Abstract
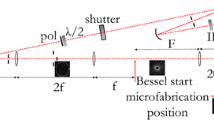
Glass welding by femtosecond laser pulses causes microscopic structural modifications, affecting the refractive index due to residual stress. Locally induced birefringence is studied by photoelasticimetry using a polarized light microscope. The study is performed on borosilicate thin glass plates using an industrial femtosecond laser generating 300 fs pulses at 500 kHz, with a 100 mm focusing length F-theta lens allowing fast welding. For low-energy deposition, the principal birefringence axes are determined to be homogenous along the seam and perpendicular and parallel to the laser scanning direction. Tensile stress is induced in the laser scanning direction by the welding seams. The induced birefringence is determined to be equivalent for in-volume irradiated track and welding seams. An inhomogeneity of the birefringence within the seam is observed for the first time at high-energy deposition. The distribution of the birefringence can be controlled with the laser scanning patterns. The amount of residual stress is measured by compensating the local birefringence. The birefringence \(\Delta ~n\) is estimated at \(2.4~\times ~10^{-4}\), corresponding to a residual stress amount around 59 MPa. The influence of the welding geometry is also illustrated.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Hülsenberg, A. Harnisch, A. Bismarck, in Microstructuring of glasses, ed. By D. Hlsenberg, A. Harnisch (Springer Ser. Mater. Science, 2008), p. 263
T. Tamaki, W. Watanabe, J. Nishii, K. Itoh, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 44, 687 (2005)
W. Watanabe, S. Onda, T. Tamaki, K. Itoh, J. Nishii, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 021106 (2006)
T. Tamaki, W. Watanabe, K. Itoh, Opt. Express 14, 10460 (2006)
S. Richter, F. Zimmermann, S. Döring, A. Tünnermann, S. Nolte, Appl. Phys. A, Mater. Sci. Process. 110, 9 (2013)
K. Cvecek, I. Miyamoto, J. Strauss, M. Wolf, T. Frick, M. Schmidt, Appl. Opt. 50, 1941 (2011)
G. Zhang, G. Cheng, Appl. Opt. 54, 8957 (2015)
D. Hélie, F. Lacroix, R. Valle, J. Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 7, 284 (2012)
C.B. Schaffer, A. Brodeur, E. Mazur, Meas. Sci. Technol. 12, 1784 (2001)
C. B. Schaffer, J. F. Garcia, E. Mazur, Appl. Phys. A, Mater. Sci. Process. 76, 351 (2003)
V.R. Bhardwaj, P.B. Corkum, D.M. Rayner, C. Hnatovski, E. Simova, R.S. Taylor, Opt. Lett. 29, 1312 (2004)
Y. Dai, B.-K. Yu, B. Lu, J.-R. Qiu, X.N. Yan, X.W. Jiang, C.S. Zhu, Chin. Phys. Lett. 22, 2626 (2005)
D. Lorenc, M. Aranyosiova, R. Buczynski, R. Stepien, I. Bugar, A. Vincze, D. Velic, Appl. Phys. B 93, 531 (2008)
S.C. Eaton, G. Cerullo, R. Osellame, in Femtosecond Laser Micromachining, ed. by R. Osellame, G. Cerullo, R. Ramponi (Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2012), p. 3
P.C. Anderson, A.K. Varshneya, J. Non-Cryst, Solids 168, 125 (1994)
K. Ramesh, V. Ramakrishnan, Opt. Laser Eng. 87, 59 (2016)
T.J. Holmquist, A.A. Wereszczak, Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 5, 345 (2014)
S. Richter, F. Zimmermann, A. Tünnermann, S. Nolte, Opt. Laser Technol. 83, 59 (2016)
F. Zimmermann, S. Richter, S. Döring, A. Tünnermann, S. Nolte, Appl. Opt. 52, 1149 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In the framework of LaserWeldCut Project funded by INSTITUT CARNOT MICA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gstalter, M., Chabrol, G., Bahouka, A. et al. Stress-induced birefringence control in femtosecond laser glass welding. Appl. Phys. A 123, 714 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1324-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1324-4