Abstract
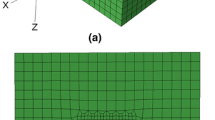
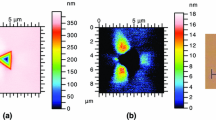
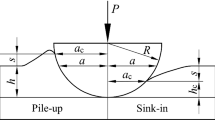
We studied single-crystal copper of three different crystallographic orientations [(100), (011) and (111)] for nanoindentation response via a numerical simulation model using spherical indenters of radius (R) 3.4 μm and 10 μm. The model uses rate-independent crystal plasticity with a finite strain implemented as a user routine in the commercial finite element software ABAQUS. The model takes into account active crystallographic slip, orientation effects during nanoindentation computation, and the effect of friction between the indenter and copper substrate. We compared the load–displacement curve and indentation pile-up patterns obtained from the simulations with experimental measurements available in the literature. The indentation load and mean effective pressure beneath the indenter p m were found to be highest for (111) orientation and lowest for (100). The simulation and experimental data agree well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Broese Van Groenou, S.E. Kadijk, Slip patterns made by sphere indentations on single crystal MnZn ferrite. Acta Metall. 37(10), 2613–2624 (1989)
Y.Y. Lim, M.M. Chaudhri, The influence of grain size on the indentation hardness of high-purity copper and aluminium. Philos. Mag., A, Phys. Condens. Matter Struct. Defects Mech. Prop. 82(10), 2071–2080 (2002)
J.D. Kiely, J.E. Houston, Nanomechanical properties of Au (111), (001), and (110) surfaces. Phys. Rev. B, Condens. Matter 57(19), 12588–12594 (1998)
M.Y. Khan, L.M. Brown, M.M. Chaudhri, Effect of crystal orientation on the indentation cracking and hardness of MgO single crystals. J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys. 25(1A), A257–A265 (1992)
N.A. Stelmashenko, M.G. Walls, L.M. Brown, Yu.V. Milman, Microindentations on W and Mo oriented single crystals: an STM study. Acta Metall. Mater. 41(10), 2855–2865 (1993)
K.W. McElhaney, J.J. Vlassak, W.D. Nix, Determination of indenter tip geometry and indentation contact area for depth-sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 13(5), 1300–1306 (1998)
W.D. Nix, H. Gao, Indentation size effects in crystalline materials: a law for strain gradient plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46(3), 411–425 (1998)
S. Qu, Y. Huang, G.M. Pharr, K.C. Hwang, The indentation size effect in the spherical indentation of iridium: A study via the conventional theory of mechanism-based strain gradient plasticity. Int. J. Plast. 22(7), 1265–1286 (2006)
R. Komanduri, N. Chandrasekaran, L.M. Raff, MD simulation of indentation and scratching of single crystal aluminum. Wear 240(1–2), 113–143 (2000)
T. Tsuru, Y. Shibutani, Anisotropic effects in elastic and incipient plastic deformation under (001), (110), and (111) nanoindentation of Al and Cu. Phys. Rev. B, Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 75(3), 35415 (2007)
T. Zhu, J. Li, K.J. Van Vliet, S. Ogata, S. Yip, S. Suresh, Predictive modeling of nanoindentation-induced homogeneous dislocation nucleation in copper. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 52(3), 691–724 (2004)
M.C. Fivel, C.F. Robertson, G.R. Canova, L. Boulanger, Three-dimensional modeling of indent-induced plastic zone at a mesoscale. Acta Mater. 46(17), 6183–6194 (1998)
Y. Liu, S. Varghese, J. Ma, M. Yoshino, H. Lu, R. Komanduri, Orientation effects in nanoindentation of single crystal copper. Int. J. Plast. 24(11), 1990–2015 (2008)
D.G. Rickerby, N.H. Macmillan, The hardness of cubic single crystals by spherical indentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. 40(2), 251–259 (1979)
D. Peirce, R.J. Asaro, A. Needleman, Material rate dependence and localized deformation in crystalline solids. Acta Metall. 31(12), 1951–1976 (1983)
D. Peirce, R.J. Asaro, A. Needleman, An analysis of nonuniform and localized deformation in ductile single crystals. Acta Metall. 30(6), 1087–1119 (1982)
L. Anand, M. Kothari, A computational procedure for rate-independent crystal plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 44(4), 525–558 (1996)
C. Miehe, J. Schroder, Comparative study of stress update algorithms for rate-independent and rate-dependent crystal plasticity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 50(2), 273–298 (2001)
J. Alcala, D. Esque-De Los Ojos, Reassessing spherical indentation: Contact regimes and mechanical property extractions. Int. J. Solids Struct. 47, 2714–2732 (2010)
Y. Liu, B. Wang, M. Yoshino, S. Roy, H. Lu, R. Komanduri, Combined numerical simulation and nanoindentation for determining mechanical properties of single crystal copper at mesoscale. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 53(12), 2718–2741 (2005)
F.B. Foss, R.C. Brumfield, Some measurements of the shape of Brunel ball indentation. ASTM Spec. Tech. Publ. 22, 312 (1922)
O. Casals, J. Alcala, The duality in mechanical property extractions from Vickers and Berkovich instrumented indentation experiments. Acta Mater. 53(13), 3545–3561 (2005)
M. Mata, O. Casals, J. Alcala, The plastic zone size in indentation experiments: The analogy with the expansion of a spherical cavity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43(20), 5994–6013 (2006)
D.F. Bahr, D.E. Kramer, W.W. Gerberich, Non-linear deformation mechanisms during nanoindentation. Acta Mater. 46(10), 3605–3617 (1998)
Y. Wang, D. Raabe, C. Kluber, F. Roters, Orientation dependence of nanoindentation pile-up patterns and of nanoindentation microtextures in copper single crystals. Acta Mater. 52(8), 2229–2238 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narayanan, K.R., Subbiah, S. & Sridhar, I. Indentation response of single-crystal copper using rate-independent crystal plasticity. Appl. Phys. A 105, 453–461 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-011-6618-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-011-6618-3