Abstract
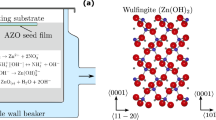
Well-controlled ZnO nanowire arrays have been synthesized using the hydrothermal method, a low temperature and low cost synthesis method. The process consists of two steps: the ZnO buffer layer deposition on the substrate by spin-coating and the growth of the ZnO nanowire array on the seed layer. We demonstrated that the microstructure and the morphology of the ZnO nanowire arrays can be significantly influenced by the main parameters of the hydrothermal method, such as pH value of the aqueous solution, growth time, and solution temperature during the ZnO nanowire growth. Scanning electron microscopy observations showed that the well oriented and homogeneous ZnO nanowire arrays can be obtained with the optimized synthesis parameters. Both x-ray diffraction spectra and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) observations revealed a preferred orientation of ZnO nanowires toward the c-axis of the hexagonal Wurtzite structure, and HRTEM images also showed an excellent monocrystallinity of the as-grown ZnO nanowires. For a deposition temperature of 90 °C, two growth stages have been identified during the growth process with the rates of 10 and 3 nm/min, respectively, at the beginning and the end of the nanowire growth. The ZnO nanowires obtained with the optimized growth parameters owning a high aspect ratio about 20. We noticed that the starting temperature of seed layer can seriously influence the nanowire growth morphology; two possible growth mechanisms have been proposed for the seed layer dipped in the solution at room temperature and at a high temperature, respectively.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.H. Zhao, Z.L. Wang, S.X. Mao, Nano Lett. 4, 587 (2004)
M.P. Lu, M.Y. Lu, L.J. Chen, Nano Energy 1, 247 (2012)
Q. Wan, Q.H. Li, Y.J. Chen, T.H. Wang, X.L. He, J.P. Li, C.L. Lin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 3654 (2004)
J.X. Wang, X.W.S, Y. Yang, H. Huang, Y.C. Lee, O.K. Tan, Nanotechnology 17, 4995 (2006)
T. Gao, T.H. Wang, Appl. Phys., A 80, 1451 (2005)
E. Comini, G. Faglia, M. Ferroni, G. Sberveglieri, Appl. Phys., A 88, 45 (2007)
Y. Lv, L. Guo, H. Xu, X. Chu, Physica E 36, 102 (2007)
E. Comini, C. Baratto, G. Faglia, M. Ferroni, G. Sberveglieri, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40, 7255 (2007)
M. Law, L.E. Greene, J.C. Johnson, R. Saykally, P. Yang, Nat. Mater. 4, 455 (2005)
J.B. Baxter, E.S. Aydil, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 053114 (2005)
Y. Sun, J.H. Seo, C.J. Takacs, J. Seifter, A.J. Heeger, Adv. Mater. 23, 1679 (2011)
Q. Simon, D. Barreca, D. Bekermann, A. Gasparotto, C. Maccato, E. Comini, V. Gombac, P. Fornasiero, O.I. Lebedev, S. Turner, A. Devi, R.A. Fischer, G. Van Tendeloo, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 36, 15527 (2011)
P.X. Gao, Z.L. Wang, J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 7534 (2004)
X. Wang, C.J. Summers, Z.L. Wang, Nano Lett. 4, 423 (2004)
P.X. Gao, Z.L. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2883 (2004)
C.L. Xu, D.H. Qin, H. Li, Y. Guo, T. Xu, H.L. Li, Mater. Lett. 58, 3976 (2004)
A. Umar, B. Karunagaran, E.-K. Suh, Y.B. Hahn, Nanotechnology 17, 4072 (2006)
X.M. Zhang, M.Y. Lu, Y. Zhang, L.J. Che, Z.L. Wang, Adv. Mater. 21, 2767 (2009)
Y. Sun, M.N.R. Ashfold, Nanotechnology 18, 245701 (2007)
S.J. Henley, M.N.R. Ashfold, D.P. Nicholls, P. Wheatley, D. Cherns, Appl. Phys. A, Mater. Sci. Process. 79, 1169 (2004)
A. Rahm, M. Lorenz, T. Nobis, G. Zimmermann, M. Grundmann, B. Fuhrmann, F. Syrowatka, Appl. Phys. A 88, 31 (2007)
M.J. Zheng, L.D. Zhang, G.H. Li, W.Z. Shen, Chem. Phys. Lett. 363, 123 (2002)
Y. Leprince-Wang, A. Yacoubi-Ouslim, G.Y. Wang, Microelectron. J. 36, 625 (2005)
C. Lévy-Clément, A. Katty, S. Bastide, F. Zenia, I. Mora, V. Munoz-Sanjose, Physica E 14, 229 (2002)
S. Yamabi, H. Imai, J. Mater. Chem. 12, 3773 (2002)
C.H. Bae, S.M. Park, S.E. Ahn, D.J. Oh, G.T. Kim, J.S. Ha, Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 1758 (2006)
G. Kenanakis, N. Katsarakis, Appl. Catal. A, Gen. 378, 227 (2010)
L.E. Greene, M. Law, J. Goldberger, F. Kim, J.C. Johnson, Y. Zhang, R.J. Saykally, P. Yang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 42, 3031 (2003)
L. Vayssieres, Adv. Mater. 15, 464 (2003)
J. Wang, L. Gao, Solid State Commun. 132, 269 (2004)
M. Guo, P. Diao, S. Cai, J. Solid State Chem. 178, 1864 (2005)
Y. Wang, Y.H. Li, Z.Z. Zhou, X.H. Zu, Y.L. Deng, J. Nanopart. Res. 13, 5193 (2011)
K. Laurent, T. Brouri, M. Capo-Chichi, D.P. Yu, Y. Leprince-Wang, J. Appl. Phys. 110, 094310 (2011)
D. Vernardou, G. Kenanakis, S. Couris, E. Koudoumas, E. Kymakis, N. Kastarakis, Thin Solid Films 515, 8764 (2007)
J.M. Jang, S.D. Kim, H.M. Choi, J.Y. Kim, W.G. Jung, Mater. Chem. Phys. 113, 389 (2009)
Z. Zhu, D. Yang, H. Liu, Adv. Powder Technol. 22, 493 (2011)
K. Laurent, B.Q. Wang, D.P. Yu, Y. Leprince-Wang, Thin Solid Films 517, 617 (2008)
B. Postels, H.-H. Wehmann, A. Bakin, M. Kreye, D. Fuhrmann, J. Blaesing, A. Hangleiter, A. Krost, A. Waag, Nanotechnology 18, 195602 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chevalier-César, C., Capochichi-Gnambodoe, M. & Leprince-Wang, Y. Growth mechanism studies of ZnO nanowire arrays via hydrothermal method. Appl. Phys. A 115, 953–960 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7908-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7908-8