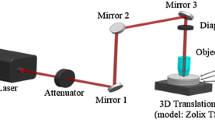
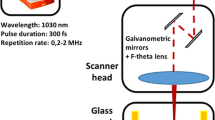
Abstract
We used 1030-nm femtosecond-laser pulses focused above/at/below the interface of two fused-silica glass substrates in optical and partial-optical contact to successfully weld them at a moderately high repetition rate of 600 kHz. Variation in the laser focal position for these two gap-distance regimes (optical and partial-optical contact) yields different bonding strengths (BSs) and machining mechanisms. The maximum bonding strength (58.2 MPa) can be achieved for a gap distance \( {\le}\lambda /4 \) for optical-contact welding when laser focused below the interface, and the corresponding height of the welding seam was 23 μm. In addition, our results demonstrated that the “filamentation welding technique” is critical to the femtosecond-laser direct welding of glasses. Furthermore, line welding is significantly easier to realize when the femtosecond laser focuses at the interface in partial-optical-contact welding applications due to the combined effects of filamentation welding and ablation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Tamaki, W. Watanabe, J. Nishii, K. Itoh, Welding of transparent materials using femtosecond laser pulses. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 44(22), 687–689 (2005)
W. Watanabe, S. Onda, T. Tamaki, K. Itoh, J. Nishii, Space-selective laser joining of dissimilar transparent materials using femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89(2), 021106 (2006)
W. Watanabe, S. Onda, T. Tamaki, K. Itoh, Direct joining of glass substrates by 1 kHz femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. B 87(1), 85–89 (2007)
K. Itoh, T. Tamaki, Ultrafast laser microwelding for transparent andheterogeneous materials. Proc. SPIE 6881, 68810V (2008)
D. Hélie, R. Vallée, Micromachining of thin glass plates with a femtosecond laser. Proc. SPIE 7386, 738639 (2009)
Y. Kim, J. Choi, Y. Lee, T. Kim, D. Kim, W. Jang, K. Lim, I. Sohn, J. Lee, Femtosecond laser bonding of glasses and ion migration in the interface. Appl. Phys. A 101(1), 147–152 (2010)
T. Tamaki, W. Watanabe, K. Itoh, Laser micro-welding of silicon and borosilicate glass using nonlinear absorption effect induced by 1558-nm femtosecond fiber laser pulses. Proc. SPIE 6460, 646018 (2007)
S. Richter, F. Zimmermann, S. Döring, A. Tünnermann, S. Nolte, Ultrashort high repetition rate exposure of dielectric materials:laser bonding of glasses analyzed by micro-Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. A 110(110), 9–15 (2013)
I. Miyamoto, K. Cvecek, Y. Okamoto, M. Schmidt, Internal modification of glass by ultrashort laser pulse and its application to microwelding. Appl. Phys. A 114(1), 187–208 (2014)
S. Richter, F. Zimmermann, A. Tünnermann, S. Nolte, Laser welding of glasses at high repetition rates—fundamentals and prospects. Opt. Laser Technol. 83, 59–66 (2016)
S. Richter, F. Zimmermann, R. Eberhardt, A. Tünnermann, S. Nolte, Toward laser welding of glasses without optical contacting. Appl. Phys. A 121(1), 1–9 (2015)
S. Eaton, H. Zhang, P. Herman, F. Yoshino, L. Shah, J. Bovatsek, A. Arai, Heat accumulation effects in femtosecond laser-written waveguides with variable repetition rate. Opt. Express 13(12), 4708–4716 (2005)
R. Osellame, S. Taccheo, M. Maríangoni, R. Ramponi, P. Laporta, D. Polli, S. Silvestri, G. Cerullo, Femtosecond writing of active optical waveguides with astigmatically shaped beams. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 20(7), 1559–1567 (2003)
I. Miyamoto, K. Cvecek, Y. Okamoto, M. Schmidt, H. Helvajian, Characteristics of laser absorption and welding in FOTURAN glass byultrashortlaser pulses. Opt. Express 19(23), 22961–22973 (2011)
N. Varkentina, N. Sanner, M. Lebugle, M. Sentis, O. Utéza, Absorption of a single 500 fs laser pulse at the surface of fused silica: energy balance and ablation efficiency. J. Appl. Phys. 114(114), 173105 (2013)
M. Lebugle, N. Sanner, N. Varkentina, M. Sentis, Dynamics of femtosecond laser absorption of fused silica in the ablationregime. J. Appl. Phys. 116(6), 063105 (2014)
I. Miyamoto, Welding of glass/glass and Si/glass using ultrashort laser pulses, in Proceedings of IEEE European Conference on Lasers and Electro-optics (IEEE, 2013), pp. 1–1
I. Miyamoto, K. Cvecek, M. Schmidt, Evaluation of nonlinear absorptivity in internal modification of bulk glass by ultrashort laser pulses. Opt. Express 19(11), 10714–10727 (2011)
I. Miyamoto, A. Horn, J. Gottmann, Local melting of glass material and its application to direct fusion welding by ps-laser pulses. JLMN 2(1), 7–14 (2007)
I. Miyamoto, K. Cvecek, Y. Okamoto, M. Schmidt, Novel fusion welding technology of glass using ultrashort pulse lasers. Phys. Proc. 5, 483–493 (2010)
I. Miyamoto, A. Horn, J. Gottmann, D. Wortmann, F. Yoshino, Fusion welding of glass using femtosecond laser pulses with high-repetitionrates. JLMN 2(1), 57–63 (2007)
K. Cvecek, R. Odato, S. Dehmel, I. Miyamoto, M. Schmidt, Gap bridging in joining of glass using ultrashort laser pulses. Opt. Express 23(5), 5681–5693 (2015)
J. Chen, R. Carter, R. Thomson, D. Hand, Avoiding the requirement for pre-existing optical contact during picosecond laser glass-to-glass welding. Opt. Express 23(14), 18645–18657 (2015)
H. Tan, J. Duan, One-step femtosecond laser welding and internal machining of three glass substrates. Appl. Phys. A 123(5), 377–381 (2017)
D. Hélie, F. Lacroix, R. Vallée, Reinforcing a direct bond between optical materials by filamentation based femtosecond laser welding. JLMN 7(3), 284–292 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51475482, 51335011, 91123035, 51475481, and 91323301), 973 of Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2011CB013000). Plan for supporting the New Century Talents of Education Ministry (Grant No. NCET-12-0548).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, H., Duan, J. Welding of glasses in optical and partial-optical contact via focal position adjustment of femtosecond-laser pulses at moderately high repetition rate. Appl. Phys. A 123, 481 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1079-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1079-y