Abstract.
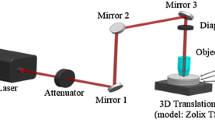
Hybrid laser processing for the precision microfabrication of glass materials, in which the interaction of a conventional pulsed laser beam and a medium on the material surface leads to effective ablation and modification, is reviewed. A major role of the medium is to produce strong absorption of the conventional laser beam by the material. Simultaneous irradiation by a vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) laser beam that possesses an extremely small laser fluence and an ultraviolet (UV) laser greatly improves the ablation quality and modification efficiency for fused silica (VUV-UV multiwavelength excitation process). The metal plasma generated by the laser beam effectively assists high-quality ablation of transparent materials by the same laser beam, resulting in microstructuring, cutting, color marking, printing, and selective metallization of glass materials (laser-induced plasma-assisted ablation (LIPAA)). The detailed discussion presented here includes the ablation mechanism of hybrid laser processing.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 December 2002 / Accepted: 20 January 2003 / Published online: 28 May 2003
RID="*"
ID="*"Corresponding author. Fax: +81-48/462-4682, E-mail: ksugioka@postman.riken.go.jp
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugioka, K., Obata, K., Hong, M. et al. Hybrid laser processing for microfabrication of glass . Appl Phys A 77, 251–257 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-003-2116-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-003-2116-6