Abstract
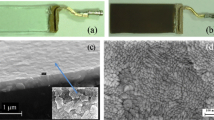
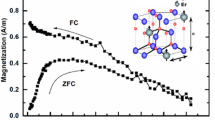
We report variable temperature resistivity measurements and mechanisms related to electrical conduction in 200 keV Ni2+ ion implanted ZnO thin films deposited by vapor phase transport. The dc electrical resistivity versus temperature curves show that all polycrystalline ZnO films are semiconducting in nature. In the room temperature range they exhibit band conduction and conduction due to thermionic emission of electrons from grain boundaries present in the polycrystalline films. In the low temperature range, nearest neighbor hopping (NNH) and variable range hopping (VRH) conduction are observed. The detailed conduction mechanism of these films and the effects of grain boundary (GB) barriers on the electrical conduction process are discussed. An attempt is made to correlate electrical conduction behavior and previously observed room temperature ferromagnetism of these films.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.A. Kröger, The Chemistry of Imperfect Crystals, 2nd edn. (North Holland, Amsterdam, 1974)
W.D. Kingery, H.K. Bowen, D.R. Uhlmann, Introduction to Ceramics (Wiley, New York, 1976), Chap. 4
J.W. Orton, M.J. Powell, Rep. Prog. Phys. 43, 1263 (1980)
L.L. Kazmerski, Polycrystalline and Amorphous Thin Films & Devices (Academic Press, New York, 1980)
Y. Natsume, H. Sakata, T. Hirayama, H. Yanagida, J. Appl. Phys. 72, 4202 (1992)
A.P. Roth, D.F. Williams, J. Appl. Phys. 52, 6686 (1981)
R.L. Petritz, Phys. Rev. 104, 1508 (1956)
Y. Natsume, H. Sakata, Thin Solid Films 372, 30 (2000)
B. Pandey, S. Ghosh, P. Srivastava, P. Kumar, D. Kanjilal, J. Appl. Phys. 105, 033909 (2009)
B. Pandey, S. Ghosh, P. Srivastava, D. Kanjilal, P. Kumar, S. Zhou, H. Schmidt, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 023901 (2010)
R. Kumar, N. Khare, Thin Solid Films 516, 1302 (2008)
J.Y.W. Seto, J. Appl. Phys. 46, 5247 (1975)
J. Han, M. Shen, W. Cao, A.M.R. Senos, P.Q. Mantas, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 67 (2003)
A. Miller, E. Abrahams, Phys. Rev. 120, 745 (1960)
S. Bandyopadhyay, G.K. Paul, R. Roy, S.K. Sen, S. Sen, Mater. Chem. Phys. 74, 83 (2002)
Y.Z. Yoo, T. Fukumura, Z. Jin, K. Hasegawa, M. Kawasaki, P. Ahmet, T. Chikyow, H. Koinuma, J. Appl. Phys. 90, 4246 (2001)
O.D. Jayakumar, I.K. Gopalakrishnan, S.K. Kulshreshtha, J. Mater. Chem. 15, 3514 (2005)
F.A. Padovani, R. Stratton, Solid-State Electron. 9, 695 (1966)
C.R. Crowell, V.L. Rideout, Solid-State Electron. 12, 89 (1969)
A. Hausmann, W. Teuerle, Z. Phys. 257, 299 (1972)
D.C. Reynolds, C.W. Litton, T.C. Collins, Phys. Status Solidi 12, 3 (1965)
A.R. Hutson, J. Appl. Phys. 32, 2287 (1961)
N.F. Mott, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1, 1 (1968)
W. Yu, L.H. Yang, X.Y. Teng, J.C. Zhang, L. Zhang, G.S. Fu, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 093901 (2008)
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Dr. Neeraj Khare, IIT Delhi for various important discussions. One of the authors (B. Joshi) gratefully acknowledges the financial support from Department of Science and Technology (DST) and University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, B., Ghosh, S., Srivastava, P. et al. Correlation between electrical transport, microstructure and room temperature ferromagnetism in 200 keV Ni2+ ion implanted zinc oxide (ZnO) thin films. Appl. Phys. A 107, 393–400 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-6785-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-6785-x