Abstract
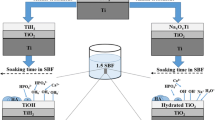
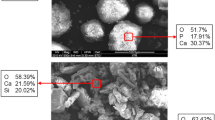
Fluorapatite (FA) has better chemical and thermal stability than hydroxyapatite (HA), and has thus attracted significant interest for biomaterial applications in recent years. In this study, porous bioceramic layers were prepared on pure titanium surfaces using a micro-arc oxidation (MAO) technique with an applied voltage of 450 V and an oxidation time of 5 min. The MAO process was performed using three different electrolyte solutions containing calcium fluoride (CaF2), calcium acetate monohydrate (Ca(CH3COO)2·H2O), and sodium phosphate monobasic dihydrate (NaH2PO4·2H2O) mixed in ratios of 0:2:1, 1:1:1, and 2:0:1, respectively. The surface morphology, composition, micro-hardness, porosity, and biological properties of the various MAO coatings were examined and compared. The results showed that as the CaF2/Ca(CH3COO)2·H2O ratio increased, the elemental composition of the MAO coating transformed from HA, A-TiO2 (Anatase) and R-TiO2 (Rutile); to A-TiO2, R-TiO2, and a small amount of HA; and finally A-TiO2, R-TiO2, CaF2, TiP2O5, and FA. The change in elemental composition was accompanied by a higher micro-hardness and a lower porosity. The coatings exhibited a similar in vitro bioactivity performance during immersion in simulated body fluid for 7–28 days. Furthermore, for in initial in vitro biocompatibility tests performed for 24 h using Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplement containing 10%Fetal bovine serum, the attachment and spreading of osteoblast-like osteosarcoma MG63 cells were found to increase slightly with an increasing CaF2/Ca(CH3COO)2·H2O ratio. In general, the results presented in this study show that all three MAO coatings possess a certain degree of in vitro bioactivity and biocompatibility.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Sennerby, P. Thomsen, L.E. Ericson, Ultrastructure of the bone-titanium interface in rabbits. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 3 (4), 262–271 (1992).
D.E. Steflif, A.L. Sisk, G.R. Parr, L.K. Garner, P.J. Hanes, F.T. Lake, D.J. Berkery, P. Brewer, Osteogenesis at the dental implant interface: high-voltage electron microscopic and conventional transmission electron microscopic observations. J. Biomed. Mater. Res 27(6), 791–800 (1993)
C.S. Chien, T.Y. Liao, T.F. Hong, T.Y. Kuo, C.H. Chang, M.L. Yeh, T.M. Lee, Surface microstructure and bioactivity of hydroxyapatite and fluorapatite coatings deposited on Ti-6Al-4V substrates using Nd-YAG laser. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 34 (2), 109–115 (2014).
C.S. Chien, Y.S. Ke, T.Y. Kuo, T.Y. Liao, T.M. Lee, T.F. Hong, Effect of TiO2 addition on surface microstructure and bioactivity of fluorapatite coatings deposited using Nd:YAG laser. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H. 228 (4), 379–387 (2014).
C.S. Chien, T.Y. Liao, T.F. Hong, T.Y. Kuo, J.L. Wu, T.M. Lee, Investigation into microstructural properties of fluorapatite Nd-YAG laser clad coatings with PVA and WG binders. Surf. Coat. Technol 205(10), 3141–3146 (2011)
C.S. Chien, T.F. Hong, T.J. Han, T.Y. Kuo, T.Y. Liao, Effects of different binders on microstructure and phase composition of hydroxyapatite Nd–YAG laser clad coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci 257(6), 2387–2393 (2011)
T.F. Hong, Z.X. Guo, R. Yang, Fabrication of porous titanium scaffold materials by a fugitive filler method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 19, 3489–3495 (2008).
C.Y. Yang, T.M. Lee, Y.Z. Lu, C.W. Yang, T.S. Lui, A. Kuo, B.W. Huang, The influence of plasma-sprayed parameters on the characteristics of fluorapatite coatings. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 30 (2), 91–98 (2010).
S.C. Mojumdar, J. Kozánková, J. Chocholoušek, J. Majling, D. Fábryová, Fluoroapatite—material for medicine, growth, morphology and thermoanalytical properties. J. Therm. Anal. Cal. 78 (1), 73–82 (2004).
Y. Chen, X. Mian, Thermal and chemical stability of fluorohydroxyapatite ceramics with different fluorine contents. Biomaterials 26(11), 1205–1210 (2005)
F.B. Ayed, J. Bouaziz, Sintering of tricalcium phosphate–fluorapatite composites by addition of alumina. Ceram. Int. 34 (8), 1885–1892 (2008).
K.A. Bhadang, K.A. Gross, Influence of fluorapatite on the properties of thermally sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. Biomaterials 25(20), 4935–4945 (2004)
Al-Noaman, N. Karpukhina, S.C.F. Rawlinson, R.G. Hill, Effect of FA on bioactivity of bioactive glass coating for titanium dental implant. Part I: Composite powder. J. Non Cryst. Solids. 364, 92–98 (2013).
W.J. Dhert, C.P. Klein, J.A. Jansen, E.A. van der Velde, R.C. Vriesde, P.M. Rozing, K. de Groot, A histological and histomorphometrical investigation of fluorapatite, magnesiumwhitlockite, and hydroxylapatite plasma-sprayed coatings in goats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res 27(1), 127–138 (1993)
C.P.A.T. Klein, J.G.C. Wolke, J.M.A. De Blieck-Hogervorst, K. de Groot, Calcium phosphate plasma-sprayed coatings and their stability: an in vivo study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res 28(8), 909–917 (1994)
M. Wei, J.H. Evans, T. Bostrom, L. Grøndahl, Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite, fluoride-substituted hydroxyapatite and fluorapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 14 (4), 311–320 (2003).
X. Zheng, M. Huang, C. Ding, Bond strength of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite/Ti composite coatings. Biomaterials 21(8), 841–849 (2000)
S.W.K. Kweh, K.A. Khor, P. Cheang, An in vitro investigation of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite (HA) coatings produced with flame-spheroidized feedstock. Biomaterials 23(3), 775–785 (2002)
W. Weng, J.L. Baptista, Preparation and characterization of hydroxyapatite coatings on Ti6Al4V alloy by a sol-gel method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82(1), 27–32 (1999)
O. Blind, L.H. Klein, B. Dailey, L. Jordan, Characterization of hydroxyapatite films obtained by pulsed-laser deposition on Ti and Ti-6Al-4V substrates. Dent. Mater. 21 (11), 1017–1024 (2005).
M.C. Kuo, S.K. Yen, The process of electrochemical deposited hydroxyapatite coatings on biomedical titanium at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 20(1–2), 153–160 (2002)
A.L. Yerokhin, X. Nie, A. Leyland, A. Matthews, S.J. Dowey, Plasma electrolysis for surface engineering. Surf. Coat. Technol 122(2–3), 73–93 (1999)
W.F. Cui, L. Jin, L. Zhou, Surface characteristics and electrochemical corrosion behavior of a pre-anodized microarc oxidation coating on titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 33(7), 3775–3779 (2013)
J.H. Ni, Y.L. Shi, F.Y. Tan, J.Z. Chen, L. Wang, Preparation of hydroxyapatite-containing titania coating on titanium substrate by micro-arc oxidation. Mater. Res. Bull 43(1), 45–53 (2008)
X.L. Shi, Q.L. Wang, F.S. Wang, S.R. Ge, Effects of electrolytic concentration on properties of micro-arc film on Ti6Al4V alloy. Mini. Sci. Technol. 19 (2), 220–224 (2009).
J.Z. Chen, Y.L. Shi, L. Wang, F.Y. Yan, F.Q. Zhang, Preparation and properties of hydroxyapatite-containing titania coating by micro-arc oxidation. Mater. Lett 60(20), 2538–2543 (2006)
Y. Huang, Y. Wang, C. Ning, K. Nan, Y. Han, Hydroxyapatite coatings produced on commercially pure titanium by micro-arc oxidation. Biomed. Mater. 2 (3), 196–201 (2007).
L.T. Duarte, C. Bolfarini, S.R. Biaggio, R.C. Rocha-Filho, P.A. Nascente, Growth of aluminum-free porous oxide layers on titanium and its alloys Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-7Nb by micro-arc oxidation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 41, 343–348 (2014)
G. Ryan, A. Pandit, D.P. Apatsidis, Fabrication methods of porous metals for use in orthopaedic applications. Biomaterials. 27(13), 2651–2670 (2006).
M. Mour, D. Das, T. Winkler, E. Hoenig, G. Mielke, M.M. Morlock, A.F. Schilling, Advances in porous biomaterials for dental and orthopaedic applications. Materials, 3, 2947–2974 (2010).
M.R. Bayati, F. Golestani-Fard, A.Z. Moshfegh, How photocatalytic activity of the MAO-grown TiO2 nano/micro-porous films is influenced by growth parameters? Appl. Surf. Sci 256(13), 4253–4259 (2010)
X.F. Xiao, R.F. Liu, Effect of suspension stability on electrophoretic deposition of hydroxyapatite coatings. Mater. Lett 60(21–22), 2627–2632 (2006)
F.A. Akin, H. Zreiqat, S. Jordan, M.B.J. Wijesundara, Preparation and analysis of macroporous TiO2 films on Ti surfaces for bone–tissue implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res 57(4), 588–596 (2001)
Q.M. Zhao, H.L. Yang, Z.T. Liu, X.F. Gu, C. Li, D.H. Feng, Fabrication of hydroxyapatite on pure titanium by micro-arc oxidation coupled with microwave-hydrothermal treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 26 (88), 1–8 (2015).
J. Wang, Y. Chao, Q. Wan, Z. Zhu, H. Yu, Fluoridated hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium obtained by electrochemical deposition. Acta Biomater 5(5), 1798–1807 (2009)
H.U. Cameron, I. Macnab, R.M. Pilliar, A porous metal system for joint replacement surgery. Int. J. Artif. Organs. 1(2), 104–109 (1978).
C.J. Chung, H.Y. Long, Systematic strontium substitution in hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium via micro-arc treatment and their osteoblast/osteoclast responses. Acta Biomater 7(11), 4081–4087 (2011)
T.M. Lee, K.C. Kung, K. Yuan, T.S. Lui, Effect of heat treatment on microstructures and mechanical behavior of porous Sr-Ca-P coatings on titanium. J. Alloy Compd 515(25), 68–73 (2012)
M.J. Kim, C.W. Kim, Y.J. Lim, S.J. Heo, Microrough titanium surface affects biologic response in MG63 osteoblast-like cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 79 (4), 1023–1032 (2006).
K.C. Kung, T.M. Lee, J.L. Chen, T.S. Lui, Characteristics and biological responses of novel coatings containing strontium by micro-arc oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol 205(6), 1714–1722 (2010)
Y. Nagai, C. Yamazaki, K. Ma, T. Nozaki, K. Toyamab, Yamashita, Response of osteoblast-like MG63 cells to TiO2 layer prepared by micro-arc oxidation and electric polarization. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc 32(11), 2647–2652 (2012)
W.H. Song, H.S. Ryu, S.H. Hong, Antibacterial properties of Ag (or Pt)-containing calcium phosphate coatings formed by micro-arc oxidation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 88 (1), 246–254 (2009).
J.Y. Martin, Z. Schwartz, T.W. Hummert, D.M. Schraub, J. Simpson, J. Lankford, D.D. Dean, D.L. Cochran, B.D. Boyan, Effect of titanium surface roughness on proliferation, differentiation, and protein synthesis of human osteoblast-like cells (MG63). J. Biomed. Mater. Res 29(3), 389–401 (1995)
B.D. Boyan, R. Batzer, K. Kieswetter, Y. Liu, D.L. Cochran, S. Szmuckler-Moncler, D.D. Dean, Z. Schwartz, Titanium surface roughness alters responsiveness of MG63 osteoblast-like cells to 1 α,25-(OH)2D3. J. Biomed. Mater. Res 39(1), 77–85 (1998)
L.H. Li, Y.M. Kong, H.W. Kim, Y.W. Kim, H.E. Kim, S.J. Heo, J.Y. Koak, Improved biological performance of Ti implants due to surface modification by micro-arc oxidation. Biomaterials 25(14), 2867–2875 (2004)
H. Eslami, M. Solati-Hashjin, M. Tahriri, The comparison of powder characteristics and physicochemical, mechanical and biological properties between nanostructure ceramics of hydroxyapatite and fluoridated hydroxyapatite. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 29(4), 1387–1398 (2009)
C.F. Dunne, B. Twomey, C. Kelly, J.C. Simpson, K.T. Stanton, Hydroxyapatite and fluorapatite coatings on dental screws: effects of blast coating process and biological response. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 26 (1), 1–14 (2015).
G.L. Darimont, R. Cloots, E. Heinen, L. Seidel, R. Legrand, In vivo behaviour of hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium implants: a quantitative study in the rabbit. Biomaterials 23(12), 2569–2575 (2002)
K.Y. Xie, Y. Wang, Y. Zhao, L. Chang, G. Wang, Z. Chen, Y. Cao, X. Liao, E.J. Lavernia, R.Z. Valiev, B. Sarrafpour, H. Zoellner, S.P. Ringer, Nanocrystalline β-Ti alloy with high hardness, low Young’s modulus and excellent in vitro biocompatibility for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 33(6), 3530–3536 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided to this study by the Chi Mei Foundation Hospital, Republic of China (Taiwan), under Contract No. 110990223, and the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China (Taiwan) under Contract No. MOST 103-2221-E-218-006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chien, CS., Hung, YC., Hong, TF. et al. Preparation and characterization of porous bioceramic layers on pure titanium surfaces obtained by micro-arc oxidation process. Appl. Phys. A 123, 204 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0765-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0765-0