Abstract
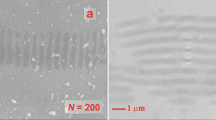
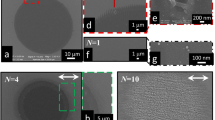
This paper deals with the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) on mesoporous silicon thin films induced by two laser regimes in the UV range: picosecond and femtosecond. Different LIPSS formation mechanisms from nanoparticles, mainly coalescence and agglomeration, have been evidenced by scanning electron microscopy analysis. The apparition of a liquid phase during both laser interaction at low fluence (20 mJ/cm2) and after a large number of laser pulses (up to 12,000) has been also shown with 100 nm size through incubation effect. Transmission electron microscopy analyses have been conducted to investigate the molten phase structures below and inside LIPSS. Finally, it has shown that LIPSS are composed of amorphous silicon when mesoporous silicon is irradiated by laser beam in both regimes. Nevertheless, mesoporous silicon located between LIPSS stays crystallized.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Bonse, J. Krüger, S. Höhm, A. Rosenfeld, Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. J. Laser Appl. 2012(24), 42006 (2012). doi:10.2351/1.4712658
A.Y. Vorobyev, C. Guo, Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structure formation on tungsten. J. Appl. Phys. 104(6), 8–11 (2008). doi:10.1063/1.2981072
S. Moradi, S. Kamal, P. Englezos, S.G. Hatzikiriakos, Femtosecond laser irradiation of metallic surfaces: effects of laser parameters on superhydrophobicity. Nanotechnology 24(41), 415302 (2013). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/24/41/415302
M. Gedvilas, J. Mikšys, G. Račiukaitis, Flexible periodical micro- and nano-structuring of a stainless steel surface using dual-wavelength double-pulse picosecond laser irradiation. RSC Adv. 5(92), 75075–75080 (2015). doi:10.1039/C5RA14210E
O. Varlamova, C. Martens, M. Ratzke, J. Reif, Genesis of femtosecond-induced nanostructures on solid surfaces. Appl. Opt. 53(31), I10–I15 (2014). doi:10.1364/AO.53.000I10
J.F. Young, J.S. Preston, Driel H.M. Van, J.E. Sipe, Laser induced periodic surface structure. II. Experiments on Ge, Si, Al and brass. Phys. Rev. B 27(2), 1155–1172 (1983). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.27.1155
T.T.D. Huynh, N. Semmar, Dependence of ablation threshold and LIPSS formation on copper thin films by accumulative UV picosecond laser shots. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 116(3), 1429–1435 (2014). doi:10.1007/s00339-014-8255-0
A. Melhem, D. De Meneses Sousa, C. Andreazza-Vignolle, T. Defforge, G. Gautier, N. Semmar, Structural, optical and thermal analysis of n-type mesoporous silicon prepared by electrochemical etching. J. Phys. Chem. C (2015). doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b04984
D. Baillis, J. Randrianalisoa, Prediction of thermal conductivity of nanostructures: influence of phonon dispersion approximation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52(11–12), 2516–2527 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2009.01.017
A. Talbi, A. Petit, A. Melhem et al., Nanoparticles based laser-induced surface structures formation on mesoporous silicon by picosecond laser beam interaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 374, 31–35 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.09.003
T.E. Itina, On nanoparticle formation by laser ablation in liquids. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(12), 5044–5048 (2011). doi:10.1021/jp1090944
O.I. Eroshova, P.A. Perminov, S.V. Zabotnov et al., Structural properties of silicon nanoparticles formed by pulsed laser ablation in liquid media. Crystallogr. Rep. 57(6), 831–835 (2012). doi:10.1134/S1063774512030066
N.G. Semaltianos, S. Logothetidis, W. Perrie et al., Silicon nanoparticles generated by femtosecond laser ablation in a liquid environment. J. Nanoparticle Res. 12(2), 573–580 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11051-009-9625-y
R. Intartaglia, K. Bagga, F. Brandi, Study on the productivity of silicon nanoparticles by picosecond laser ablation in water: towards gram per hour yield. Opt. Express 22(3), 3117–3127 (2014). doi:10.1364/OE.22.003117
J. Bonse, A. Rosenfeld, J. Krüger, On the role of surface plasmon polaritons in the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of silicon by femtosecond-laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 106(10), 104910 (2009). doi:10.1063/1.3261734
M. Guillermin, F. Garrelie, N. Sanner, E. Audouard, H. Soder, Single- and multi-pulse formation of surface structures under static femtosecond irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(19), 8075–8079 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.02.093
J. Bonse, J. Krüger, Pulse number dependence of laser-induced periodic surface structures for femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 108(3), 034903 (2010). doi:10.1063/1.3456501
O. Varlamova, J. Reif, S. Varlamov, M. Bestehorn. Self-Organized Surface Patterns Originating From Laser-Induced Instability (2015). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-12217-5_1
J. Reif, O. Varlamova, S. Uhlig, S. Varlamov, M. Bestehorn, On the physics of self-organized nanostructure formation upon femtosecond laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A 117(1), 179–184 (2014). doi:10.1007/s00339-014-8339-x
M. Gedvilas, G. Raciukaitis, V. Kucikas, K. Regelskis, Driving forces for self-organization in thin metal films during their partial ablation with a cylindrically focused laser beam. AIP Conf. Proc. 2012(1464), 229–243 (2012). doi:10.1063/1.4739877
A. Talbi, C.T. Tameko, A. Stolz, E. Millon, C. Boulmer-Leborgne, N. Semmar, Nanostructuring of titanium oxide thin film by UV femtosecond laser beam: from one spot to large surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. (2017). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.033
Z. Zhou, W. Ma, Investigation of thermomechanical responses in ultrafast laser heating of metal nanofilms. Thin Solid Films 519(22), 7940–7946 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2011.05.062
M. Shimizu, M. Hashida, Y. Miyasaka, S. Tokita, S. Sakabe, Unidirectionally oriented nanocracks on metal surfaces irradiated by low-fluence femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103(17), 174106 (2013). doi:10.1063/1.4827296
S. Gräf, F.A. Müller, Polarisation-dependent generation of fs-laser induced periodic surface structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 331, 150–155 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.056
A. Rousse, C. Rischel, S. Fourmaux et al., Non-thermal melting in semiconductors measured at femtosecond resolution. Nature 410(6824), 65–68 (2001). doi:10.1038/35065045
T.T.D. Huynh, M. Vayer, A. Sauldubois, A. Petit, N. Semmar, Evidence of liquid phase during laser-induced periodic surface structures formation induced by accumulative ultraviolet picosecond laser beam. Appl. Phys. Lett. 107(19), 193105 (2015). doi:10.1063/1.4935413
N.M. Bulgakova, Theoretical models and qualitative interpretations of fs laser material processing. J. Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 2(1), 76–86 (2007). doi:10.2961/jlmn.2007.01.0014
E.L. Gurevich, S.V. Gurevich, Laser induced periodic surface structures induced by surface plasmons coupled via roughness. Appl. Surf. Sci. 302, 118–123 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.10.141
J. Bonse, S. Baudach, J. Krüger, W. Kautek, M. Lenzner, Femtosecond laser ablation of silicon–modification thresholds and morphology. Appl. Phys. A 74(1), 19–25 (2002). doi:10.1007/s003390100893
A.A. Ionin, E.V. Golosov, R.K. Yu et al., Formation of quasi-periodic nano- and microstructures on silicon surface under IR and UV femtosecond laser pulses. Quantum Electron. 41(9), 829 (2011). doi:10.1070/Qe2011v041n09abeh014530
G. Raciukaitis, M. Brikas, P. Gecys, M. Gedvilas, Accumulation effects in laser ablation of metals with high-repetition-rate lasers. SPIE 7005, 70052L (2008). doi:10.1117/12.782937
J. Jia, M. Li, C.V. Thompson, Amorphization of silicon by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(16), 3205–3207 (2004). doi:10.1063/1.1719280
M.S. Rogers, C.P. Grigoropoulos, A.M. Minor, S.S. Mao, Absence of amorphous phase in high power femtosecond laser-ablated silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94(1), 2007–2010 (2009). doi:10.1063/1.3052693
Y. Izawa, Y. Izawa, Y. Setsuhara et al., Ultrathin amorphous Si layer formation by femtosecond laser pulse irradiation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(4), 1–3 (2007). doi:10.1063/1.2431709
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talbi, A., Kaya-Boussougou, S., Sauldubois, A. et al. Laser-induced periodic surface structures formation on mesoporous silicon from nanoparticles produced by picosecond and femtosecond laser shots. Appl. Phys. A 123, 463 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1075-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1075-2