Abstract
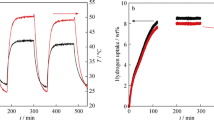
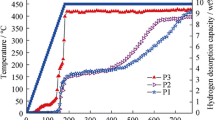
LiBH4 possesses a high hydrogen content, and though it is highly stable, its restoration from LiH+B+H2 can only be accomplished under unacceptable high temperature and pressure conditions (650 °C and 15 MPa). Recently, it has been reported that destabilizing LiBH4 by, i.e., MgH2, transition metal oxides and chlorides presents a promising approach to exert its potential for hydrogen storage. In the present study, we find that simple mechanical milling with Al in a mole ratio of 2:1, markedly improves the reversible dehydrogenation performance of LiBH4. The system possesses a theoretical capacity of 8.5 wt. % and could be reversibly operated at 400–450 °C. The combined property and phase examinations suggest that the observed property improvement should be associated with the formation of AlB2 in the dehydriding process. Further cyclic examination found that the system suffered from a serious capacity loss in the dehydriding/rehydriding cycles. A better understanding of the degradation mechanism may provide a means for further material property improvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Schüth, B. Bogdanović, M. Felderhoff, Chem. Commun. 2249 (2004)
A. Züttel, S. Rentsch, P. Fischer, P. Wenger, P. Sudan, P. Mauron, C. Emmenegger, J. Alloys Compd. 356–357, 515 (2003)
M. Au, A. Jurgensen, J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 7062 (2006)
Y. Nakamori, S. Orimo, J. Alloys Compd. 370, 271 (2004)
S. Orimo, Y. Nakamori, G. Kitahara, K. Miwa, N. Ohba, S. Towata, A. Zuttel, J. Alloys Compd. 404–406, 427 (2005)
K. Miwa, N. Ohba, S. Towata, Y. Nakamori, S. Orimo, Phys. Rev. B 69, 245120 (2004)
J. Vajo, L. Skeith, J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 3719 (2005)
I. Barin, Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 1988)
J.W. Jang, J.H. Shim, Y.W. Cho, B.J. Lee, J. Alloys Compd. 420, 286 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
81.05.Zx; 84.60.Ve; 82.30.-b; 82.33.Pt; 82.65.+r
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, XD., Wang, P., Ma, LP. et al. Reversible hydrogen storage in LiBH4 destabilized by milling with Al. Appl. Phys. A 89, 963–966 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-4198-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-4198-z