Abstract
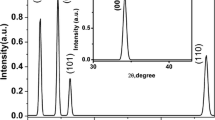
GaN nanoparticles were prepared on sapphire (0001) substrates with ZnO sacrificial layers by self assembly of Ga2O3 films in their reaction with NH3. ZnO sacrificial layers with different thicknesses and Ga2O3 films were deposited on sapphire substrates in turn by a radio frequency (RF) magnetron sputtering system. Nitridation of the Ga2O3 films was then carried out in a quartz tube furnace. The effect of ZnO sacrificial layer thickness on the structure and optical properties of nanoparticles prepared by RF magnetron sputtering were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and photoluminescence (PL). GaN nanoparticles with ZnO sacrificial layers of different thicknesses possess hexagonal wurtzite crystal structure and have a preferred orientation with c axis perpendicular to the sapphire substrates. XRD, SEM, and AFM results reveal that the better-crystallinity, uniform, and well-dispersed GaN nanoparticles (∼30 nm) without agglomeration were obtained with a ZnO sacrificial layer 300-nm thick. The PL result reveals that the optical properties of the GaN nanoparticles are improved with a ZnO sacrificial layer 300-nm thick. Therefore, we suggest that a ZnO sacrificial layer 300-nm thick is the most suitable condition for obtaining better-quality GaN nanoparticles with good luminescence performance. Moreover, the mechanism of the formation of GaN nanoparticles with ZnO sacrificial layers is also discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Nakamura, Science 281, 956 (1998)
Y. Azuma, M. Shimada, K. Okuyama, Chem. Vap. Depos. 10, 11 (2004)
J.F. Janik, R.L. Wells, Chem. Mater. 8, 2708 (1996)
J.L. Coffer, M.A. Johnson, L. Zhang, R.L. Wells, Chem. Mater. 9, 2671 (1997)
Y. Yang, V.J. Leppert, S.H. Risbud, B. Twamley, P.P. Power, H.W.H. Lee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, 2262 (1999)
Y. Yang, C. Tran, V. Leppert, S.H. Risbud, Mater. Lett. 43, 240 (2000)
O.I. Mićić, S.P. Arhenkiel, D. Bertram, A.J. Nozik, Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 478 (1999)
F. Hamdani, A. Botchkarev, W. Kim, M. Yeadon, J.M. Gibson, S.-C.Y. Tsen, D.J. Smith, D.C. Reynolds, D.C. Look, K. Evans, C.W. Litton, W.C. Mitchel, P. Hemenger, Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 467 (1997)
L. Cui, H.-Y. Zhang, G.-G. Wang, F.-X. Yang, X.-P. Kuang, R. Sun, J.-C. Han, Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 2479 (2012)
Y. Li, C.S. Xue, C.M. Wang, H.C. Li, Y.W. Ren, Rare Met. 22, 221 (2003)
J.P. Zheng, H.S. Kwok, Thin Solid Films 232, 99 (1993)
T. Ogino, M. Aoki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 19, 2395 (1980)
D.M. Hofmann, D. Kovalev, G. Steude, B.K. Meyer, A. Hoffmann, L. Eckey, R. Heitz, T. Detchprom, H. Amano, I. Akasaki, Phys. Rev. B 52, 16702 (1995)
E.R. Glaser, T.A. Kennedy, K. Doverspike, L.B. Rowland, D.K. Gaskill, J.A. Freitas Jr., M.A. Khan, D.T. Olson, J.N. Kuznia, D.K. Wickenden, Phys. Rev. B 51, 13326 (1995)
S. Christiansen, M. Albrecht, W. Dorsch, H.P. Strunk, MRS Internet J. Nitride Semicond. Res. 1, U136 (1996)
P.T. Hsieh, Y.C. Chen, K.S. Kao, C.M. Wang, Physica B 403, 178 (2008)
C.N.R. Rao, F.L. Deepak, F.L. Deepak, G. Gundiah, A. Govindaraj, Prog. Solid State Chem. 31, 5 (2003)
V. Darakchieva, J. Birch, P.P. Paskov, S. Tungasmita, T. Paskova, B. Monemar, Phys. Status Solidi A 190, 59 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 50902028 and 51172054), the International Sino-Russian Science & Technology Cooperation Program (Grant No. 2009DFR50350), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 9451805707003351), the Basic Research Plan Program of Shenzhen City (Grant No. JC200903120169A), and the Natural Scientific Research Innovation Foundation in Harbin Institute of Technology (Grant No. HIT.NSFIR.2011123).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, L., Zhang, HY., Wang, GG. et al. Effect of ZnO sacrificial layer thickness on the structure and optical properties of GaN nanoparticles prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Appl. Phys. A 113, 161–166 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7506-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7506-1