Abstract
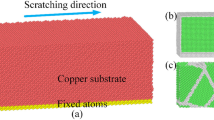
The effects of scratch depth, scratch speed, and alloy composition on the mechanical deformation and nanotribology properties of CuZr metallic glasses are studied using molecular dynamics simulations based on the second-moment approximation of the many-body tight-binding potential. These effects are investigated in terms of atomic trajectories, slip vectors, friction force, normal force, and friction coefficient. The simulation results show that a few shear transformation zones independently develop at the contact area between the probe tip and the film. Pileup occurs in the nanoscratch process but not during nanoindentation at a depth of 2.4 nm. There are two areas on the surface where the atoms have high slip vector values during nanoscratching. These areas form due to the removal of atoms that piled up around the probe tip and those behind the probe tip, respectively. Both the friction force and the normal force increase with increasing scratch depth and scratch speed. Friction coefficients decrease with increasing scratch depth, scratch speed, and Zr content in films.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Telford, Mater. Today 7, 36 (2004)
A.I. Salimon, M.F. Ashby, Y. Brechet, A.L. Greer, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375, 385 (2004)
A. Peker, W.L. Johnson, Appl. Phys. Lett. 63, 2342 (1993)
J. Schroers, W.L. Johnson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 255506 (2004)
R.D. Conner, Y. Li, W.D. Nix, W.L. Johnson, Acta Mater. 52, 2429 (2004)
W.L. Johnson, J. Miner. Metall. Mater. Soc. 54, 40 (2002)
C.L. Chiang, J.P. Chu, F.X. Liu, P.K. Liaw, R.A. Buchanan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 131902 (2006)
J. Schroers, Processing of bulk metallic glass. Adv. Mater. 22, 1566 (2010)
G. Kumar, H.X. Tang, J. Schroers, Nature 457, 868 (2009)
S.N. Sambandam, S. Bhansali, V.R. Bhethanabotla, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 806, MM8 (2004)
Y. Saotome, Y. Noguchi, T. Zhang, A. Inoue, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375–377, 389 (2004)
S.R. Ning, J. Gao, Y.G. Wang, Adv. Mater. Res. 129–131, 1366 (2010)
V. Keryvin, R. Crosnier, R. Laniel, V.H. Hoang, J.C. Sangleboeuf, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 074029 (2008)
J. Sort, N.V. Steenberge, A. Gimazov, A. Concustell, S. Suriñach, A. Gebert, J. Eckert, M.D. Baró, Open Mater. Sci. J. 2, 1 (2008)
Y. Huang, Y.L. Chiu, J. Shen, Y. Sun, J.J.J. Chen, Intermetallics 18, 1056 (2010)
K.W. Chen, J.F. Lin, Int. J. Plast. 26, 1645 (2010)
D. Tranchida, S. Piccarolo, R.A.C. Deblieck, Meas. Sci. Technol. 17, 2630 (2016)
C.D. Wu, T.H. Fang, C.C. Wu, J. Appl. Phys. 117(1), 014307 (2015)
C.D. Wu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 343, 153 (2015)
C.D. Wu, T.H. Fang, C.Y. Chen, C.I. Weng, Appl. Surf. Sci. 292, 500 (2014)
C.D. Wu, T.H. Fang, J.F. Lin, Mater. Lett. 80, 59 (2012)
C.D. Wu, T.H. Fang, J.F. Lin, Micron 44, 410 (2013)
C.D. Wu, T.H. Fang, T.T. Wu, Polymer 53, 857 (2012)
F. Li, X.J. Liu, Z.P. Lu, Comput. Mater. Sci. 85, 147 (2014)
S.S. Dalgic, M. Celtek, EPJ Web Conf. 15, 03008 (2011)
M.P. Allen, D.J. Tildesley, Computer Simulation of Liquids (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1987)
A.L. Greer, Y.Q. Cheng, E. Ma, Mater. Sci. Eng. R74, 71 (2013)
M.Z. Ma, H.T. Zong, H.Y. Wang, W.G. Zhang, A.J. Song, S.X. Liang, Q. Wang, X.Y. Zhang, Q. Jing, G. Li, R.P. Liu, Mater. Lett. 62, 4348 (2008)
E. Fleury, S.M. Lee, H.S. Ahn, W.T. Kid, D.H. Kim, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 375–377, 276 (2004)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Council of Taiwan under Grants MOST 104-2221-E-033-062-MY2 and MOST NSC 104-2622-E-033-006-CC3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, CD. Molecular dynamics simulation of nanotribology properties of CuZr metallic glasses. Appl. Phys. A 122, 486 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9998-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9998-6