Abstract
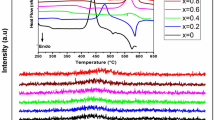
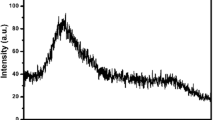
The Nd3+-doped lithium–zinc–phosphate glasses were prepared by means of conventional melt quenching method. X-ray diffraction results confirmed the glassy nature of the studied glasses. The physical parameters such as the density, molar volume, ion concentration, polaron radius, inter-ionic distance, field strength and oxygen packing density were calculated using different formulae. The transmittance and reflectance spectra of glasses were recorded in the wavelength range 190–1200 nm. The values of optical band gap and Urbach energy were determined based on Mott–Davis model. The refractive indices for the studied glasses were evaluated from optical band gap values using different methods. The average electronic polarizability of the oxide ions, optical basicity and an interaction parameter were investigated from the calculated values of the refractive index and the optical band gap for the studied glasses. The variations in the different physical and optical properties of glasses with Nd2O3 content were discussed in terms of different parameters such as non-bridging oxygen and different concentrations of Nd cation in glass system.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Dorosz, M. Kochanowicz, J. Dorosz, Multicore optical fibres for an external talbot cavity. Acta. Phys. Pol. A 116, 298–301 (2009)
R. Balda, J. Fernandez, M. Sanz, A. de Pablon, J.M.F. Navarro, J. Mugnier, Laser spectroscopy of Nd3+ ions in GeO2–PbO–Bi2O3 glasses. Phys. Rev. B 61, 3384–3390 (2000)
N.S. Hussain, K. Annapurna, Y.P. Reddy, S. Buddhuda, Photoluminescence spectra of Sm3+:PbO–Bi2O3–GeO2 glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 21, 397–399 (2002)
S. Xu, Z. Yong, G. Wang, S. Dai, J. Zhang, L. Hu, Z. Jiang, Optical transitions and upconversion mechanisms in Er3+-doped heavy metal oxyfluoride germanate glass. J. Alloys Compd. 377, 253–258 (2004)
M. Eugenia, B. Bruno, G. Dominique, P. Guillaume, Optical properties of pristine and γ-irradiated Sm doped borosilicate glasses. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 537, 411–414 (2005)
L. Zur, Structural and luminescence properties of Eu3+, Dy3+ and Tb3+ ions in lead germanate glasses obtained by conventional high-temperature melt-quenching technique. J. Mol. Struct. 1041, 50–54 (2013)
G.D. Khattak, E.E. Khawaja, L.E. Wenger, D.J. Thompson, M.A. Salim, A.B. Hallak, M.A. Daous, Composition-dependent loss of phosphorus in the formation of transition-metal phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 194, 1–12 (1996)
S.W. Martin, Review of the structures of phosphate glasses. Eur. J. Solid State Inorg. Chem. 28, 163–205 (1991)
D.E. Day, Z. Wu, C.S. Ray, P. Hrma, Chemically durable iron phosphate glass wasteforms. J. Non Cryst. Solids 241, 1–12 (1998)
R.K. Brow, Review: the structure of simple phosphate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 263–264, 1–28 (2000)
J.A. Caird, A.J. Romponi, P.R. Staves, Quantum efficiency and excited-state relaxation dynamics in neodymium-doped phosphate laser glasses. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 8, 1391–1403 (1991)
P. Pascuta, M. Bosca, G. Borodi, E. Culea, Thermal, structural and magnetic properties of some zinc phosphate glasses doped with manganese ions. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 4314–4319 (2011)
C.E. Smith, R.K. Brow, The properties and structure of zinc magnesium phosphate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 390, 51–58 (2014)
K. Aida, T. Komatsu, V. Dimitrov, Thermal stability, electronic polarisability and optical basicity of ternary tellurite glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses 42(2), 103–111 (2001)
P.W. McMillan, Glass ceramics, 2nd edn. (Academic Press, London, 1979)
H. Lin, E.Y.B. Pun, S.Q. Man, X.R. Liu, Optical transitions and frequency upconversion of Er3+ ions in Na2O·Ca3Al2Ge3O12 glasses. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 18, 602–609 (2001)
H. Lin, E.Y.B. Pun, L.H. Huang, X.R. Liu, Optical and luminescence properties of Sm3+-doped cadmium–aluminum–silicate glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 2642–2644 (2002)
Y.G. Choi, K.H. Kim, B.J. Park, J. Heo, 1.6 μm emission from Pr3+: (3F3,3F4) → 3H4 transition in Pr3+- and Pr3+/Er3+-doped selenide glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 1249–1251 (2001)
H. Higuchi, M. Takahashi, Y. Kamamoto, K. Kadono, T. Ohtsuki, N. Peyghambarian, N. Kitamura, Optical transitions and frequency upconversion emission of Er3+ ions in Ga2S3–GeS2–La2S3 glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 83, 19–27 (1998)
M. Shaweta, S.T. Kulwant, S. Gopi, G. Leif, Spectroscopic investigations of Nd3+ doped flouro- and chloro-borate glasses. Spectrochim. Acta 70, 1173–1179 (2008)
L.R. Moorthy, T.S. Rao, M. Jayasimhadri, A. Radhapathy, D.V.R. Murthy, Spectroscopic investigations of Nd3+-doped alkali chloroborophosphate glasses. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 60, 2449–2458 (2004)
K. Boonin, J. Kaewkhao, T. Ratana, Preparation and properties of Bi2O3–B2O3–Nd2O3 glass system. Proc. Eng. 8, 207–211 (2011)
V.C. Veeranna Gowda, Effect of Bi3+ ions on physical, thermal, spectroscopic and optical properties of Nd3+ doped sodium diborate glasses. Phys. B 426, 58–64 (2013)
M.A. Algradee, A. Elwhab, B. Alwany, M. Sultan, M. Elgoshimy, Q. Almoraisy, Physical and optical properties for Nd2O3 doped lithium–zinc–phosphate glasses. Optik 142, 13–22 (2017)
M.A. Algradee, A. Elwhab, B. Alwany, A.A. Higazy, Mechanical and optical properties for Li2O–ZnO–P2O5:xYb2O3 glasses. J Adv. Phys. 6, 163–170 (2017)
H.A.A. Sidek, M. Hamezan, A.W. Zaidan, Z.A. Talib, K. Kaida, Optical characterization of lead–bismuth phosphate glasses. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2(8), 1266–1269 (2005)
K. Nanda, N. Berwal, R.S. Kundu, R. Punia, N. Kishore, Effect of doping of Nd3+ ions in BaO–TeO2–B2O3 glasses: a vibrational and optical study. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 147–154 (1088)
Y.B. Saddeek, E.R. Shaaban, E.S. Moustafa, H.M. Moustafa, Spectroscopic properties, electronic polarizability, and optical basicity of Bi2O3–Li2O–B2O3 glasses. Phys. B 403, 2399–2407 (2008)
N.F. Mott, E.A. Davis, Electronic process in the non crystalline materials, 2nd edn. (Clarendon Press/Oxford University, New York, 1979)
K. Annapurna, S. Buddhudu, Characterization of fluorophosphate optical glasses. J. Solid State Chem. 93, 454–460 (1991)
A. Wagh, Y. Raviprakash, V. Upadhyaya, S.D. Kamath, Composition dependent structural and optical properties of PbF2–TeO2–B2O3–Eu2O3 glasses. Spectrochim. Acta A 151, 696–706 (2015)
S. Inaba, S. Fujino, K. Morinaga, Young’s modulus and compositional parameters of oxide glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 3501–3507 (1999)
M. Abdel-Baki, F.A. Abdel-Wahab, F. El-Diasty, One-photon band gap engineering of borate glass doped with ZnO for photonics applications. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 073506–0735010 (2012)
D.R. Lide (ed.), CRC handbook of chemistry and physics, 85th edn. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2004)
S.B. Mallur, T. Czarnecki, A. Adhikari, P.K. Babu, Compositional dependence of optical band gap and refractive index in lead and bismuth borate glasses. Mater. Res. Bull. 68, 27–34 (2015)
E.A. Davis, N.F. Mott, Conduction in non-crystalline systems V. Conductivity, optical absorption and photoconductivity in amorphous semiconductors. Philos. Mag. 22, 903–922 (1970)
M. Farouk, A. Abd El-Maboud, M. Ibrahim, A. Ratep, I. Kashif, Optical properties of Lead bismuth borate glasses doped with neodymium oxide. Spectrochim. Acta A 149, 338–342 (2015)
F. Ahmad, E. Hassan Aly, M. Atef, M.M. ElOkr, Study the influence of zinc oxide addition on cobalt doped alkaline earth borate glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 593, 250–255 (2014)
F. Urbach, The long-wavelength edge of photographic sensitivity and of the electronic absorption of solids. Phys. Rev. 92, 1324 (1953)
Y. Chen, Q. Nie, T. Xu, S. Dai, X. Wang, X. Shen, A study of nonlinear optical properties in Bi2O3–WO3–TeO2 glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 354, 3468–3472 (2008)
H. Mahr, Ultraviolet absorption of KI diluted in KCl crystals. Phys. Rev. 125, 1510–1516 (1962)
F. Yakuphanoglu, M. Arslan, The fundamental absorption edge and optical constants of some charge transfer compounds. Opt. Mater. 27, 29–37 (2004)
V. Kumar, J.K. Singh, Model for calculating the refractive index of different materials. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 48, 571–574 (2010)
T.S. Moss, Relations between the refractive index and energy gap of semiconductors. Phys. Status Solidi B 131, 415–427 (1985)
V. Dimitrov, S. Sakka, Linear and nonlinear optical properties of simple oxides. II. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 1741–1745 (1996)
R.R. Reddy, Y.N. Ahammed, K.R. Gopal, D.V. Raghuram, Optical electronegativity and refractive index of materials. Opt. Mater. 10, 95–100 (1998)
X. Zhao, X. Wang, H. Lin, Z. Wang, A new approach to estimate refractive index, electronic polarizability, and optical basicity of binary oxide glasses. Phys. B 403, 2450–2460 (2008)
P. Chimalawong, J. Kaewkhao, C. Kedkaew, P. Limsuwan, Optical and electronic polarizability investigation of Nd3+-doped soda-lime silicate glasses. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71, 965–970 (2010)
E.A. Moelwyn-Hughes, Physical chemistry (Pergamon, London, 1961)
V. Dimitrov, T. Komatsu, An interpretation of optical properties of oxides and oxide glasses in terms of the electronic ion polarizability and average single bond strength (review). J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall. 45, 219–250 (2010)
X. Zhao, X. Wang, H. Lin, Z. Wang, Electronic polarizability and optical basicity of lanthanide oxides. Phys. B 392, 132–136 (2007)
S.S. Rao, G. Ramadevudu, M. Shareefuddin, A. Hameed, M.N. Chary, M.L. Rao, Optical properties of alkaline earth borate glasses. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 4, 25–35 (2012)
S.S. Sastry, B.R. Venkateswara Rao, Structural and optical properties of vanadium doped alkaline earth lead zinc phosphate glasses. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 52, 491–498 (2014)
J.A. Duffy, Electronic polarisability and related properties of the oxide ion. Phys. Chem. Glasses 30, 1–4 (1989)
E.S. Yousef, M.M. Elokr, Y.M. AbouDeif, Optical, elastic properties and DTA of TNZP host tellurite glasses doped with Er3+ ions. J. Mol. Struct. 1108, 257–262 (2016)
V. Dimitrov, T. Komatsu, Classification of simple oxides: a polarizability approach. J. Solid Stat. Chem. 163, 100–112 (2002)
J. Yamashita, T. Kurosawa, The theory of the dielectric constant of ionic crystals III. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 10, 610–633 (1955)
U.C. Dikshit, M. Kumar, Analysis of electronic polarizabilities in ionic crystals. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 165, 599–610 (1991)
V. Dimitrov, T. Komatsu, Effect of interionic interaction on the electronic polarizability, optical basicity and binding energy of simple oxides. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 107, 1012–1018 (1999)
V. Dimitrov, T. Komatsu, Interionic interactions, electronic polarizability and optical basicity of oxide glasses. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 108, 330–338 (2000)
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out using the National Research Centre facilities at the Spectroscopy Department, Physics Division, 33 El Buhouth St., Dokki, 12311Giza, Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Algradee, M.A., Sultan, M., Samir, O.M. et al. Electronic polarizability, optical basicity and interaction parameter for Nd2O3 doped lithium–zinc–phosphate glasses. Appl. Phys. A 123, 524 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1136-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1136-6