Abstract
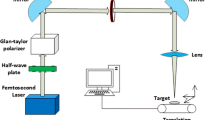
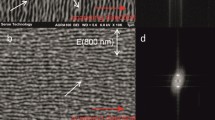
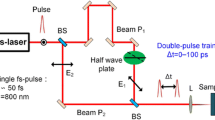
In this paper, the effect of the irradiation pulse number on the morphology of the near-wavelength ripples perpendicular to the laser polarization was investigated. The results show that the ripple spacing first fast decreases with the increased irradiation pulse number and finally reaches a stable value. The change of ripple morphology with different incidence angles was also studied. The ripples are found keeping always perpendicular to the laser polarization and have respective ripple spacings of 650, 480 and 390 nm upon the laser irradiation with pulse number N = 16 and fluence of 1.33 J/cm2 at the incidence angles of 0°, 30° and 60°. The change of the ripple spacing with different excitation levels was also studied. The theory for interference of the incident wave with the surface plasmon polariton wave (SPP) and the Sipe–Drude theory are both employed to analyze the experimental results. Detailed calculations show that the Sipe–Drude theory works better for explaining the main features of the ripples on silicon wafer surface. We suggest that the interaction of the incident wave with some form of surface electromagnetic wave except SPP is most possibly responsible for the ripple formation on silicon surface.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.R. Gattass, E. Mazur, Femtosecond laser micromachining in transparent materials. Nat. Photonics 2, 219 (2008)
J. Bonse, M. Munz, H. Sturm, Structure formation on the surface of indium phosphide irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 013538 (2005)
Y. Shimotsuma, P.G. Kazansky, J. Qiu, K. Hirao, Self-organized nanogratings in glass irradiated by ultrashort light pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 247405 (2003)
T.Q. Jia, H.X. Chen, M. Huang, F.L. Zhao, J.R. Qiu, R.X. Li, Z.Z. Xu, X.K. He, J. Zhang, H. Kuroda, Formation of nanogratings on the surface of a ZnSe crystal irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses. Phys. Rev. B 72, 125429 (2005)
Y. Liao, Y. Shen, L. Qiao, D. Chen, Y. Cheng, K. Sugioka, K. Midorikawa, Femtosecond laser nanostructuring in porous glass with sub-50 nm feature sizes. Opt. Lett. 38, 187 (2013)
Y. Kondo, T. Suzuki, H. Inouye, K. Miura, T. Mitsuyu, K. Hirao, Three-dimensional microscopic crystallization in photosensitive glass by femtosecond laser pulses at nonresonant wavelength. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 37, L94 (1998)
K. Miura, J. Qiu, T. Mitsuyu, K. Hirao, Space-selective growth of frequency-conversion crystals in glasses with ultrashort infrared laser pulses. Opt. Lett. 25, 408 (2000)
K. Miura, J. Qiu, S. Fujiwara, S. Sakaguchi, K. Hirao, Three-dimensional optical memory with rewriteable and ultrahigh density using the valence-state change of samarium ions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 2263–2265 (2002)
A.Y. Vorobyev, C. Guo, Colorizing metals with femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 041914 (2008)
M. Birnbaum, Semiconductor surface damage produced by ruby lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 36, 3688 (1965)
D. Dufft, A. Rosenfeld, S.K. Das, R. Grunwald, J. Bonse, Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures revisited: a comparative study on ZnO. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 034908 (2009)
F. Liang, R. Vallée, S.L. Chin, Mechanism of nanograting formation on the surface of fused silica. Opt. Express 20, 4389 (2012)
E.L. Gurevich, On the influence of surface plasmon-polariton waves on pattern formation upon laser ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 278, 52 (2013)
J. Bonse, A. Rosenfeld, J. Krüger, On the role of surface plasmon polaritons in the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of silicon by femtosecond laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 104910 (2009)
M. Huang, F. Zhao, Y. Cheng, N. Xu, Z. Xu, Origin of laser-induced near-subwavelength ripples: interference between surface plasmons and incident laser. ACS Nano 3, 4062 (2009)
Jörn Bonse, Jörg Krüger, Pulse number dependence of laser-induced periodic surface structures for femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 034903 (2010)
T.J.-Y. Derrien, T.E. Itina, R. Torres, T. Sarnet, M. Sentis, Possible surface plasmon polariton excitation under femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 083104 (2013)
K. Sokolowski-Tinten, D. von der Linde, Generation of dense electron-hole plasmas in silicon. Phys. Rev. B 61, 2643 (2000)
J.E. Sipe, J.F. Young, J.S. Preston, H.M. van Driel, Laser-induced periodic surface structure. I. Theory. Phys. Rev. B 27, 1141 (1983)
J. Bonse, M. Munz, H. Sturm, Structure formation on the surface of indium phosphide irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 013538 (2005)
S. Höhm, A. Rosenfeld, J. Krüger, J. Bonse, Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on silica. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 014901 (2012)
C. Zhang, J. Yao, C. Li, Q. Dai, S. Lan, V.A. Trofimov, T.M. Lysak, Asymmetric femtosecond laser ablation of silicon surface governed by the evolution of surface nanostructures. Opt. Express 21, 4439 (2013)
S. Höhm, M. Rohloff, A. Rosenfeld, J. Krüger, J. Bonse, Dynamics of the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures on dielectrics and semiconductors upon femtosecond, laser pulse irradiation sequences. Appl. Phys. A 110, 553 (2013)
Y. Han, S. Qu, The ripples and nanoparticles on silicon irradiated by femtosecond laser. Chem. Phys. Lett. 495, 241–244 (2010)
W. Han, L. Jiang, X. Li, P. Liu, L. Xu, Y. Lu, Continuous modulations of femtosecond laser induced periodic surface structures and scanned line-widths on silicon by polarization changes. Opt. Express 21, 15505 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors greatly appreciate the laser ablation experimental contributions from Junyi Ye. Thanks for the experimental conditions provided by the laboratory of ultrafast photonics of Shanghai University. Thanks for the AFM characterization help from Yan Jiang. Thanks for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61205128, 60908007, 11102075 and 51302111), the Research Foundation for Advanced Talents of Jiangsu University (No. 09JDG022) and Shanghai Municipal Natural Science Foundation (No. 13ZR1414800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Ye, J., Lin, X. et al. Discussion of the possible formation mechanism of near-wavelength ripples on silicon induced by femtosecond laser. Appl. Phys. A 118, 1119–1125 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8926-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8926-x