Abstract
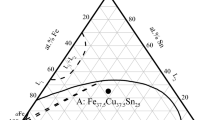
The active control of microstructure evolution is still a challenging factor for the development of advanced immiscible alloys. Here, we make an attempt to modulate the solidification pathways of undercooled Cu62.5Fe27.5Sn10 alloy by glass fluxing and drop tube techniques. Through regulating the liquid undercooling, three types of microstructures, dendrite, dispersive structure and macrosegregation pattern, were formed under the normal gravity condition. Below the first critical undercooling of 15 K, the alloy melt displayed the normal peritectic solidification. At moderate undercoolings above 15 K, the metastable liquid phase separation took place and the solidified microstructure appeared as homogeneously dispersed structure. If undercooling further overtook the second threshold of 107 K, macrosegregation occurred and the bulk alloy separated into an Fe-rich zone and a Cu-rich zone. Under the free fall condition, the alloy droplets with the droplet diameter beyond 805 μm showed the equilibrium peritectic solidification. If the droplet diameter decreased below 805 μm, the metastable liquid phase separation was induced and the microstructural morphology of Cu62.5Fe27.5Sn10 alloy droplet evolved from dendrite into dispersive structure. Furthermore, experimental and simulated results revealed that the temperature gradient had great influence on the size distribution of Fe-rich globules.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.Y. Heriot, R.A.L. Jones, Nat. Mater. 4, 782–786 (2005)
N. Pavlenko, T. Kopp, J. Mannhart, Phys. Rev. B 88, 201104 (2013)
C.W. Chu, H.C. Yang, W.J. Hou, J.S. Huang, G. Li, Y. Yang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 103306 (2008)
G. Lestari, M. Abolhasani, D. Bennett, P. Chase, A. Günther, E. Kumacheva, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 11972–11979 (2014)
K. Murata, H. Tanaka, Nat. Mater. 11, 436–443 (2012)
S. Kababya, A. Gal, K. Kahil, S. Weiner, L. Addadi, A. Schmidt, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 990–998 (2015)
J.J.Z. Li, W.K. Rhim, C.P. Kim, K. Samwer, W.L. Johnson, Acta Mater. 59, 2166–2171 (2011)
E.S. Park, D.H. Kim, Acta Mater. 54, 2597–2604 (2006)
S.B. Luo, W.L. Wang, Z.C. Xia, Y.H. Wu, B. Wei, Appl. Phys. A 119, 1003–1011 (2015)
J.C. Oh, T. Ohkubo, Y.C. Kim, E. Fleury, K. Hono, Scripta Mater. 53, 165–169 (2005)
A.K. Gangopadhyay, T.K. Croat, K.F. Kelton, Acta Mater. 48, 4035–4043 (2000)
S.B. Luo, W.L. Wang, J. Chang, Z.C. Xia, B. Wei, Acta Mater. 69, 355–364 (2014)
B.J. Park, H.J. Chang, D.H. Kim, W.T. Kim, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 6353–6355 (2004)
J.Z. Zhao, Scripta Mater. 54, 247–250 (2006)
W.L. Wang, Y.H. Wu, L.H. Li, W. Zhai, X.M. Zhang, B. Wei, Sci. Rep. 5, 16335 (2015)
J. Zhang, Y. Tang, K. Lee, M. Ouyang, Science 327, 1634–1638 (2010)
F. Chen, R.L. Johnston, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 023112 (2008)
Z.C. Xia, W.L. Wang, S.B. Luo, B. Wei, J. Appl. Phys. 117, 054901 (2015)
C.H. Liebscher, V.R. Radmilović, U. Dahmen, N.Q. Vo, D.C. Dunand, M. Asta, G. Ghosh, Acta Mater. 92, 220–232 (2015)
B.J. Park, Y.M. Chen, T. Ohkubo, Intermetallics 17, 958–961 (2009)
S. Khmelevskyi, P. Mohn, Phys. Rev. B 71, 144423 (2005)
L. Battezzati, S. Curiotto, E. Johnson, N.H. Pryds, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 449, 7–11 (2007)
A. Bachmaier, M. Pfaff, M. Stolpe, H. Aboulfadl, C. Motz, Acta Mater. 96, 269–283 (2015)
A. Munitz, A. Venkert, P. Landau, M.J. Kaufman, R. Abbaschian, J. Mater. Sci. 47, 7955–7970 (2012)
J.R. Rogers, R.H. Davis, Metall. Trans. A 21, 59–68 (1990)
X.R. Liu, N. Wang, B. Wei, Acta Phys. Sin. 54, 1671–1678 (2005)
X. Shan, H. Chen, Phys. Rev. E 47, 1815 (1993)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the help of Dr. D. L. Geng and Mr. S. J. Yang about their helpful discussions and critical comments in this work. And we express our appreciation for the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos: 51371150, 51271150, 51571163 and 51327901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Z.C., Wang, W.L., Wu, Y.H. et al. Solidification pathways of ternary Cu62.5Fe27.5Sn10 alloy modulated through liquid undercooling and containerless processing. Appl. Phys. A 122, 985 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0505-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0505-x