Abstract
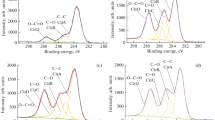
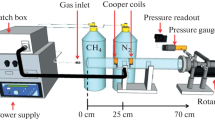
This paper aims to provide an analysis of the correlation between various plasma effects on polymers exposed to atmospheric pressure plasma. The relationship linking the surface polarity, the chemical structure and composition and the crystalline/amorphous phase contribution in the surface modification mechanisms of plasma-exposed polymers is explored. Different polymers were chosen comprising of various structures, functionality, degree of oxidation, crystallinity, and were treated under a particular experimental configuration, and dielectric barrier discharge-type. The plasma parameters and the treatment settings are observed, in relation to relevant surface properties, as surface energy components, surface topography, structural changes and chemical composition, under conditions where the gaseous environment chosen, He-N2, allows complex surface modification, by combined functionalisation and crosslinking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. D’Agostino, Plasma Deposition, Treatment, and Etching of Polymers (Academic, San Diego, 1990)
M. Strobel, C.S. Lyons, K.L. Mittal (Eds.), Plasma surface Modification of Polymers: Relevance to Adhesion (VSP, Zeist, 1995)
N. Inagaki, Plasma Surface Modification and Plasma Polymerization (Technomic, Basel, 1996)
F.S. Denes, S. Manolache, Prog. Polym. Sci. 29, 815 (2004)
J.M. Grace, L.J. Gerenser, J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 24, 305 (2003)
G. Borcia, A. Chiper, I. Rusu, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 15, 849 (2006)
F. Massines, A. Rabehi, P. Decomps, R. Ben Gadri, P. Segur, C. Mayoux, J. Appl. Phys. 83, 2950 (1998)
D.T. Clark, A. Dilks, J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 16, 911 (1978)
G. Placinta, F. Arefi-Khonsari, M. Gheorghiu, J. Amouroux, G. Popa, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 66, 1367 (1997)
A. Meyer-Plath, K. Schröder, B. Finke, A. Ohl, Vacuum 71, 391 (2003)
V. Gauvreau, P. Chevallier, K. Vallières, E. Petitclerc, R. Gaudreault, G. Laroche, Bioconjugate Chem. 15, 1146 (2004)
P.H. Hermans, A. Weidinger, Makromol. Chem. 24, 44 (1961)
R.A. Fava (Ed.), Methods of Experimental Physics: Polymers (Academic, New York, 1973)
H.P. Klug, L.E. Alexander, X-ray Difraction Procedure for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials (Wiley, New York, 1954)
G. Beamson, D. Briggs, High Resolution XPS of Organic Polymers: The Scienta ESCA300 Database (Wiley, Chichester, 1992)
N. Dumitrascu, G. Borcia, N. Apetroaei, G. Popa, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 11, 127 (2002)
R.H. Hansen, H. Schonhorn, J. Polym. Sci. B 4, 203 (1966)
R. Hussain, D. Mohammad, Turk. J. Chem 28, 725 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
81.65.-b; 81.05.-t; 52.77.-j
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borcia, C., Borcia, G. & Dumitrascu, N. Relating plasma surface modification to polymer characteristics. Appl. Phys. A 90, 507–515 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-4313-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-4313-1