Abstract
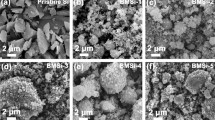
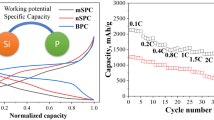
N-type silicon wafers with electrical resistivity of 0.001 Ω cm were ball-milled to powders and part of them was further mechanically crushed by sand-milling to smaller particles of nano-size. Both the sand-milled and ball-milled silicon powders were, respectively, mixed with graphite powder (silicon:graphite = 5:95, weight ratio) as anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochemical measurements, including cycle and rate tests, present that anode using sand-milled silicon powder performed much better. The first discharge capacity of sand-milled silicon anode is 549.7 mAh/g and it is still up to 420.4 mAh/g after 100 cycles. Besides, the D50 of sand-milled silicon powder shows ten times smaller in particle size than that of ball-milled silicon powder, and they are 276 nm and 2.6 μm, respectively. In addition, there exist some amorphous silicon components in the sand-milled silicon powder excepting the multi-crystalline silicon, which is very different from the ball-milled silicon powder made up of multi-crystalline silicon only.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Sato, M. Noguchi, A. Demachi, N. Oki, M. Endo, Science 264, 556 (1994)
D. Ma, Z. Cao, A. Hu, Nano-Micro Lett. 6, 347 (2014)
D. Leblanc, P. Hovington, C. Kim, A. Guer, D. Belanger, K. Zaghib, J. Power Sources 299, 529 (2015)
C. Wang, J. Ren, H. Chen, Y. Zhang, K. Ostrikov, W. Zhang, Y. Li, Mater. Chem. Phys. 173, 89 (2016)
L. Liu, J. Lyu, T. Li, T. Zhao, Nanoscale 8, 701 (2016)
M. Ko, S. Chae, S. Jeong, P. Oh, J. Cho, ACS Nano 8, 8591 (2014)
Y. Zhang, X. Xia, X. Wang, Y. Mai, S. Shi, Y. Tang, C. Gu, J. Tu, J. Power Sources 213, 106 (2012)
G. Radhakrishnan, P. Adams, M. Quinzio, Appl. Phys. A 115, 135 (2014)
G. Lee, S. Schweizer, R. Wehrspohn, Appl. Phys. A 117, 973 (2014)
M. Wang, Z. Geng, Appl. Phys. A 122, 528 (2016)
Y. Chen, L. Liu, J. Xiong, T. Yang, Y. Qin, C. Yan, Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 6701 (2015)
Y. Bie, J. Yu, J. Yang, W. Lu, Y. Nuli, J. Wang, Electrochim. Acta 178, 65 (2015)
Q. Hao, D. Zhao, H. Duan, Q. Zhou, C. Xu, Nanoscale 7, 5320 (2015)
Z. Yue, L. Zhou, C. Jin, L. Liu, G. Xu, H. Tang, H. Huang, J. Yuan, C. Gao, Mater. Lett. 186, 217 (2017)
R. Huang, J. Zhu, Mater. Chem. Phys. 121, 519 (2010)
Z. Wang, W.H. Tian, X.H. Liu, Y. Li, X.G. Li, Mater. Chem. Phys. 100, 92 (2006)
M. Rahman, G. Song, A. Bhatt, Y. Wong, C. Wen, Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 647 (2016)
P. Zuo, G. Yin, Z. Yang, Z. Wang, X. Cheng, D. Jia, C. Du, Mater. Chem. Phys. 115, 757 (2009)
H. Jung, M. Lee, B. Yeo, K. Lee, S. Han, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 32078 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016M592115), Jiangxi Postdoctoral Foundation (2015KY12), National Nature Science Foundation of China (61464007) and Nature Science Foundation of Jiangxi province (2015BAB207055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, Z., Zhou, L., Jin, C. et al. N-type nano-silicon powders with ultra-low electrical resistivity as anode materials in lithium ion batteries. Appl. Phys. A 123, 417 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1036-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1036-9