod cathodes by the polyol method. J. Mater. Chem. 22(33), 17215–17221 (2012)
C.J. Jafta, F. Nkosi, L. le Roux et al.: Manganese oxide/graphene oxide composites for high-energy aqueous asymmetric electrochemical capacitors. Electrochim. Acta 110, 228–233 (2013)
Z. Wang, L. Yuan, W. Zhang, Y. Huang, LiFe0.8Mn0.2PO4/C cathode material with high energy density for lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 532, 25–30 (2012)
Y. Mi, C. Yang, Z. Zuo et al.: Positive effect of minor manganese doping on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C under extreme conditions. Electrochim Acta 176, 642–648 (2015)
I. Seo, B. Senthilkumar, K. Kim, J. Kim, Y. Kim, J. Ahn, Atomic structural and electrochemical impact of fe substitution on nano porous LiMnPO4. J. Power Source 320, 59–67 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Pretoria, South Africa. CA Rossouw would like to thank the CSIR for doctoral studentship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossouw, C.A., Raju, K., Zheng, H. et al. Capacity and charge-transport enhancement of LFP/RGO by doping with α-MnO2 in a microwave-assisted synthesis. Appl. Phys. A 123, 769 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1355-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1355-x