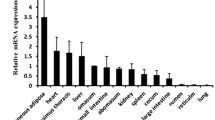
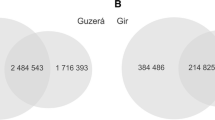
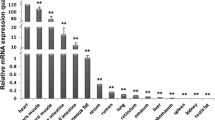
Abstract
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) represents the mammalian form of the core component of a kinase cascade that is conserved between fungi, plants, and animals. AMPK plays a major role in protecting mammalian cells from metabolic stress by switching off biosynthetic pathways that require ATP and switching on ATP-regenerating pathways. In this report, we describe the isolation and characterization of the gene for the noncatalytic bovine γ1 subunit of AMPK. The bovine ampkγ1 (PRKAG1) gene spans in excess of 14 kb and is located at BTA 5q21–q22. It consists of 12 exons ranging in size from 38 b to 166 b, interspersed with 11 introns that range between 97 b and 6753 b in length. The coding region of the bovine gene shares 93% and 90% nucleotide sequence similarity with its human and rat counterparts, and the bovine AMPKγ1 protein is 98% and 95% identical to its human and rat homologs, respectively, in amino acid sequence. SNP discovery using a cattle DNA panel revealed a number of polymorphisms that may be useful for the evaluation of ampkγ1 as a candidate gene for energy metabolism-related production traits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Bateman (1997) ArticleTitleThe structure of a domain common to archaebacteria and the homocystinuria disease protein Trends Biochem Sci 22 12–13
BF Benkel Y Fong (1996) ArticleTitleLong range-inverse PCR: extending the useful range of inverse PCR Genet Anal Biomol Eng 13 23–127
N Bierne SA Lehnert E Bedier F Bonhomme SS Moore (2000) ArticleTitleScreening for intron-length polymorphisms in penaeid shrimps using exon-primed intron-crossing (EPIC)-PCR Mol Ecol 9 233–235
E Blair C Redwood H Ashrafian M Oliveira J Broxholme et al. (2001) ArticleTitleMutations in the gamma2 subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase cause familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: evidence for the central role of energy compromise in disease pathogenesis Hum Mol Genet 10 1215–1220
JL Celenza FJ Eng M Carlson (1989) ArticleTitleMolecular analysis of the SNF4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Evidence for physical association of the SNF4 protein with the SNF1 protein kinase Mol Cell Biol 9 5045–5054
PC Cheung IP Salt SP Davies DG Hardie D Carling (2000) ArticleTitleCharacterization of AMP-activated protein kinase gamma-subunit isoforms and their role in AMP binding Biochem J 346 659–669
P Chomczynski N Sacchi (1987) ArticleTitleSingle-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction Anal Biochem 162 156–159
T Daniel D Carling (2002) ArticleTitleFunctional analysis of mutations in the gamma2 subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase associated with cardiac hypertrophy and Wolff–parkinson–White Syndrome J Biol Chem 277 51017–51024
XG da Silva I Leclerc IP Salt B Doiron DG Hardie et al. (2000) ArticleTitleRole of AMP-activated protein kinase in the regulation by glucose of islet beta cell gene expression Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97 4023–4028
TA Hall (1999) ArticleTitleBioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41 95–98
DG Hardie D Carling (1997) ArticleTitleThe AMP-activated protein kinase—fuel gauge of the mammalian cell? Eur J Biochem 246 259–273
DG Hardie D Carling M Carlson (1998) ArticleTitleThe AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinase subfamily: Metabolic sensors of the eukaryotic cell? Annu Rev Biochem 67 821–855
F Jeanmougin JD Thompson M Gouy DG Higgins TJ Gibson (1998) ArticleTitleMultiple sequence alignment with Clustal X Trends Biochem Sci 23 403–405
JA Lenstra JAF Boxiel Particlevan KA Zwaagstra M Schwerin (1993) ArticleTitleShort interspersed nuclear element (SINE) sequences of the Bovidae Anim Genet 24 33–39
HS Malik TH Eickbush (1998) ArticleTitleThe RTE class of non-LTR retrotransposons is widely distributed in animals and is the origin of many SINEs Mol Biol Evol 15 1123–1134
SD McKay SN White SR Kata R Loan JE Womack (2003) ArticleTitleThe bovine 5′AMPK gene family: mapping and single nucleotide polymorphism detection Mamm Genome 14 853–858
D Milan J-T Jeon C Looft V Amarger A Robic et al. (2000) ArticleTitleA mutation in PRKAG3 associated with excess glycogen content in pig skeletal muscle Science 288 1248–1251
GA Rutter XG da Silva I Leclerc (2003) ArticleTitleRoles of 5′AMP-activated kinase in mammalian glucose homeostasis Biochemical J 375 1–16
N Saitou M Nei (1987) ArticleTitleThe neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees Mol Biol Evol 4 406–425
A Sazanov BF Benkel DA Hickey S Kollers R Fries (1999) ArticleTitleThe bovine AMP-activated protein kinase subunit gamma 1 gene (PRKAG1) maps to 5q21–q22 Anim Genet 30 473–474
D Stapleton E Woollatt KI Mitchelhill JK Nicholl CS Fernandez et al. (1997) ArticleTitleAMP-activated protein kinase isoenzyme family: subunit structure and chromosomal location FEBS Lett 409 452–456
J Szemraj G Plucienniczak J Jaworski A Plucienniczak (1995) ArticleTitleBovine Alu-like sequences mediate transposition of a new site-specific retroelement Gene 153 261–264
Y Peer ParticleVan de R Wachter ParticleDe (1993) ArticleTitleTREECON: a software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees Comput Applic Biosci 9 177–182
J Weekes SA Hawley J Corton D Shugar DG Hardie (1994) ArticleTitleActivation of rat liver AMP-activated protein kinase by kinase kinase in a purified, reconstituted system. Effects of AMP and AMP analogues Eur J Biochem 219 751–757
A Wierinckx D Mercier A Oulmouden JM Petit R Julien (1999) ArticleTitleComplete genomic organization of futb encoding a bovine alpha 3-fucosyltransferase: exons in human orthologous genes emerged from ancestral intronic sequences Mol Biol Evol 16 1535–1547
A Woods D Azzout–Marniche M Foretz SC Stein P Lemarchand et al. (2000) ArticleTitleCharacterization of the role of AMP-activated protein kinase in the regulation of glucose-activated gene expression using constitutively active and dominant negative forms of the kinase Mol Cell Biol 20 6704–6711
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Mr. Y. Fong, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Centre for Food and Animal Research, Ottawa, Canada, in the cloning of the bovine ampkγ1 gene.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abbreviations:
ampk - gene, cDNA, or mRNA coding for AMPK; AMPK - AMP-activated protein kinase; AMP - adenosine 3′, 5′-monophosphate; ATP - adenosine 3′ 5′-triphosphate; b - base(s); kb - kilobase(s) or 1000 b; CBS - cystathionine β-synthase domain; PCR - polymerase chain reaction; RTase - reverse transcriptase; SNP - single nucleotide polymorphism.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benkel, B., Kollers, S., Fries, R. et al. Characterization of the bovine ampkγ1 gene. Mamm Genome 16, 194–200 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-004-2426-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-004-2426-9