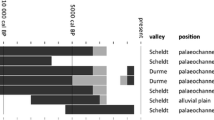
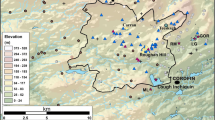
Abstract
Sediments from the small lake Ilsø situated in the Illerup/Alken Enge Valley were studied in order to investigate past landscape development at the time of a probably ritual human mass burial following battle during the Roman Iron Age (ad 1–400). A pollen record from Ilsø and a number of other records from Jutland were combined using the Landscape Reconstruction Algorithm to reconstruct local vegetation changes through the last 2,800 years. These methods were supplemented by studies of catchment-related geochemistry of the Ilsø lake sediments. The results show a marked reforestation event associated with a strong decrease in erosion levels at the very beginning of the first century ad, contemporaneous with the finds of human remains at Alken Enge. Comparison with a pollen record 10 km away and with those from other sites, reveals that this reforestation occurs unusually early and rapidly, and is an unparalleled development in a Danish context. We suggest that the major landscape changes at the beginning of the Roman Iron Age and forest cover for the next few centuries comprise a possible example of ritual control of local land-use.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaby B (1986a) Trees as anthropogenic indicators in regional pollen diagrams from eastern Denmark. In: Behre K-E (ed) Anthropogenic Indicators in Pollen Diagrams. Balkema, Amsterdam, pp 73–93
Aaby B (1986b) Mennesket og naturen på Abkæregnen gennem 6000 år. Sønderjysk Månedsskrift 1986:277–290
Abraham V, Kozáková R (2012) Relative pollen productivity estimates in the modern agricultural landscape of Central Bohemia (Czech Republic). Rev Palaeobot Palynol 179:1–12
Andersen H (1959) Voldsom død. Skalk 1959:8–9
Andersen ST (1979) Identification of wild grass and cereal pollen. Danmarks Geologiske Undersøgelse, Årbog 1978:69–92
Andersen ST (1989) Natural and cultural landscapes since the Ice Age shown by pollen analysis from small hollows in a forested area in Denmark. J Dan Archaeol 8:188–199
Andersen ST (1995) Pollenanalyser fra Ovesø. Geol Surv Den Kunderapport 1995–12:36–55
Barbour MM, Roden JS, Farquhar GD, Ehleringer JR (2004) Expressing leaf water and cellulose oxygen isotope ratios as enrichment above source water reveals evidence of a Péclet effect. Oecologia 138:426–435
Benedictow OJ (2004) The black death 1346–1353: the complete history. Boydell Press, Woodbridge
Bennett KD (1996) Determination of the number of zones in a biostratigraphical sequence. New Phytol 132:155–170
Bennett KD (2015) Manual for psimpoll and pscomb. http://www.chrono.qub.ac.uk/psimpoll/psimpoll_manual/4.27/psimpoll.htm. Accessed 29 July 2015
Bronk Ramsey C (2013) OxCal version 4.2.4. https://c14.arch.ox.ac.uk. Accessed 25 May 2015
Broström A, Nielsen AB, Gaillard MJ, Hjelle K, Mazier F, Binney H, Bunting J, Fyfe R, Meltsov V, Poska A, Räsänen S, Soepboer W, Von Stedingk H, Suutari H, Sugita S (2008) Pollen productivity estimates of key European plant taxa for quantitative reconstruction of past vegetation: a review. Veget Hist Archaeobot 17:461–478
Church M, Slaymaker O (1989) Disequilibrium of Holocene sediment yield in glaciated British Columbia. Nature 337:452–454
Heyng AM, Mayr C, Lücke A, Wissel H, Striewski B (2014) Late Holocene hydrologic changes in northern New Zealand inferred from stable isotope values of aquatic cellulose in sediments from Lake Pupuke. J Paleolimnol 51:485–497
Ilkjær J (1991) Illerup Ådal 1–2: die Lanzen und Speere. Jysk Arkæol Selsk Skr 25:1–404
Kylander ME, Ampel L, Wohlfarth B, Veres D (2011) High-resolution X-ray fluorescence core scanning analysis of Les Echets (France) sedimentary sequence: new insights from chemical proxies. J Quat Sci 26:109–117
Lowemark L, Chen HF, Yang TN, Kylander M, Yu EF, Hsu YW, Lee TQ, Song SR, Jarvis S (2011) Normalizing XRF-scanner data: a cautionary note on the interpretation of high-resolution records from organic-rich lakes. J Asian Earth Sci 40:1250–1256
Mayr C, Lücke A, Wagner S, Wissel H, Ohlendorf C, Haberzettl T, Oehlerich M, Schäbitz F, Wille M, Zhu J, Zolitschka B (2013) Intensified southern hemisphere westerlies regulated atmospheric CO2- during the last glaciation. Geology 41:831–834
Mazier F, Gaillard MJ, Kuneš P, Sugita S, Trondman AK, Broström A (2012) Testing the effect of site selection and parameter setting on REVEALS-model estimates of plant abundance using the Czech Quaternary Palynological Database. Rev Palaeobot Palynol 187:38–49
Meyers PA, Teranes JL (2001) Sediment Organic Matter. In: Last WM, Smol JP (eds) Tracking environmental change using lake sediments: physical and geochemical methods, vol 2. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 239–269
Mingram J, Negendank JF, Brauer A, Berger D, Hendrich A, Köhler M, Usinger H (2007) Long cores from small lakes—recovering up to 100 m-long lake sediment sequences with a high-precision rod-operated piston corer (Usinger-corer). J Paleolimnol 37:517–528
Nesbitt HW, Markovics G, Price RC (1980) Chemical processes affecting alkalis and alkaline earths during continental weathering. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 44:1659–1666
Nielsen AB, Odgaard BV (2010) Quantitative landscape dynamics in Denmark through the last three millennia based on the Landscape Reconstruction Algorithm approach. Veget Hist Archaeobot 19:375–387
Nielsen AB, Giesecke T, Teuerkauf M, Feeser I, Behre KE, Beug HJ, Chen SH, Christiansen J, Dörfler W, Endtmann E, Jahns S, De Klerk P, Kühl N, Latałowa M, Odgaard BV, Rasmussen P, Stockholm JR, Voigt R, Wiethold J, Wolters S (2012) Quantitative reconstructions of changes in regional openness in north-central Europe reveal new insights into old questions. Quat Sci Rev 47:131–149
Odgaard BV (1993) The sedimentary record of spheroidal carbonaceous fly-ash particles in shallow Danish lakes. J Paleolimnol 8:171–187
Odgaard BV (1994) The holocene vegetation history of northern west Jutland, Denmark. Opera Bot 123:1–171
Odgaard B (1999a) Pollenanalytiske undersøgelser 1998. Pollenanalyser fra Dallerup Sø, Østjylland. Danmarks og Grønlands Geologiske Undersøgelse Rapport 1999/14:1–10
Odgaard BV (1999b) Fossil pollen as a record of past biodiversity. J Biogeogr 26:7–17
Odgaard BV (2000) Fra skov til hede: Vegetationens historie i Ulfborg herred. In: Dalsgaard K (ed) Mellem hav og hede. Aarhus University Press, Aarhus, pp 28–35
Odgaard BV, Rasmussen P (2000) Origin and temporal development of macro-scale vegetation patterns in the cultural landscape of Denmark. J Ecol 88:733–748
Pawlowsky-Glahn V, Egozcue JJ (2006) Compositional data and their analysis: an introduction. In: Buccianti A, Meteu-Figueras G, Pawlowsky-Glahn V (eds) Compositional data analysis in the geosciences: from theory to practice, vol 264. Geological Society Special Publication. Geological Society, London, pp 1–10
Pienitz R, Smol JP (1993) Diatom assemblages and their relationship to environmental variables in lakes from the boreal forest-tundra ecotone near Yellowknife, Northwest Territories, Canada. Hydrobiologia 269–270:391–404
Rasmussen P (2005) Mid- to late-Holocene land-use change and lake development at Dallund Sø, Denmark: vegetation and landuse history inferred from pollen data. Holocene 15:1116–1129
Reimer PJ, Bard E, Bayliss A et al (2013) IntCal13 and Marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0–50,000 years cal bp. Radiocarbon 55:1869–1887
Renberg I, Hansson H (2008) The HTH sediment corer. J Paleolimnol 40:655–659
Snowball I, Sandgren P, Petterson G (1999) The mineral magnetic properties of an annually laminated Holocene lake-sediment sequence in northern Sweden. Holocene 9:353–362
Sugita S (1993) A model of pollen source area for an entire lake surface. Quat Res 39:239–244
Sugita S (2007a) Theory of quantitative reconstruction of vegetation. I: pollen from large sites REVEALS regional vegetation composition. Holocene 17:229–241
Sugita S (2007b) Theory of quantitative reconstruction of vegetation. II: all you need is LOVE. Holocene 17:243–257
Sugita S, Parshall T, Calcote R, Walker K (2010) Testing the Landscape Reconstruction Algorithm for spatially explicit reconstruction of vegetation in northern Michigan and Wisconsin. Quat Res 74:289–300
Talbot MR (2001) Nitrogen isotopes in palaeolimnology. In: Last WM, Smol JP (eds) Tracking environmental change using lake sediments: physical and geochemical methods, vol 2. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 401–439
Ter Braak CJF, Šmilauer P (2012) Canoco reference manual and user’s guide: software for ordination, version 5.0. Microcomputer Power, Ithaca, USA
Weltje GJ, Tjallingii R (2008) Calibration of XRF core scanners for quantitative geochemical logging of sediment cores: theory and application. Earth Planet Sci Lett 274:423–438
Wissel H, Mayr C, Lücke A (2008) A new approach for the isolation of cellulose from aquatic plant tissue and freshwater sediments for stable isotope analysis. Org Geochem 39:1545–1561
Wolfe BB, Edwards TW (1997) Hydrologic control on the oxygen-isotope relation between sediment cellulose and lake water, western Taimyr Peninsula, Russia: implications for the use of surface-sediment calibrations in paleolimnology. J Paleolimnol 18:283–291
Wolfe BB, Edwards TW, Aravena R, Forman SL, Warner BG, Velichko AA, MacDonald GM (2000) Holocene paleohydrology and paleoclimate at treeline, north-central Russia, inferred from oxygen isotope records in lake sediment cellulose. Quat Res 53:319–329
Wolfe BB, Edwards TW, Elgood RJ, Beuning KR (2001) Carbon and oxygen isotope analysis of lake sediment cellulose: methods and applications. In: Last WM, Smol JP (eds) Tracking environmental change using lake sediments: physical and geochemical methods, vol 2. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 373–400
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by The Carlsberg Foundation (2012_01_0495) and carried out during a Ph.D. co-funded by the Graduate School of Science and Technology, Aarhus University. We thank Andreas Lücke for advice and analysis of stable isotopes on cellulose samples at the Jülich Research Center, Germany. Richard Bradshaw is acknowledged for improving the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M.-J. Gaillard.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Søe, N.E., Odgaard, B.V., Nielsen, A.B. et al. Late Holocene landscape development around a Roman Iron Age mass grave, Alken Enge, Denmark. Veget Hist Archaeobot 26, 277–292 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00334-016-0591-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00334-016-0591-x