Abstract
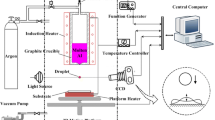
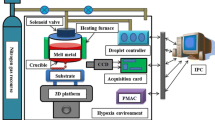
Successive deposition of uniform metal droplet is a new kind of 3D printing and rapid prototyping technology. This paper presents a systematic numerical investigation of the transient transport phenomenon during the fusion of successive droplets impinging onto a substrate surface. The physical mechanisms of the fusion process, including the bulk liquid, capillarity effects at the liquid–solid interface, heat transfer, and solidification, are identified and quantified numerically. The 3D models based on a volume of fluid method were developed to investigate the successive deposition of molten metal droplets on a horizontally aluminum substrate surface. The numerical models are validated with experiments. The comparison between numerical simulations and experimental findings shows a good agreement. The effects of relative distances between two successive molten droplets on the end-shapes of impact regime are examined. This investigation is essential to implement effective process control in metal micro-droplet deposition manufacture.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Gao, A. Sonin, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 444, 533 (1994)
L.J. Zarzalejo, K.S. Schmaltz, C.H. Amon, Heat Mass Transf 34, 477 (1999)
J.P. Kruth, Ann. CIRP 40(2), 603 (1991)
M. Orme, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2(3), 399 (1993)
M. Orme, C. Huang, J. Courte. Miner. Metals Mater. Soc., Warren dale, PA, 125(1996)
M.E. Orme, C. Huang, J. Courter, At. Sprays 6, 305 (1996)
Q. Liu, M. Orem, J. Eng. Manuf. 215(10), 1333 (2001)
C.H. Amon, K.S. Schmaltz, R. Merz et al., J. Heat Transf. 118(1), 164 (1996)
M. Neagu, Technol. Mech. Eng. 5, 35 (2004)
J.D. Benrnardin, C.J. Stebbins, I. Mudawar, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 40(2), 247 (1997)
G.E. Cossali, M. Marengo, M. Santini, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 29, 167 (2008)
M. Pasandideh-Fard, S.D. Aziz, S. Chandra, J. Mostaghimi, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 22, 201 (2001)
N. Nikolopoulos, A. Theodorakakos, G. Bergeles, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 303 (2007)
G. Strotos, M. Gavaises, Andreas, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 45, 213 (2007)
J. Fukai, Y. Shiliba, Yanmaoto et al., Phys. Fluids 7, 236 (1995)
L.J. Zarzalejo, K.S. Schmaltz, C.H. Amon, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 34, 477 (1999)
S. Haferl, D. Poulikakos, J. Heat Mass Transf. 46, 535 (2003)
Y.P. Chao, L.H. Qi et al., China Mech Eng 20, 207 (2009)
M. Fang, S. Chandra, C.B. Park, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 129, 311 (2007)
C. Escure, M. Vardelle, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 23(2), 185 (2003)
J. Luo, L.H. Qi et al., Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 48, 289 (2008)
M. Fang, S. Chandra, C.B. Park, J. Heat Transf. 131, 112101 (2009)
X.S. Jiang, L.H. Qi, J. Luo, H. Huang, J.M. Zhou, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 49, 535 (2010)
V. Butty, D. Poulikakos, J. Giannakouros, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 23, 232 (2002)
S. Kamnis, S. Gu, T.J. Lu, C. Chen, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 165303 (2008)
R. Ghafouri-Azar, S. Shakeri, S. Chandra, J. Mostaghimi, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46, 1395 (2003)
Q. Xu, V.V. Gupta, E.J. Lavernia, Acta Mater. 48, 835 (2000)
B. Kang, J. Waldvogel, D. Poulikakos, J. Mater. Sci. 30, 4912 (1995)
R.K. Chin, J.L. Beuth, C.H. Amon, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 123, 623 (2001)
S. Alavi, M. Passandideh-Fard, Front. Heat Mass Transf. (FHMT) 2, 023007 (2011)
Y.Z. Zheng et al., Appl. Surf. Sci. 317, 526 (2014)
Acknowledgments
The research is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 31370944, the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi province (Grant 2014JQ7238), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant 2014M560764).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Wei, Z., Du, J. et al. The fusion process of successive droplets impinging onto a substrate surface. Appl. Phys. A 120, 35–42 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9146-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9146-8