Abstract
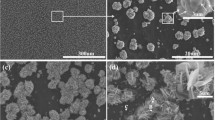
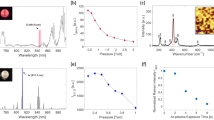
In our work, large-scale silver NPs (nanoparticles) are successfully synthesized on zinc foils with controllable size by regulating the temperature of the displacement reaction. Our results show that when the temperature is 70 °C, the average size of silver NPs is approximately 88 nm in diameter, and they exhibit the strongest SERS activity. The gap between nanoparticles is simultaneously regulated as near as possible, which produces abundant “hot spots” and nanogaps. Crystal violet (CV) was used as probe molecules, and the SERS signals show that the values of relative standard deviation in the intensity of the main vibration modes are less than 10%, demonstrating excellent reproducibility of the silver NPs. Furthermore, the high surface-average enhancement factor of ~3.86 × 107 is achieved even when the concentration of CV is 10−7 M, which is sufficient for single-molecule detection. We believe that this low cost and rapid route would get wide applications in chemical synthesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Fleischmann, P.J. Hendra, A.J. McQuillan, Raman spectra of pyridzne adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 26(2), 163–166 (1974)
K. Kim, K.S. Shin, Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: a powerful tool for chemical identification. Anal. Sci. 27(8), 775–783 (2011)
J. Kneipp, H. Kneipp, K. Kneipp, SERS—a single-molecule and nanoscale tool for bioanalytics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 37(5), 1052–1060 (2008). doi:10.1039/b708459p
S. Yang, X. Dai, B.B. Stogin, T.S. Wong, Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection in common fluids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113(2), 268–273 (2016). doi:10.1073/pnas.1518980113
F.J. Garcia-Vidal, J.B. Pendry, Collective theory for surface enhanced Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(6), 1163–1166 (1996). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.1163
H. Xu, J. Aizpurua, M. Käll, P. Apell, Electromagnetic contributions to single-molecule sensitivity in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. E 62(3), 4318–4324 (2000)
X. Gong, Y. Bao, C. Qiu, C. Jiang, Individual nanostructured materials: fabrication and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Chem. Commun. 48(56), 7003–7018 (2012). doi:10.1039/c2cc31603j
C.L. Haynes, A.D. McFarland, L.L. Zhao, R.P. Van Duyne, G.C. Schatz, Nanoparticle optics: the importance of radiative dipole coupling in two-dimensional nanoparticle arrays. J. Phys. Chem. B 107(30), 7337–7342 (2003)
L. Zhang, X. Gong, Y. Bao, Y. Zhao, M. Xi, C. Jiang, H. Fong, Electrospun nanofibrous membranes surface-decorated with silver nanoparticles as flexible and active/sensitive substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Langmuir 28(40), 14433–14440 (2012). doi:10.1021/la302779q
E.Z. Tan, P.G. Yin, T.T. You, H. Wang, L. Guo, Three dimensional design of large-scale TiO(2) nanorods scaffold decorated by silver nanoparticles as SERS sensor for ultrasensitive malachite green detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4(7), 3432–3437 (2012). doi:10.1021/am3004126
C.H. Xiao, B.X. Xiao, Y.D. Wang, J. Zhang, S.M. Wang, P. Wang, T.Y. Yang, R. Zhao, H. Yu, Z.F. Li, M.Z. Zhang, Synthesis of ZnO nanosheets decorated with Au nanoparticles and its application in recyclable 3D surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates. RSC Adv. 5(23), 17945–17952 (2015). doi:10.1039/c4ra15193c
Y. Sun, Y. Xia, Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science 298(13), 2176–2179 (2002)
S.K. Yang, W.P. Cai, L.C. Kong, Y. Lei, Surface nanometer-scale patterning in realizing large-scale ordered arrays of metallic nanoshells with well-defined structures and controllable properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20(15), 2527–2533 (2010). doi:10.1002/adfm.201000467
S. Nie, S.R. Emory, Probing single molecules and single nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Science 275(5303), 1102–1106 (1997). doi:10.1126/science.275.5303.1102
H.H. Wang, C.Y. Liu, S.B. Wu, N.W. Liu, C.Y. Peng, T.H. Chan, C.F. Hsu, J.K. Wang, Y.L. Wang, Highly Raman-enhancing substrates based on silver nanoparticle arrays with tunable sub-10 nm gaps. Adv. Mater. 18(4), 491–495 (2006). doi:10.1002/adma.200501875
P.P. Zhang, J. Gao, X.H. Sun, An ultrasensitive, uniform and large-area surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate based on Ag or Ag/Au nanoparticles decorated Si nanocone arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106(4), 043103 (2015). doi:10.1063/1.4906800
T.R. Jensen, G. Schatz, R.P. Van Duyne, Nanosphere lithography: surface plasmon resonance spectrum of a periodic array of silver nanoparticles by ultraviolet-visible extinction spectroscopy and electrodynamic modeling. J. Phys. Chem. B 103(13), 2394–2401 (1999)
L. Gunnarsson, E.J. Bjerneld, H. Xu, S. Petronis, B. Kasemo, M. Käll, Interparticle coupling effects in nanofabricated substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78(6), 802 (2001). doi:10.1063/1.1344225
C.L. Haynes, R.P. Van Duyne, Plasmon-sampled surface-enhanced raman excitation spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 107(30), 7426–7433 (2003)
Y. Lu, G.L. Liu, L.P. Lee, High-density silver nanoparticle film with temperature-controllable interparticle spacing for a tunable surface enhanced Raman scattering substrate. Nano Lett. 5(1), 5–9 (2005). doi:10.1021/nl048965u
Y.L. Kuo, T.Y. Juang, S.H. Chang, C.M. Tsai, Y.S. Lai, L.C. Yang, C.L. Huang, Influence of temperature on the formation of silver nanoparticles by using a seed-free photochemical method under sodium-lamp irradiation. ChemPhysChem: Eur. J. Chem. Phys. Phys. Chem. 16(15), 3254–3263 (2015). doi:10.1002/cphc.201500485
E. de Barros Santos, N.V. Madalossi, F.A. Sigoli, I.O. Mazali, Silver nanoparticles: green synthesis, self-assembled nanostructures and their application as SERS substrates. New J. Chem. 39(4), 2839–2846 (2015). doi:10.1039/c4nj02239d
Q. Fu, Z. Zhan, J. Dou, X. Zheng, R. Xu, M. Wu, Y. Lei, Highly reproducible and sensitive SERS substrates with Ag inter-nanoparticle gaps of 5 nm fabricated by ultrathin aluminum mask technique. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(24), 13322–13328 (2015). doi:10.1021/acsami.5b01524
Y. Xia, S.E. Skrabalak, J. Chen, X. Lu, Galvanic replacement reaction: a simple and powerful route to hollow and porous metal nanostructures. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part N: J. Nanoeng. Nanosyst. 221(1), 1–16 (2007). doi:10.1243/17403499jnn111
W. Song, Y. Cheng, H. Jia, W. Xu, B. Zhao, Surface enhanced Raman scattering based on silver dendrites substrate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 298(2), 765–768 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2006.01.037
J.J. Fu, W.C. Ye, C.M. Wang, Facile synthesis of Ag dendrites on Al foil via galvanic replacement reaction with [Ag(NH3)(2)]Cl for ultrasensitive SERS detecting of biomolecules. Mater. Chem. Phys. 141(1), 107–113 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.04.031
B. Goris, L. Polavarapu, S. Bals, G. Van Tendeloo, L.M. Liz-Marzan, Monitoring galvanic replacement through three-dimensional morphological and chemical mapping. Nano Lett. 14(6), 3220–3226 (2014). doi:10.1021/nl500593j
E.C. Le Ru, E. Blackie, M. Meyer, P.G. Etchegoin, Surface enhanced Raman scattering enhancement factors: a comprehensive study. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(37), 13794–13803 (2007)
Y. Gu, S. Xu, H. Li, S. Wang, M. Cong, J.R. Lombardi, W. Xu, Waveguide-enhanced surface plasmons for ultrasensitive SERS detection. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 4(18), 3153–3157 (2013). doi:10.1021/jz401512k
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61371057), the National Special Fund for the Development of Major Research Equipment and Instruments (Grant No. 2011YQ03013403) and the Open Research Fund Program of Jiangsu Provincial Key Lab. of Center (GZ201309).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest that can inappropriately influence our work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Fang, J., Cheng, M. et al. Facile fabrication of silver nanoparticles with temperature-responsive sizes as highly active SERS substrates. Appl. Phys. A 122, 1065 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0584-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0584-8