Abstract
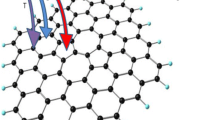
Using density functional theory combined with non-equilibrium Green’s function method, we have investigated the electronic and transport properties of graphenes defected by one and two carbon ad-dimers (CADs), placed parallel to the graphene lattice. Addition of these CADs to graphenes creates 3D paired pentagon–heptagon defects (3D-PPHDs). The band structure, density of states (DOS), quantum conductance, projected DOS, as well as the current–voltage characteristic per graphene super-cells containing each type of 3D-PPHD are calculated. The local strain introduced to graphene by 3D-PPHDs forces the C-bonds in the dimers to hybridize in sp 3-like rather than sp 2-like orbitals, creating localized states at the center of the corresponding defect below the Fermi energy. Simulations show that the zero-bias conductances per super-cells containing defects created by one and two CADs exhibit dip about ~0.579 and ~0.253 eV below their corresponding Fermi levels, respectively. These can be attributed to the localized states around the same energy levels. Simulations also show that the enhanced carriers scatterings within the graphenes defected by the 3D-PPHDs have increased their overall resistances, as compared with the pristine graphene. Moreover, the current–voltage characteristic calculated per super-cell for each case shows that the current for those containing one and two CADs, at an applied voltage of 0.5 V, is ~5 and 13 % less than the current calculated for the pristine super-cell of the same size.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S.V. Dubonos, I.V. Grigorieva, Science 306, 666–669 (2004)
S.M.M. Dubois, Z. Zanolli, X. Declerck, J.C. Charlier, Eur Phys. J. B. 72, 1–24 (2009)
A.V. Rozhkov, G. Giavaras, Y. Bliokh, V. Freilikher, F. Nori, Phys. Rep. 503, 77–114 (2011)
P. Avouris, Nano Lett. 10, 4285–4294 (2010)
A. Geim, K. Novoselov, Nat. Mater. 6, 183–191 (2007)
S. Adam, E.H. Hwang, V.M. Galitski, S. Das Sarma, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 18392–18397 (2007)
M.F. Craciun, S. Russo, M. Yamamoto, S. Tarucha, Nonotoday 6, 42–60 (2011)
M.I. Katsnelson, Materialstoday 10, 20–27 (2007)
L. Liao, J.W. Bai, Y.Q. Qu, Y. Huang, X.F. Duan, Nanotechnology 21, 015705 (2010)
M. Ishigami, J.H. Chen, W.G. Cullen, M.S. Fuhrer, E.D. Williams, Nano Lett. 7, 1643–1648 (2007)
H. Gao, Y. Xu, M. Li, Z. Guo, H. Chen, Z. Jin, B. Yu, Nanotechnology 22, 365202 (2011)
C. Tayran, Z. Zhu, M. Baldoni, D. Selli, G. Seifert, D. Tománek, Phys. Rev. lett. 110, 176805 (2013)
H. Zeng, J.P. Leburton, Y. Xu, J. Wei, Nanoscale Res Lett. 6, 254 (2011)
J. Ma, D. Alfè, A. Michaelides, E. Wang, Phys. Rev. B 80, 033407 (2009)
S. Bhowmick, U.V. Waghmare, Phys. Rev. B 81, 155416 (2010)
M.T. Lusk, D.T. Wu, L.D. Carr, Phys. Rev. B 81, 155444 (2010)
S. Fotoohi, M.K. Moravvej-Farshi, R. Faez, Appl. Phys. A (in press). doi:10.1007/s00339-013-8120-6
J.M. Soler, E. Artacho, J.D. Gale, A. Garc′ıa, J. Junquera, P. Ordej′on, D. S′anchez-Portal, J. Phys Condens Matter 14, 2745 (2002)
N. Troullier, J.L. Martins, Phys. Rev. B 43, 1993–2006 (1991)
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Phys. Rev Lett. 77, 3865 (1996)
C. Fiolhais, F. Nogueira, M. Marques, A primer in density functional theory (Springer, Heidelberg, 2003)
S. Datta, Quantum transport: atom to transistor (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2005)
D.J. Appelhans, Z. Lin, M.T. Lusk, Nanotechnology 23, 385704 (2012)
M. Brandbyge, J.L. Mozos, P. Ordejón, J. Taylor, K. Stokbro, Phys. Rev. B 65, 165401 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fotoohi, S., Moravvej-Farshi, M.K. & Faez, R. Electronic and transport properties of monolayer graphene defected by one and two carbon ad-dimers. Appl. Phys. A 116, 2057–2063 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8400-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8400-9