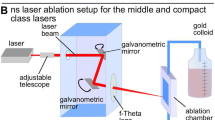
Abstract
This study presents results on pulsed laser ablation of gold target immersed in different liquids. In the experiments chloroform, toluene and ethanol are used as liquid media for the laser ablation. Two different wavelengths: the fundamental (1064 nm) and second harmonic (532 nm) of a Nd:YAG laser, are utilized to produce various colloids. The optical properties of the colloids were evaluated by optical transmittance measurements in the UV–Vis spectral range. The morphology of the colloidal nanoparticles created and the evaluation of their size distribution are investigated by transmission electron microscopy. The selected area electron diffraction is employed for chemical phase identification of the created nanostructures. Ablation in chloroform resulted in formation of spherical and spheroidal gold nanoparticles with the similar mean size at both laser wavelengths used—11.5 nm at 1064 and 9.3 nm at 532 nm. Nanoparticles with smaller mean size (below 5 nm) in the case of ablation in toluene were observed. Spherical nanoparticles with mean diameter of 7.7 nm produced by 1064 nm and thin elongated nanostructures with thickness of about 5 nm using 532 nm are observed in the case of ablation in ethanol. An additional laser irradiation of the colloids demonstrated the changing of the optical properties and size distribution of the nanostructures produced by ablation in ethanol and chloroform. The irradiation of toluene-based colloid does not induce observable change of the colloid properties.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.C. Daniel, D. Astruc, Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 104, 293–346 (2004)
S.J. Guo, E.K. Wang, Synthesis and electrochemical applications of gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 598, 181–192 (2007)
E. Boisselier, D. Astruc, Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 1759–1782 (2009)
S.H. Radwan, H.M.E. Azzazy, Gold nanoparticles for molecular diagnostics. Exp. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 9, 511–524 (2009)
W.R. Algar, M. Massey, U.J. Krull, The application of quantum dots, gold nanoparticles and molecular switches to optical nucleic-acid diagnostics. Trends Anal. Chem. 28, 292–306 (2009)
W.E. Bawarski, E. Chidlowsky, D.J. Bharali, S.A. Mousa, Emerging nano-pharmaceuticals. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 4, 273–282 (2008)
V.V. Mody, R. Siwale, A. Singh, H.R. Mody, Introduction to metallic nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2, 282–289 (2010)
C.F. Bohren, D.F. Hufman, Absorption and scattering of light by small particles (Wiley, New York, 1983)
U. Kreibig, M. Vollmer, Optical properties of metal clusters (Springer, Berlin, 1995)
M.H. Abdellatif, S. Ghosh, I. Liakos, A. Scarpellini, S. Marras, A. Diaspro, M. Salerno, Effect of nanoscale size and medium on metal work function in oleylamine-capped gold nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 89, 7–14 (2016)
D. Pissuwan, T. Niidome, M.B. Cortie, The forth-coming applications of gold nanoparticles in drug and gene delivery systems. J. Control. Release 149, 65–71 (2011)
P. Ghosh, G. Han, M. De, C.K. Kim, V.M. Rotello, Gold nanoparticles in delivery applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60, 1307–1315 (2008)
D.T. Nguyen, D.-J. Kim, K.-S. Kim, Controlled synthesis and biomolecular probe application of gold nanoparticles. Micron 42, 207–227 (2011)
A.B. Etame, C.A. Smith, W.C.W. Chan, J.T. Rutka, Design and potential application of PEGylated gold nanoparticles with size-dependent permeation through brain microvasculature, nanomedicine: nanotechnology. Biol. Med. 7, 992–1000 (2011)
M. Shakibaie, H. Forootanfar, K. Mollazadeh-Moghadam, Z. Bagherzadeh, N. Nafissi-Varcheh, A.R. Shahverdi, M.A. Faramarzi, Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles by the marine microalga Tetraselmis suecica. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 57, 71–75 (2010)
Y.L. Luo, Y.S. Shiao, Y.F. Huang, Release of photoactivatable drugs from plasmonic nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. ACS Nano 5, 7796–7804 (2011)
M. Vinod, K.G. Gopchandran, Au, Ag and Au: Ag colloidal nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation as SERS substrates. Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. Int. 24, 569–578 (2014)
C. Toccafondi, S. Thorat, R. La Rocca, A. Scarpellini, M. Salerno, S. Dante, G. Das, Multifunctional substrates of thin porous alumina for cell biosensors. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 25, 2411–2420 (2014)
D. Huang, F. Liao, S. Molesa, D. Redinger, V. Subramanian, Plastic-compatible low resistance printable gold nanoparticle conductors for flexible electronics. J. Electrochem. Soc. 150, 412–417 (2003)
D.T. Thompson, Using gold nanoparticles for catalysis. Nano Today 2, 40–43 (2007)
F. Schulz, T. Homolka, N.G. Bastus, V. Puntes, H. Weller, T. Vossmeyer, Little adjustments significantly improve the turkevich synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 30, 10779–10784 (2014)
P.R. Teixeira, M.S.C. Santos, A.L.G. Silva, S.N. Báo, R.B. Azevedo, M.J.A. Sales, L.G. Paterno, Photochemically-assisted synthesis of non-toxic and biocompatible gold nanoparticles. Coll. Surf. B 148, 317–323 (2016)
S. Singh, D.V.S. Jain, M.L. Singla, One step electrochemical synthesis of gold-nanoparticles–polypyrrole composite for application in catechin electrochemical biosensor. Anal. Methods 5, 1024–1032 (2013)
R.A.B. Alvarez, M. Cortez-Valadez, L.O.N. Bueno, R.B. Hurtado, O. Rocha-Rocha, Y. Delgado-Beleño, C.E. Martinez-Nuñez, L.I. Serrano-Corrales, H. Arizpe-Chávez, M. Flores-Acosta, Vibrational properties of gold nanoparticles obtained by green synthesis. Physica E 84, 191–195 (2016)
G. Compagnini, A. Scalisi, O. Puglisi, C. Spinella, Synthesis of gold colloids by laser ablation in thiol alkane solutions. J. Mater. Res. 19, 2795–2798 (2004)
H. Zeng, X.W. Du, S.C. Singh, S.A. Kulinich, S. Yang, J. He, W. Cai, Nanomaterials via laser ablation/irradiation in liquid: a review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 1333–1353 (2012)
V. Amendola, M. Meneghetti, What controls the composition and the structure of nanomaterials generated by laser ablation in liquid solution? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 3027–3046 (2013)
R.G. Nikov, A.S. Nikolov, N.N. Nedyalkov, P.A. Atanasov, M.T. Alexandrov, D.B. Karashanova, Processing condition influence on the characteristics of gold nanoparticles produced by pulsed laser ablation in liquids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 274, 105–109 (2013)
A. Pyatenko, K. Shimokawa, M. Yamaguchi, O. Nishimura, M. Suzuki, Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in pure water. Appl. Phys. A 79, 803–806 (2004)
R. Intartaglia, M. Rodio, M. Abdellatif, M. Prato, M. Salerno, Extensive characterization of oxide-coated colloidal gold nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation in liquid. Materials 9, 775 (2016)
G. Compagnini, A.A. Scalisi, O. Puglisi, Production of gold nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid alkanes. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 7874–7877 (2003)
V. Amendola, S. Polizzi, M. Meneghetti, Laser ablation synthesis of gold nanoparticles in organic solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 7232–7237 (2006)
V. Amendola, S. Polizzi, M. Meneghetti, Laser ablation synthesis of silver nanoparticles embedded in graphitic carbon matrix. Sci. Adv. Mater. 4, 497–500 (2012)
G. Compagnini, A.A. Scalisi, O. Puglisi, Ablation of noble metals in liquids: a method to obtain nanoparticles in a thin polymeric film. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 4, 2787–2791 (2002)
V. Amendola, G.A. Rizzi, S. Polizzi, M. Meneghetti, Synthesis of gold nanoparticles by laser ablation in toluene: quenching and recovery of the surface plasmon absorption. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 23125–23128 (2005)
T. Mortier, T. Verbiest, A. Persoons, Laser ablation of gold in chloroform solutions of cetyltrimethylammoniumbromide. Chem. Phys. Lett. 382, 650–653 (2003)
V. Amendola, G. Mattei, C. Cusan, M. Prato, M. Meneghetti, Fullerene non-linear excited state absorption induced by gold nanoparticles light harvesting. Synth. Met. 155, 283–286 (2005)
S.-P. Chen, H.-L. Chiu, P.-H. Wang, Y.-C. Liao, Inkjet printed conductive tracks for printed electronics. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 4, 3026–3033 (2015)
M.J. Beliatis, S.J. Henley, S. Han, K. Gandhi, A.A.D.T. Adikaari, E. Stratakis, E. Kymakis, S.R.P. Silva, Organic solar cells with plasmonic layers formed by laser nanofabrication. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 8237–8244 (2013)
J. Macicek, Adv. X-ray Anal. 35, 687–691 (1992)
A.O. Simm, C.E. Banks, S.J. Wilkins, N.G. Karousos, J. Davis, R.G. Compton, A comparison of different types of gold–carbon composite electrode for detection of arsenic(III). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 381, 979–985 (2005)
H. Sakai, Surface-induced melting of small particles. Surf. Sci. 351, 285–291 (1996)
A.S. Nikolov, R.G. Nikov, N.N. Nedyalkov, P.A. Atanasov, M.T. Alexandrov, D.B. Karashanova, Modification of the silver nanoparticles size-distribution by means of laser light irradiation of their water suspensions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 280, 55–59 (2013)
J. Liao, Y. Zhang, W. Yu, L. Xu, C. Ge, J. Liu, N. Gu, Linear aggregation of gold nanoparticles in ethanol. Colloid. Surf. A 223, 177–183 (2003)
P. Boyer, M. Meunier, Modeling solvent influence on growth mechanism of nanoparticles (Au, Co) synthesized by surfactant free laser processes. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 8014–8019 (2012)
G. Cristoforetti, E. Pitzalis, R. Spiniello, R. Ishak, F. Giammanco, M. Muniz-Miranda, S. Caporali, Physico-chemical properties of Pd nanoparticles produced by pulsed laser ablation in different organic solvents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 3289–3297 (2012)
E. Giorgetti, M. Muniz-Miranda, P. Marsili, D. Scarpellini, F. Giammanco, Stable gold nanoparticles obtained in pure acetone by laser ablation with different wavelengths. J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 1–13 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the project DFNP-185 “Preparation of colloids by laser ablation in liquids for printing of two-dimensional and three-dimensional structures” under scientific program “Assistance for young scientists”, BAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikov, R.G., Nedyalkov, N.N., Atanasov, P.A. et al. Laser-assisted fabrication and size distribution modification of colloidal gold nanostructures by nanosecond laser ablation in different liquids. Appl. Phys. A 123, 490 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1105-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1105-0