Abstract
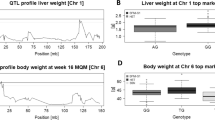
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of chronic liver disease in the western world, with spectrum from simple steatosis to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, which can progress to cirrhosis. NAFLD developments are known to be affected by host genetic background. Herein we emphasize the power of collaborative cross (CC) mouse for dissecting this complex trait and revealing quantitative trait loci (QTL) controlling hepatic fat accumulation in mice. 168 female and 338 male mice from 24 and 37 CC lines, respectively, of 18–20 weeks old, maintained on standard rodent diet, since weaning. Hepatic fat content was assessed, using dual DEXA scan in the liver. Using the available high-density genotype markers of the CC line, QTL mapping associated with percentage liver fat accumulation was performed. Our results revealed significant fatty liver accumulation QTL that were specifically, mapped in females. Two significant QTLs on chromosomes 17 and 18, with genomic intervals 3 and 2 Mb, respectively, were mapped. A third QTL, with a less significant P value, was mapped to chromosome 4, with genomic interval of 2 Mb. These QTLs were named Flal1–Flal3, referring to Fatty Liver Accumulation Locus 1–3, for the QTLs on chromosomes 17, 18, and 4, respectively. Unfortunately, no QTL was mapped with males. Searching the mouse genome database suggested several candidate genes involved in hepatic fat accumulation. Our results show that susceptibility to hepatic fat accumulations is a complex trait, controlled by multiple genetic factors in female mice, but not in male.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J, Sanderson SO, Lindor KD, Feldstein A et al (2005) The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 129:113–121
Aylor DL, Valdar W, Foulds-Mathes W, Buus RJ, Verdugo RA, Baric RS et al (2011) Genetic analysis of complex traits in the emerging collaborative cross. Genome Res 21:1213–1222
Baba M, Imai T, Nishimura M, Kakizaki M, Takagi S, Hieshima K et al (1997) Identification of CCR6, the specific receptor for a novel lymphocyte-directed CC chemokine LARC. J Biol Chem 272:14893–14898
Beck JA, Lloyd S, Hafezparast M, Lennon-Pierce M, Eppig JT, Festing MF et al (2000) Genealogies of mouse inbred strains. Nat Genet 24:23–25
Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC et al (2004) Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 40:1387–1395
Caldwell SH, Oelsner DH, Iezzoni JC, Hespenheide EE, Battle EH, Driscoll CJ (1999) Cryptogenic cirrhosis: clinical characterization and risk factors for underlying disease. Hepatology 29:664–669
Chalasani N, Guo X, Loomba R, Goodarzi MO, Haritunians T, Kwon S et al (2010) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis clinical research network. Genome-wide association study identifies variants associated with histologic features of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 139:1567–1576
Charlton M (2004) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a review of current understanding and future impact. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:1048–1058
Charlton MR, Burns JM, Pedersen RA, Watt KD, Heimbach JK, Dierkhising RA (2011) Frequency and outcomes of liver transplantation for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in the United States. Gastroenterology 141:1249–1253
Chatzikyriakidou A, Voulgari PV, Lambropoulos A, Georgiou I, Drosos AA (2013) Validation of the TAGAP rs212389 polymorphism in rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Jt Bone Spine 80:543–544
Chen R, Stahl EA, Kurreeman FA, Gregersen PK, Siminovitch KA, Worthington J et al (2011) Fine mapping the TAGAP risk locus in rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun 12:314–318
Cheverud JM, Ehrich TH, Hrbek T, Kenney JP, Pletscher LS, Semenkovich CF (2004) Quantitative trait loci for obesity- and diabetes-related traits and their dietary responses to high-fat feeding in LGXSM recombinant inbred mouse strains. Diabetes 53:3328–3336
Churchill GA, Airey DC, Allayee H, Angel JM, Attie AD, Beatty J et al (2004) The collaborative cross, a community resource for the genetic analysis of complex traits. Nat Genet 36:1133–1137
Cusi K (2012) Role of obesity and lipotoxicity in the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Gastroenterology 142:711–725
Deruytter N, Boulard O, Garchon HJ (2004) Mapping non-class II H2-linked loci for type 1 diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Diabetes 53:3323–3327
Durrant C, Tayem H, Yalcin B, Cleak J, Goodstadt L, de Villena FP et al (2011) Collaborative cross mice and their power to map host susceptibility to Aspergillus fumigatus infection. Genome Res 21:1239–1248
Ekstedt M, Franzén LE, Mathiesen UL, Thorelius L, Holmqvist M, Bodemar G et al (2006) Long-term follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes. Hepatology 44:865–873
Eyre S, Hinks A, Bowes J, Flynn E, Martin P, Wilson AG et al (2010) Overlapping genetic susceptibility variants between three autoimmune disorders: rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes and coeliac disease. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R175
Hollis-Moffatt JE, Hook SM, Merriman TR (2005) Colocalization of mouse autoimmune diabetes loci Idd21.1 and Idd21.2 with IDDM6 (human) and Iddm3 (rat). Diabetes 54:2820–2825
Iraqi FA, Churchill G, Mott R (2008) The collaborative cross, developing a resource for mammalian systems genetics: a status report of the Wellcome Trust cohort. Mamm Genome 19:379–381
Iraqi FA, Mahajne M, Salaymeh A, Sandovsky H, Tayem H, Vered K et al (2012) The genome architecture of the collaborative cross mouse genetic reference population. Genetics 190:389–401
Iraqi FA, Athamni H, Dorman A, Salymah Y, Tomlinson I, Nashif A et al (2014) Heritability and coefficient of genetic variation analyses of phenotypic traits provide strong basis for high-resolution QTL mapping in the collaborative cross mouse genetic reference population. Mamm Genome 25:109–119
Ishimori N, Li R, Kelmenson PM, Korstanje R, Walsh KA, Churchill GA et al (2004) Quantitative trait loci that determine plasma lipids and obesity in C57BL/6J and 129S1/SvImJ inbred mice. J Lipid Res 45:1624–1632
Keane TM, Goodstadt L, Danecek P, White MA, Wong K, Yalcin B et al (2011) Mouse genomic variation and its effect on phenotypes and gene regulation. Nature 477:289–294
Larter CZ, Chitturi S, Heydet D, Farrell GC (2010) A fresh look at NASH pathogenesis. Part 1: the metabolic movers. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:672–690
Lee IH, Dinudom A, Sanchez-Perez A, Kumar S, Cook DI (2007) Akt mediates the effect of insulin on epithelial sodium channels by inhibiting Nedd4-2. J Biol Chem 282:29866–29873
Loomba R, Abraham M, Unalp A, Wilson L, Lavine J, Doo E et al (2012) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis clinical research network. Association between diabetes, family history of diabetes, and risk of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis. Hepatology 56:943–951
Masuoka HC, Chalasani N (2013) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an emerging threat to obese and diabetic individuals. Ann NY Acad Sci 1281:106–122
Mott R, Talbot CJ, Turri MG, Collins AC, Flint J (2000) A method for fine mapping quantitative trait loci in outbred animal stocks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12649–12654
Philip VM, Sokoloff G, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Striz M, Branstetter L, Beckmann MA et al (2011) Genetic analysis in the collaborative cross breeding population. Genome Res 21:1223–1238
Ratziu V, Poynard T (2006) Assessing the outcome of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis? It’s time to get serious. Hepatology 44:802–805
Romeo S, Kozlitina J, Xing C, Pertsemlidis A, Cox D, Pennacchio LA et al (2008) Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Genet 40:1461–1465
Targher G, Bertolini L, Padovani R, Rodella S, Zoppini G, Zenari L et al (2006) Relations between carotid artery wall thickness and liver histology in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Care 29:1325–1330
Valenti L, Al-Serri A, Daly AK, Galmozzi E, Rametta R, Dongiovanni P et al (2010) Homozygosity for the patatin-like phospholipase-3/adiponutrin I148M polymorphism influences liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 51:1209–1217
Vardi P, Alkalai KS, Sprecher E, Koren I, Zadik Z, Sabbah M et al (2007) Components of the metabolic syndrome (MTS), hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance in obese Israeli children and adolescents. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev 1:97–103
Vered K, Durrant C, Mott R, Iraqi FA (2014) Susceptibility to Klebsiella pneumonaie infection in collaborative cross mice is a complex trait controlled by at least three loci acting at different time points. BMC Genom 15:865
Vernon G, Baranova A, Younossi ZM (2011) Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 34:274–285
Welsh CE, Miller DR, Manly KF, Wang J, McMillan L, Morahan G et al (2012) Status and access to the collaborative cross population. Mamm Genome 23:706–712
Yang H, Ding Y, Hutchins LN, Szatkiewicz J, Bell TA, Paigen BJ et al (2009) A customized and versatile high-density genotyping array for the mouse. Nat Methods 6:663–666
Zhang F, Liang Z, Matsuki N, Van Kaer L, Joyce S, Wakeland EK et al (2003) A murine locus on chromosome 18 controls NKT cell homeostasis and Th cell differentiation. J Immunol 171:4613–4620
Acknowledgments
The present work is part of a Ph.D. thesis by Hanifa J. Atamni theses. The authors declare no competing financial interests or other associations that might pose a conflict of interest (e.g., pharmaceutical stock ownership, consultancy). This work was supported by the Hendrech and EiranGotwert Fund for studying diabetes, Wellcome Trust grants 085906/Z/08/Z, 075491/Z/04, Wellcome Trust core funding grant 090532/Z/09/Z, and core funding by Tel Aviv University. This work was supported by the Israeli Centers of Research Excellence (I-CORE): Center No. 41/11 (MB, I.G-V) and a fellowship from the Edmond J. Safra Center for Bioinformatics at Tel Aviv University (MB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest with respect to financial or non-financial competing interests, the authorship, and/or publication of this article, e.g., pharmaceutical stock ownership and consultancy.
Additional information
H. J. A. -T. Atamni and M. Botzman have equal contribution.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atamni, H.J.AT., Botzman, M., Mott, R. et al. Mapping liver fat female-dependent quantitative trait loci in collaborative cross mice. Mamm Genome 27, 565–573 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-016-9658-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-016-9658-3