Abstract
By relying on the photonic immobilization technique of antibodies onto surfaces, we realized portable biosensors for light molecules based on the use of quartz crystal microbalances, given the linear dependence of the method on the laser pulse intensity. Here, we compare the quality of the anchoring method when using nanosecond (260 nm, 25 mJ/pulse, 5 ns, 10 Hz rep. rate) and femtosecond (258 nm, 25 μJ/pulse, 150 fs, 10 kHz rep. rate) laser source, delivering the same energy to the sample with the same average power. As a reference, we also tethered untreated antibodies by means of the passive adsorption. The results are striking: When the antibodies are irradiated with the femtosecond pulses, the deposition on the gold plate is much more ordered than in the other two cases. The effects of UV pulses irradiation onto the antibodies are also analyzed by measuring absorption and fluorescence and suggest the occurrence of remarkable degradation when nanosecond pulses are used likely induced by a larger thermal coupling. In view of the high average power required to activate the antibodies for the achievement of the photonic immobilization technique, we conclude that femtosecond rather than nanosecond laser pulses have to be used.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L. Arlett, E.B. Myers, M.L. Roukes, Nat. Nanotechnol. 6(4), 203–215 (2011)
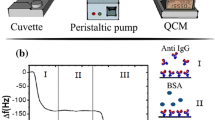
B. Della Ventura, L. Schiavo, C. Altucci, R. Esposito, R. Velotta, Biomed. Opt. Expr. 2(11), 3223–3231 (2011)
J. Cheng, G. Zhu, L. Wu, X. Du, H. Zhang, B. Wolfrum, Q. Jin, J. Zhao, A. Offenhäuser, Y. Xu, J. Neurosci. Methods 213(2), 196–203 (2013)
M.T. Neves-Petersen, T. Snabe, S. Klitgaard, M. Duroux, S.B. Petersen, Protein Sci. 15(2), 343–351 (2006)
R. Funari, B. Della Ventura, L. Schiavo, R. Esposito, C. Altucci, R. Velotta, Anal. Chem. 85, 6392–6397 (2013)
M.T. Neves-Petersen, Z. Gryczynski, Z. Fojan, S. Pedersen, E. Petersen, S.B. Petersen, Protein Sci. 11, 588–600 (2002)
C. Russmann, M. Beato, J. Stollhof, C. Weiss, R. Beigang, Nucl. Acid Res. 26, 3697 (1998)
C. Altucci, A. Nebbioso, R. Benedetti, R. Esposito, V. Carafa, M. Conte, M. Micciarelli, L. Altucci, R. Velotta, Laser Phys. Lett. 9, 234–239 (2012)
F. Caruso, E. Rodda, D.N. Furlong, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 178, 104–115 (1996)
J. Pribyl, M. Hepel, J. Halámek, P. Skládal, Sens. Actuators, B 91, 333–341 (2003)
R. Hao, D. Wang, X. Zhang, G. Zuo, H. Wei, R. Yang, Z. Zhang, Z. Cheng, Y. Guo, Z. Cui, Y. Zhou, Biosens. Bioelectron. 24, 1330–1335 (2009)
H. Sharma, R. Mutharasan, Anal. Chem. 85, 2472–2477 (2013)
G.L. Ellman, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 82, 70–77 (1959)
C. Davies, The immunoassay handbook (Stockton Press, New York, 1994)
P. Peluso, D.S. Wilson, D. Do, H. Tran, M. Venkatasubbaiah, D. Quincy, B. Heidecker, K. Poindexter, N. Tolani, M. Phelan, K. Witte, L.S. Jung, P. Wagner, S. Nock, Anal. Biochem. 312, 113–124 (2003)
P. Garidel, M. Hegyi, S. Bassarab, M. Weichel, Biotechnol. J. 3, 1201–1211 (2008)
C.A. Janeway Jr., P. Travers, M. Walport, and M.J. Schlomchiket, Immunobiology, Garland Science Ed. (2001)
J.R. Lakowicz, Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy, 3rd edn. (Springer, New York, 2006)
C. Consani, G. Auböck, F. van Mourik, M. Chergui, Science 339, 1586–1589 (2013)
J. Léonard, E. Portuondo-Campa, A. Cannizzo, F. Van Mourik, G. Van der Zwan, J. Tittor, S. Haacke, M. Chergui, Proc. Nat. Ac. Sci. 106, 7718–7723 (2009)
S.B. Hansen, Z. Radi¢, T.T. Talley, B.E. Molles, T. Deerinck, I. Tsigelny, P. Taylor, J. Biol. Chem. 277, 41299–41302 (2002)
J.R. Albani, J. Fluoresc. 19, 1061–1071 (2009)
Acknowledgments
Partial funding for this research was provided by the Italian Ministry for Research and Education through the Grant PON01_01517.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lettieri, S., Avitabile, A., Della Ventura, B. et al. Nano- and femtosecond UV laser pulses to immobilize biomolecules onto surfaces with preferential orientation. Appl. Phys. A 117, 185–190 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8340-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8340-4