Abstract
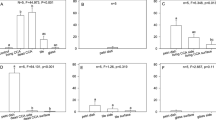
Settlement preferences of Pocillopora damicornis larvae were examined on artificial substrata. Planulation of P. damicornis followed a lunar cycle and the release of larvae occurred after new moon. P. damicornis larvae had the highest rates of settlement within 3 days of being presented settlement substrata. Cumulative settlement gradually increased from 3 to 8 days, and post-settlement mortality was most frequent after 8 days. Settlement experiments showed greatest settlement preference to cement tiles containing 10% coral rubble. This study suggests that physical cues are important in the settlement process, which may be useful for coral reef rehabilitation projects.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babcock R, Mundy C (1996) Coral recruitment: consequences of settlement choice for early growth and survivorship in two scleractinians. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 206:179–201
Baird AH, Morse ANC (2004) Induction of metamorphosis in larvae of the brooding corals Acropora palifera and Stylophora pistillata. Mar Freshw Res 55:469–472
Bartlett MS (1937) Some examples of statistical methods of research in agriculture and applied biology. J Roy Stat Soc Suppl 4:137–170
Clark S, Edwards AJ (1994) Use of artificial reef structures to rehabilitate reef flats degraded by coral mining in the Maldives. Bull Mar Sci 55:724–744
Daume S, Krsinich A, Farrell S, Gervis M (2000) Settlement, early growth and survival of Haliotis rubra in response to different algal species. J Appl Phycol 12:479–488
Dobretsov S, Qian PY (2004) The role of epibotic bacteria from the surface of the soft coral Dendronephthya sp. in the inhibition of larval settlement. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 299:35–50
Fan TY, Li JJ, Ie SX, Fang LS (2002) Lunar periodicity of larval release by pocilloporid corals in southern Taiwan. Zool Stud 41:288–294
Field S (1998) Settlement biology of larvae of Montipora verrucosa and Porites lobata in Hawaii. In: Cox EF, Krupp DA, Jokiel PL (eds) Reproduction in reef corals: Results of the 1997 Edwin W Pauley Summer Program in Marine Biology. Hawaii Institute of Marine Biology, Technical Report No 42, pp 111–119
Gleason DF, Edmunds PJ, Gates RD (2006) Ultraviolet radiation effects on the behavior and recruitment of larvae from the reef coral Porites astreoides. Mar Biol 148:503–512
Goh BPL (1991) Mortality and settlement success of Pocillopora damicornis planula larvae during recovery from low levels of nickel. Pac Sci 45:276–286
Harriott VJ, Fisk DA (1987) A comparison of settlement plate types for experiments on the recruitment of scleractinian corals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 37:201–208
Heyward AJ, Negri AP (1999) Natural inducers for coral larval metamorphosis. Coral Reefs 18:273–279
Hunte W, Wittenberg M (1992) Effects of eutrophication and sedimentation on juvenile corals. Mar Biol 114:625–631
Keough MJ, Downes BJ (1982) Recruitment of marine invertebrates: the role of active larval choices and early mortality. Oecologia 54:348–352
Kitamura M, Koyama T, Nakano Y, Uemura D (2007) Characterization of a natural inducer of coral larval metamorphosis. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 340:96–102
Kuffner IB, Paul VJ (2004) Effects of the benthic cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula on larval recruitment of the reef coral Acropora surculosa and Pocillopora damicornis. Coral Reefs 23:455–458
Lewis JB (1974) The settlement behavior of planulae larvae of the hermatypic coral Favia fragum (Esper). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 15:165–172
Maida M, Sammarco PW, Coll JC (1995) Effects of soft corals on scleractinian coral recruitment. I: directional allelopathy and inhibition of settlement. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 121:191–202
Morse DE, Morse ANC (1991) Enzymatic characterization of the morphogen recognized by Agaricia humilis (scleractinian coral) larvae. Biol Bull 181:104–122
Morse ANC, Iwao K, Baba M, Shimoike K, Hayashibara T, Omori M (1996) An ancient chemosensory mechanism brings new life to coral reefs. Biol Bull 191:149–154
Norström AV, Lokrantz J, Nyström M, Yap HT (2006) Influence of dead coral substrate morphology on patterns of juvenile coral distribution. Mar Biol 150:1145–1152
Oren U, Benayahu Y (1997) Transplantation of juvenile corals: a new approach for enhancing colonization of artificial reefs. Mar Biol 127:499–505
Palaki A (1998) The effect of salinity on fertilization and larval survivorship and settlement in Fungia scutaria and Pocillopora damicornis. In: Cox EF, Krupp DA, Jokiel PL (eds) Reproduction in reef corals: results of the 1997 Edwin W Pauley Summer Program in Marine Biology. Hawaii Institute of Marine Biology, Technical Report No 42, pp 68–77
Petersen D, Laterveer M, Schuhmacher H (2005a) Innovative substrate tiles to spatially control larval settlement in coral culture. Mar Biol 146:937–942
Petersen D, Laterveer M, Schuhmacher H (2005b) Spatial and temporal variation in larval settlement of reefbuildling corals in mariculture. Aquaculture 249:317–327
Stephenson TA (1931) Development and the formation of colonies in Pocillopora and Porites. Part I. Scientific Reports, Great Barrier Reef Expedition 1928–29, vol III. No. 3 British Museum (Natural History), London, pp 113–134
Tomascik T (1991) Settlement patterns of Caribbean scleractinian corals on artificial substrata along an eutrophication gradient, Barbados, West Indies. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 77:261–269
Vaughan TW (1959) Rearing coral colonies from coral planulae. In: Needham G (ed) Culture methods for invertebrate animals. Dover Publications Inc., New York, pp 145–147
Webster NS, Smith LD, Heyward AJ, Watts JEM, Webb RI, Blackall LL, Negri AP (2004) Metamorphosis of a scleractinian coral in response to microbial biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1213–1221
Wilson J (1998) The effect of temperature on settlement patterns of Pocillopora damicornis in Hawaii. In: Cox EF, Krupp DA, Jokiel PL (eds) Reproduction in reef corals: results of the 1997 Edwin W Pauley Summer Program in Marine Biology. Hawaii Institute of Marine Biology, Technical Report No 42, pp 89–97
Wilson JR, Harrison PL (1998) Settlement-competency periods of larvae of three species of scleractinian corals. Mar Biol 131:339–345
Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical analysis, 4th edn. Prentice-Hall International, New Jersey
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Sin Tsai Min and staff from Tropical Marine Science Institute for invaluable assistance in the research work, and Angie Seow for field assistance. We also thank Shaifudin, and the two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments. This research was partially funded by the NIE/NTU AcRF Grant (RP 5/02 GPL), Natural Sciences and Science Education at National Institute of Education, Nanyang Technological University, held by the corresponding author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Environment Editor Prof. Rob van Woesik
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C.S., Walford, J. & Goh, B.P.L. Adding coral rubble to substrata enhances settlement of Pocillopora damicornis larvae. Coral Reefs 28, 529–533 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-009-0467-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-009-0467-y