Abstract
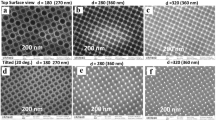
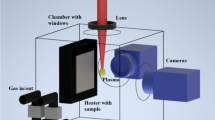
A reactive ion etching technique for the preparation of statistical “Black Germanium” antireflection surfaces, relying on self-organization in a Cl2 etch chemistry, is presented. The morphology of the fabricated Black Germanium surfaces is the result of a random lateral distribution of pyramidal etch pits with heights around (1450 ± 150) nm and sidewall angles between 80° and 85°. The pyramids’ base edges are oriented along the <110> crystal directions of Germanium, indicating a crystal anisotropy of the etching process. In the Vis–NIR, the tapered Black Germanium surface structure suppresses interface reflection to <2.5 % for normal incidence and still to <6 % at an angle of incidence of 70°. The presented Black Germanium might find applications as low-cost AR structure in optoelectronics and IR optics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.H. Southwell, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 8, 549 (1991)
C. Pacholski, C. Morhard, J. Spatz, D. Lehr, M. Schulze, E.-B. Kley, A. Tünnermann, M. Helgert, M. Sundermann, R. Brunner, Appl. Opt. 51, 8 (2012)
D.S. Hobbs, B.D. Macleod, Proc. SPIE 5786(5786), 578640 (2005)
Q. Chen, G. Hubbard, P. Shields, C. Liu, D.W.E. Allsopp, W.N. Wang, S. Abbott, Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 263118 (2009)
C. Brückner, T. Käsebier, B. Pradarutti, S. Riehemann, G. Notni, E.-B. Kley, A. Tünnermann, Opt. Express 17, 3063 (2009)
T. Lohmüller, M. Helgert, M. Sundermann, R. Brunner, J.P. Spatz, Nano Lett. 8, 1429 (2008)
Y. Wang, N. Lu, H. Xu, G. Shi, M. Xu, X. Lin, H. Li, W. Wang, D. Qi, Y. Lu, L. Chi, Nano Res. 3, 520 (2010)
A. Frommhold, A.P.G. Robinson, E. Tarte, Microelectron. Eng. 99, 43 (2012)
M. Schulze, M. Damm, M. Helgert, E.-B. Kley, S. Nolte, A. Tünnermann, Opt. Express 20, 1422 (2012)
U. Schulz, P. Munzert, R. Leitel, I. Wendling, N. Kaiser, A. Tünnermann, Opt. Express 15, 13108 (2007)
S.H. Zaidi, D.S. Ruby, J.M. Gee, I.E.E.E. Trans, Electron Devices 48, 1200 (2001)
G.C. Schwartz, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 16, 410 (1979)
M. Steglich, T. Käsebier, F. Schrempel, E.-B. Kley, A. Tünnermann, Infrared Phys. Technol. 69, 218 (2015)
R. Dussart, X. Mellhaoui, T. Tillocher, P. Lefaucheux, M. Volatier, C. Socquet-Clerc, P. Brault, P. Ranson, J. Phys. D 38, 3395 (2005)
T. Tillocher, R. Dussart, X. Mellhaoui, P. Lefaucheux, N.M. Maaza, P. Ranson, M. Boufnichel, L.J. Overzet, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 24, 1073 (2006)
H. Jansen, M. de Boer, R. Legtenberg, M. Elwenspoek, J. Micromech. Microeng. 5, 115 (1995)
M. Steglich, T. Käsebier, M. Zilk, T. Pertsch, E.-B. Kley, A. Tünnermann, J. Appl. Phys. 116, 173503 (2014)
H. Jansen, H. Gardeniers, M. de Boer, M. Elwenspoek, J. Fluitman, J. Micromech. Microeng. 6, 14 (1996)
S. Schicho, A. Jaouad, C. Sellmer, D. Morris, V. Aimez, R. Arès, Mater. Lett. 94, 86 (2013)
M. Köhler, Etching in microsystem technology, 1st edn. (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 1999)
M. Lindblom, J. Reinspach, O. von Hofsten, M. Bertilson, H.M. Hertz, A. Holmberg, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 27, L1 (2009)
H. Okano, Y. Horiike, M. Sekine, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 24, 68 (1985)
M. Seel, P.S. Bagus, Phys. Rev. B 23, 5464 (1981)
M. Kroll, T. Käsebier, M. Otto, R. Salzer, R. Wehrspohn, B. Kley, A. Tünnermann, T. Pertsch, Proc. SPIE 7725(7725), 772505 (2010)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the fo+ (Contract No. 03WKCK1D) funding program of the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steglich, M., Käsebier, T., Kley, EB. et al. Black Germanium fabricated by reactive ion etching. Appl. Phys. A 122, 836 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0318-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0318-y