Abstract
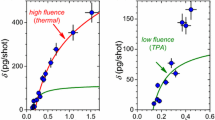
We show that the mechanism of nanoparticle formation during femtosecond laser ablation of silicon is affected by the presence of a background gas. Femtosecond laser ablation of silicon in a H2 or H2S background gas yields a mixture of crystalline and amorphous nanoparticles. The crystalline nanoparticles form via a thermal mechanism of nucleation and growth. The amorphous material has smaller features and forms at a higher cooling rate than the crystalline nanoparticles. The background gas also results in the suspension of plume material in the gas for extended periods, resulting in the formation (on a thin film carbon substrate) of unusual aggregated structures including nanoscale webs that span tears in the film. The presence of a background gas provides additional control of the structure and composition of the nanoparticles during short pulse laser ablation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Cavalleri, K. Sokolowski-Tinten, J. Bialkowski, M. Schreiner, D. von der Linde, J. Appl. Phys. 85, 3301 (1999)
D. von der Linde, K. Sokolowski-Tinten, Appl. Surf. Sci. 154, 1 (2000)
T.E. Glover, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 20, 125 (2003)
S. Amoruso, R. Bruzzese, N. Spinelli, R. Velotta, M. Vitiello, X. Wang, G. Ausanio, V. Iannotti, L. Lanotte, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 4502 (2004)
A.V. Bulgakov, I. Ozerov, W. Marine, Appl. Phys. A 79, 1591 (2004)
T.E. Glover, G.D. Ackerman, R.W. Lee, D.A. Young, Appl. Phys. B 78, 995 (2004)
D.B. Williams, C.B. Carter, Transmission Electron Microscopy (Plenum, New York, 1996)
Y. Shao, F. Spaepen, D. Turnbull, Metall. Trans. A 29, 1825 (1998)
Y.W. Kim, H.M. Lin, T.F. Kelly, Acta Metall. 37, 247 (1989)
P.V. Evans, G. Devaud, T.F. Kelly, Y.W. Kim, Acta Metall. Mater. 38, 719 (1990)
M.O. Thompson, J.W. Mayer, A.G. Cullis, H.C. Webber, N.G. Chew, J.M. Poate, D.C. Jacobson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 50, 896 (1983)
P.L. Liu, R. Yen, N. Bloembergen, R.T. Hodgson, Appl. Phys. Lett. 34, 864 (1979)
P.H. Bucksbaum, J. Bokor, Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 182 (1984)
G. Devaud, D. Turnbull, Appl. Phys. Lett. 46, 844 (1985)
C.G. Granqvist, R.A. Buhrman, J. Appl. Phys. 47, 2200 (1976)
J. Soderlund, L.B. Kiss, G.A. Niklasson, C.G. Granqvist, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2386 (1998)
L.B. Kiss, J. Soderlund, G.A. Niklasson, C.G. Granqvist, Nanostruct. Mater. 12, 327 (1999)
M. Wilkinson, B. Mehlig, Europhys. Lett. 71, 186 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
81.16.-c
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tull, B., Carey, J., Sheehy, M. et al. Formation of silicon nanoparticles and web-like aggregates by femtosecond laser ablation in a background gas. Appl. Phys. A 83, 341–346 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-006-3502-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-006-3502-7