Abstract
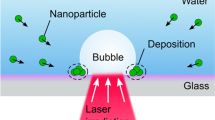
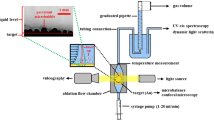
This work is aimed at an analysis of the influence on the efficiency of nanoparticle production of a cavitation bubble (CB), which forms during the laser ablation process in high-fluence regime. The CB is produced on an Au metal target immersed in water by 1064 nm ps Nd:YAG laser pulses at different fluences. Its time–space evolution is monitored by a shadowgraphic set-up, while the Au nanoparticles production rate is tagged by the growth of the plasmon resonance, which is detected by measuring shot-by-shot the UV-Vis absorbance. We analyze the dependence of bubble size on the experimental parameters. Our results appear of interest to enhance the nanoparticle production efficiency in a liquid medium.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.K. Jain, K.S. Lee, M.A. El-Sayed, J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 7238 (2006)
A. Kumar, P. Kumar Vemula, P.M. Ajayan, J. John, Nat. Mater. 7, 236 (2008)
M. Alloisio, A. Demartini, C. Cuniberti, G. Dellepiane, S. Jadhav, S. Thea, E. Giorgetti, C. Gellini, M.J. Muniz-Miranda, Phys. Chem. C 113, 19475 (2009)
C. Loo, A. Lowery, N. Halas, J. West, R. Drezek, Nano Lett. 5, 709 (2005)
V. Amendola, M. Meneghetti, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 3805 (2009)
C.E. Brennen, Cavitation Bubble Dynamics (Oxford University Press, London, 1995)
K. Sugioka, M. Meunier, A. Piqué, Laser Precision Microfabrication (Springer, Berlin, 2010)
F. Giammanco, E. Giorgetti, P. Marsili, A. Giusti, J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 3354 (2010)
F. Mafune, J. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow, J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 9111 (2000)
J. Noack, D.X. Hammer, G.D. Noojin, B.A. Rockwell, A. Vogel, J. Appl. Phys. 83, 7489 (1998)
F. Mafune, J.y. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow, J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 4218 (2003)
W.T. Nichols, T. Sasaki, N. Koshizaki, J. Appl. Phys. 100, 114912 (2006)
P.B. Johnson, R.W. Christy, Phys. Rev. B 6, 4370 (1972)
Acknowledgements
Funding from the project NABLA (Decree n. 4508-September 1, 2010 by Regione Toscana-Italy, PAR FAS 2007–2013 funds, Action 1.1.a.3) and PRIN2009 “Novel plasmon-based processes and materials for sensor applications” of the Italian Ministry of Research is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiberi, M., Simonelli, A., Cristoforetti, G. et al. Effect of picosecond laser induced cavitation bubbles generated on Au targets in a nanoparticle production set-up. Appl. Phys. A 110, 857–861 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7165-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-7165-2