Abstract
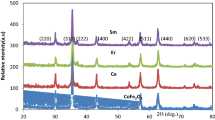
Pure nanoparticles of the rare earth-substituted cobalt and copper ferrites with general formula Me Gd0.025 Er0.05 Fe1.925 O4 (Me = Co, Cu) were prepared by the chemical citrate method. X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, BET analysis are utilized to study the effect of rare earth substitution and its impact on the physical properties of the investigated samples. Rare earth-doped cobalt shows type IV isotherm suggesting mesopore structure with its hysteresis loop. The estimated crystallite sizes are found in the range of 21.49 and 36.11 nm for the doped Co and Cu samples, respectively. The magnetic properties of rare earth-substituted cobalt and copper ferrites showed a definite hysteresis loop at room temperature. An increase in coercivity and a decrease in saturation magnetization were detected. This can be explained in view of weaker nature of the Re3+–Fe3+ interaction compared to Fe3+–Fe3+ interaction. Greater than 1.13-fold increase in coercivity (Hc = 2184 Oe) was observed in doped cobalt nanoferrite samples compared to copper (Hc = 1936 Oe). It was found that the decreasing in temperature leads to great improvement in the magnetic properties of the investigated samples. As the magnetic recording performance of the magnetic samples is improved for well-crystallized samples with nano-structural, the effect of rare earth substitution seems to be particularly valuable in this regard.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.R. Tatarchuk, M. Bououdina, N.D. Paliychuk, I.P. Yareminy, V.V. Moklyak, Structural characterization and antistructure modeling of cobalt-substituted zinc ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 694, 777–791 (2017)
P. Samoila, C. Cojocaru, L. Sacarescu, P.P. Dorneanu, A.-A. Domocos, A. Rotaru, Remarkable catalytic properties of rare-earth doped nickel ferrites synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion with maleic acid as fuel for CWPO of dyes. Appl. Catal. B 202, 21–32 (2017)
E.E. Ateia, A.T. Mohamed, Nonstoichiometry and phase stability of Al and Cr substituted Mg ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by citrate method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 217–224 (2017)
K. Chandra Babu Naidu, W. Madhuri, Microwave processed bulk and nano NiMg ferrites: a comparative study on X-band electromagnetic interference shielding properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 187, 164–176 (2017)
R.N. Panda, J.C. Shih, T.S. Chin, Magnetic properties of nano-crystalline Gd- or Pr-substituted CoFe2O4 synthesized by the citrate precursor technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 257, 79–86 (2003)
P. Kumar, J. Chand, M. Singh, Ferromagnetic ordering in lanthanum substituted nano-cobalt ferrite at room temperature. Integr. Ferroelectr. 134, 53–57 (2012)
V.A. Zhuravlev, R.V. Minin, V.I. Itin, I. Yu Lilenko, Structural parameters and magnetic properties of copper ferrite nanopowders obtained by the sol–gel combustion. J. Alloys Compd. 692, 705–712 (2017)
I. Mindru, D. Gingasu, L. Patron, G. Marinescu, J.M. Calderon-Moreno, L. Diamandescu, S. Preda, O. Oprea, Chromium substituted copper ferrites via gluconate precursor route. Ceram. Int. 41, 5318–5330 (2015)
Fu-Xiang Cheng, Jiang-Tao Jia, Chun-Sheng Liao, Xu Zhi-Gang, Biao Zhou, Chun-Hua Yan, Liang-Yao Chen, Hai-Bin Zhao, Microstructure and magneto-optical properties of CoFe1.9RE0.1O4 nanocrystalline films on quartz substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 6779 (2000)
L. Ben Tahar, M. Artus, S. Ammar, L.S. Smiri, F. Herbst, M.-J. Vaulay, V. Richard, J.-M. Grenèche, F. Villain, F. Fiévet, Magnetic properties of CoFe1.9RE0.1O4 nanoparticles (RE = La, Ce, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Ho) prepared in polyol. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 3242–3250 (2008)
L. Zhao, H. Yang, L. Yu, Y. Cui, X. Zhao, Y. Yan, S. Feng, The studies of nanocrystalline Ni0.7Mn0.3NdxFe2-xO4 (x = 0–0.1) ferrites. Phys. Lett. A 332, 268–278 (2004)
G. Chandra, R.C. Srivastava, K. Ashokan, Structural and Magnetic Properties of Cerium Doped Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles. In: 1st International Congress on Computer, Electronics, Electrical, and Communication Engineering (ICCEECE2014) IPCSIT vol. 59 (2014) © (2014) (IACSIT Press, Singapore)
S.M. Rathod, V.G. Deonikar, P.P. Mirage, Synthesis of nano sized cerium doped copper ferrite, their magnetic and optical studies. Adv. Sci. Lett. 22, 964–966 (2016)
N.C. Sena, T.J. Castro, V.K. Garg, A.C. Oliveira, P.C. Morais, S.W. da Silva, Gadolinium ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis and morphological, structural and magnetic properties. Ceram. Int. (2016). doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.11.155
A.B. Gadkari, T.J. Shinde, P.N. Vasambekar, Structural analysis of Y3+-doped Mg–Cd ferrites prepared by oxalate co-precipitation method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 505–510 (2009)
T.J. Shinde, A.B. Gadkari, P.N. Vasambekar, Effect of Nd3+ substitution on structural and electrical properties of nanocrystalline zinc ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2777–2781 (2010)
M.H. Abdellatif, C. Innocenti, I. Liakos, A. Scarpellini, S. Marras, M. Salerno, Effect of Jahn–Teller distortion on the short range magnetic order in copper ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 424, 402–409 (2017)
N. Sharma, P. Aghamkar, S. Kumar, M. Bansal, R.P.Tondon Anji, Study of structural and magnetic properties of Nd doped zinc ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 369, 162–167 (2014)
H. Harzali, F. Saida, A. Marzouki, A. Megriche, F. Baillon, F. Espitalier, A.A. Mgaidi, Structural and magnetic properties of nano-sized NiCuZn ferrites synthesized by co-precipitation method with ultrasound irradiation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 50–56 (2016)
R. Zahir, F.-U.-Z. Chowdhury, M.M. Uddin, M.A. Hakim, Structural, magnetic and electrical characterization of Cd-substituted Mg ferrites synthesized by double sintering technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 410, 55–62 (2016)
E.E. Ateia, A.A. El-Bassuony, G. Abdelatif, F.S. Soliman, Novelty characterization and enhancement of magnetic properties of Co and Cu nanoferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 241–249 (2017)
Zhiqing Liu, Zhijian Peng, Changchun Lv, Fu Xiuli, Doping effect of Sm3+ on magnetic and dielectric properties of Ni–Zn ferrites. Ceram. Int. 43, 1449–1454 (2017)
V.S. Puli, S. Adireddy, C.V. Ramana, Chemical bonding and magnetic properties of gadolinium (Gd) substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Comp. 644, 470–475 (2015)
R. Sharma, S. Dinghal, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of zinc doped nickel ferrite and their application in photo catalytic degradation of methylene blue. Phys B 414, 83–90 (2013)
D.E. Newbury, D.C. Joy, P. Echlin, C.E. Fiori, J.I. Goldstein, Advanced Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis, (Plenum Press, New York, 1986), ISBN 0-0306-42140-2
Recommendations: Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity, IUPAC commission on colloid and surface chemistry including catalysis. Pure Appl. Chem. 57, 603 (1985)
Recommendations for the Characterization of Porous Solids, IUPAC commission on colloid and surface chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 66, 1739 (1994)
P. Paramasivan, P. Venkatesh, A novel approach: hydrothermal method of fine stabilized superparamagnetics of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 29, 2805–2811 (2016)
M.D. Donohue, G.L. Aranovich, Classification of Gibbs adsorption isotherms. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 76–77, 137–152 (1998)
Z.A. ALOthman, A review: fundamental aspects of silicate mesoporous materials. Materials 5, 2874–2902 (2012)
M.N. Akhtar, M.A. Khan, M. Ahmad, M.S. Nazir, M. Imran, A. Ali, A. Sattar, G. Mutazza, Evaluation of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of CuZnNi (CuxZn0.5-xNi0.5Fe2O4) nanocrystalline ferrites for core, switching and mlciʼs applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 421, 260–268 (2017)
A. Ghasemi, Stoner–Wohlfarth rotation or domain wall motion mechanism in W-type magnetic hexaferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 42, 4143–4149 (2016)
V. Naidu, A.K. Sahib, M. Suganthi, C. Prakash, Study of electrical and magnetic properties in nano sized ce–gd doped magnesium ferrite. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 27, 40–45 (2011)
M.V. Vaganov, J. Linke, S. Odenbach, YuL Raikher, Model FORC diagram for hybrid magnetic elastomers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2016). doi:10.1016/j.mmm.2016.08.084
S. Rimi Sharma, Bansal and Sonal Singhal, Tailoring the photo-Fenton activity of spinel ferrites (MFe2O4) by incorporating different cations (M = Cu, Zn, Ni and Co) in the structure. RSC Adv. 5, 6006–6018 (2015)
A.M. Elseman, D.A. Rayan, M.M. Rashad, Structure, optical and magnetic behavior of nanocrystalline Cuo nanopowders synthesized via a new technique using Schiff base complex. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 2652–2661 (2016)
A.S. Ahmed, S.M. Muhamed, M.L. Singla, S. Tabassum, A.H. Naqvi, A. Azam, Band gap narrowing and fluorescence properties of nickel doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 131, 1–6 (2011)
S.K. Tripathy, A. Pattanaik, Optical and electronic properties of some semiconductors from energy gaps. Opt. Mater. 53, 123–133 (2016)
W.H. Strehlow, E.L. Cook, Compilation of energy band gaps in elemental and binary compounds semiconductors and insulators. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data (1973). doi:10.1063/1.3253115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ateia, E.E., Soliman, F.S. Modification of Co/Cu nanoferrites properties via Gd3+/Er3+doping. Appl. Phys. A 123, 312 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0948-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0948-8