Abstract.
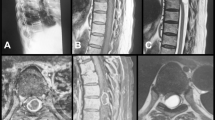
Spinal neural foraminal widening is usually caused by benign lesions, most commonly neurofibromas. Rare lesions can also cause spinal neural foraminal widening. Computed tomography and/or MRI are the modalities of choice for studying the spinal foraminal widening. The present pictorial review describes six rare lesions, namely a lateral thoracic meningocele, a malignant fibrous histiocytoma, a tuberculous abscess, an osteoblastoma, a chondrosarcoma and a malignant tumour of the lung which caused spinal neural foraminal widening.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 November 1998; Revised: 4 March 1999; Accepted: 20 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zibis, A., Markonis, A. & Karantanas, A. Unusual causes of spinal foraminal widening. Eur Radiol 10, 144–148 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300050022
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300050022