Abstract
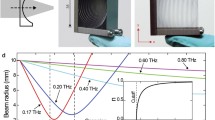
Optical devices for the terahertz wave band are being developed now and require better designs. This paper proposes an artificial dielectric lens with metallic corrugated structures for the terahertz wave band. A periodic analysis model extracted from the full model by assuming periodicity confirms the phase delay, which produces the focusing effect. Full model analysis also confirms the focusing effect. The full model analysis also confirms that the focusing length is longer as the spacing of corrugated baffles is wider. The focusing length is longer the metallic groove width is wider. The focusing length is longer as the groove depth is shallower. The lens shape without grooves does not produce the focusing effect. The results of the full model analysis are qualitatively consistent with those of the periodic model ones. This implies that the design for an exact size lens is possible by using the periodic model.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.E. Kock, Metallic delay lenses. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27(1), 58–82 (1948)
S.S.D. Jones, J. Brown, Metallic delay lenses. Nature 163, 324–325 (1949)
J. Brown, The design of metallic delay dielectrics. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng., Part 3, Radio Commun. Eng. 97(45), 45–48 (1950)
S.B. Cohn, Microwave measurements on metallic delay media. Proc. IRE 41(9), 1177–1183 (1953)
J. Brown, W. Jackson, The relative permittivity of tetragonal arrays of perfectly conducting thin discs. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng., Part 3, Radio Commun. Eng. 102(1), 37–42 (1955)
W.E. Kock, Metal-lens antennas. Proc. IRE 34(11), 828–836 (1946)
N.I. Landy, S. Sajuyigbe, J.J. Mock, D.R. Smith, W.J. Padilla, Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 207402-1–207402-4 (2008)
H. Tao, N.I. Landy, C.M. Bingham, X. Zhang, R.D. Averitt, W.J. Padilla, A metamaterial absorber for the terahertz regime: design, fabrication and characterization. Opt. Express 16(10), 7181–7188 (2008)
H. Tao, C.M. Bingham, A.C. Strikwerda, D. Pilon, D. Shrekenhamer, N.I. Landy, K. Fan, X. Zhang, W.J. Padilla, R.D. Averitt, Highly flexible wide angle of incidence terahertz metamaterial absorber: design, fabrication, and characterization. Phys. Rev. B 78, 241103-1–241103-4 (2008)
N.I. Landy, C.M. Bingham, T. Tyler, N. Jokerst, D.R. Smith, W.J. Padilla, Design, theory, and measurement of a polarization-insensitive absorber for terahertz imaging. Phys. Rev. B 79, 125104-1–125104-6 (2009)
H.-T. Chen, J. Zhou, J.F. O’Hara, F. Chen, A.K. Azad, A.J. Taylor, Antireflection coating using metamaterials and identification of its mechanism. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 073901-1–073901-4 (2010)
M. Choi, S.H. Lee, Y. Kim, S.B. Kang, J. Shin, M.H. Kwak, K.-Y. Kang, Y.-H. Lee, N. Park, B. Min, A terahertz metamaterial with unnaturally high refractive index. Nature 470, 369–374 (2011)
F. Miyamaru, M.W. Takeda, K. Taima, Characterization of terahertz metamaterials fabricated on flexible plastic films: toward fabrication of bulk metamaterials in terahertz region. Appl. Phys. Express 2, 042001-1–042001-3 (2009)
F. Miyamaru, S. Kubota, K. Taima, K. Takano, M. Hangyo, M.W. Takeda, Three-dimensional bulk metamaterials operating in the terahertz range. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 081105-1–081105-3 (2010)
J. Shin, J.-T. Shen, P.B. Catrysse, S. Fan, Cut-through metal slit array as an anisotropic metamaterial film. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 12(6), 1116–1122 (2006)
K. Akiyama, K. Takano, Y. Abe, Y. Tokuda, M. Hangyo, Optical transmission anomalies in a double-layered metallic slit array. Opt. Express 18(17), 17876–17882 (2010)
K. Sato, K. Sudo, J. Hirokawa, M. Ando, Analysis of slot coupling in a corrugated radial waveguide, in 2005 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP 2005), WB1-3, 3–5 August, vol. 1 (2005), pp. 3–5
K. Sakakibara, J. Hirokawa, M. Ando, N. Goto, Periodic boundary condition for evaluation of external mutual couplings in a slotted waveguide array. IEICE Trans. Commun. E 79-B(8), 1156–1164 (1996)
C.A. Balanis, Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, 3rd edn. (Wiley, New York, 2005). Sect. 4.7.1
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by the Strategic Information and Communications R&D Promotion Programme (SCOPE) from the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas “Electromagnetic Metamaterial” (No. 23109505) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan, the Takayanagi Memorial Foundation, the Yazaki Memorial Foundation for Science & Technology, and the Iketani Science and Technology Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konno, T., Suzuki, T., Young, J.C. et al. Proposal and analysis of artificial dielectric lens with metallic corrugated structures for terahertz wave band. Appl. Phys. A 109, 1103–1108 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7394-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7394-4