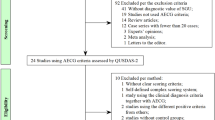
Abstract
Objective
To systematically evaluate the diagnostic performance of ultrasound elastography (USE) in distinguishing primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) from healthy/disease controls.
Methods
We searched the PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases for published literature on USE for diagnosing pSS. Bivariate random effects models were used to calculate the pooled sensitivity and specificity of USE. To determine the factors influencing heterogeneity, meta-regression and subgroup analyses were performed to assess country, diagnostic criteria, imaging mechanisms, shear wave elastography techniques, measurement location, control group category, and patient age. Publication bias was assessed using the asymmetry of the Deeks funnel plot.
Results
Fifteen articles covering 816 patients and 735 control participants were included. USE showed a pooled sensitivity of 0.80 (95% CI: 0.71–0.87) and specificity of 0.87 (95% CI: 0.78–0.92). Meta-regression and subgroup analyses revealed that shear wave elastography techniques, measurement location, and patient age were significant factors that affected study heterogeneity (p < 0.05). Elastography performs better in diagnosing patients aged ≤ 51 years compared to patients aged > 51 years. There was no significant publication bias.
Conclusion
USE demonstrates high accuracy in differentiating between pSS and healthy/disease control groups.
Clinical relevance statement
Ultrasound elastography, as a non-invasive and cost-effective technique, can be used to distinguish primary Sjögren’s syndrome from disease/healthy control groups by measuring the stiffness of salivary glands.
Key Points
• Ultrasound elastography is an acceptable technique for the diagnosis of primary Sjögren’s syndrome.
• The pooled sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound elastography for diagnosing primary Sjögren’s syndrome were 0.80 and 0.87, respectively.
• In patients aged ≤ 51 years with primary Sjögren’s syndrome, ultrasound elastography showed good diagnostic performance.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARFI:
-
Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging
- CI:
-
Confidence intervals
- HSROC:
-
Hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic
- pSS:
-
Primary Sjögren’s syndrome
- SI:
-
Strain imaging
- SWE:
-
Shear wave elastography
- SWI:
-
Shear wave imaging
- USE:
-
Ultrasound elastography
References
Brito-Zerón P, Baldini C, Bootsma H et al (2016) Sjögren syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16047
Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zerón P, Sisó-Almirall A, Bosch X (2012) Primary Sjogren syndrome. BMJ 344:e3821
Mariette X, Criswell LA (2018) Primary Sjögren’s syndrome. N Engl J Med 378(10):931–939
Ramsubeik K, Motilal S, Sanchez-Ramos L, Ramrattan LA, Kaeley GS, Singh JA (2020) Diagnostic accuracy of salivary gland ultrasound in Sjögren’s syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 12:1759720X20973560
Shiboski CH, Shiboski SC, Seror R et al (2016) 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts. Arthritis Rheumatol 69(1):35–45
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R et al (2002) European Study Group on Classification Criteria for Sjögren’s Syndrome. Classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis 61(6):554–8
Milic VD, Petrovic RR, Boricic IV et al (2009) Diagnostic value of salivary gland ultrasonographic scoring system in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: a comparison with scintigraphy and biopsy. J Rheumatol 36(7):1495–1500
Chikui T, Okamura K, Tokumori K et al (2006) Quantitative analyses of sonographic images of the parotid gland in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Ultrasound Med Biol 32(5):617–622
Cindil E, Oktar SO, Akkan K et al (2018) Ultrasound elastography in assessment of salivary glands involvement in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Imaging 50:229–234
Gürüf A, Öztürk M, Bayrak IK, Polat AV (2019) Shear wave versus strain elastography in the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions. Turk J Med Sci 49(5):1509–1517
Sigrist RMS, Liau J, Kaffas AE, Chammas MC, Willmann JK (2017) Ultrasound elastography: review of techniques and clinical applications. Theranostics 7(5):1303–1329
García-Carrasco M, Fuentes-Alexandro S, Escárcega RO, Salgado G, Riebeling C, Cervera R (2006) Pathophysiology of Sjögren’s syndrome. Arch Med Res 37(8):921–32
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2010) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg 8(5):336–41
Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J (2003) The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol 3:25
Kim KW, Lee J, Choi SH, Huh J, Park SH (2015) Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies evaluating diagnostic test accuracy: a practical review for clinical researchers-part I. General guidance and tips. Korean J Radiol 16(6):1175–87
Lee J, Kim KW, Choi SH, Huh J, Park SH (2015) Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies evaluating diagnostic test accuracy: a practical review for clinical researchers-part II. Statistical methods of meta-analysis. Korean J Radiol 16(6):1188–96
DevilléevillBuntinx F, Bouter LM et al (2002) Conducting systematic reviews of diagnostic studies: didactic guidelines. BMC Med Res Methodol 2:9
Arslan S, Durmaz MS, Erdogan H, Esmen SE, Turgut B, Iyisoy MS (2020) Two-dimensional shear wave elastography in the assessment of salivary gland involvement in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J Ultrasound Med 39(5):949–956
Bădărînză M, Serban O, Maghear L et al (2020) Shear wave elastography as a new method to identify parotid lymphoma in primary Sjögren syndrome patients: an observational study. Rheumatol Int 40(8):1275–1281
Dejaco C, De Zordo T, Heber D et al (2014) Real-time sonoelastography of salivary glands for diagnosis and functional assessment of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ultrasound Med Biol 40(12):2759–2767
Chen S, Wang Y, Zhang G, Chen S (2016) Combination of salivary gland ultrasonography and virtual touch quantification for diagnosis of Sjögren’s syndrome: a preliminary study. Biomed Res Int 2016:2793898
Hofauer B, Mansour N, Heiser C et al (2016) Sonoelastographic modalities in the evaluation of salivary gland characteristics in Sjögren’s syndrome. Ultrasound Med Biol 42(9):2130–2139
Knopf A, Hofauer B, Thürmel K et al (2015) Diagnostic utility of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) imaging in primary Sjoegren`s syndrome. Eur Radiol 25(10):3027–3034
Moisoiu V, Badarinza M, Stefancu A et al (2020) Combining surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) of saliva and two-dimensional shear wave elastography (2D-SWE) of the parotid glands in the diagnosis of Sjögren’s syndrome. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 235:118267
Oruk YE, Çildağ MB, Karaman CZ, Çildağ S (2021) Effectiveness of ultrasonography and shear wave sonoelastography in Sjögren syndrome with salivary gland involvement. Ultrasonography 40(4):584–593
Özer H, Tezcan D, Hakbilen S et al (2023) Diagnostic performance of gray-scale ultrasound and shear wave elastography in assessing salivary gland involvement in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J Clin Ultrasound 51(1):187–194
Prata AR, Freitas JP, Marques ML et al (2020) Shear-wave elastography evaluation of major salivary glands in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. ARP Rheumatol 1(3):197–204
SatARP RhCindil E, Salman RB et al (2020) Parotid elastography: a potential alternative to replace labial biopsy in classification of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome? Clin Rheumatol 39(12):3707–3713
Świecka M, Paluch Ł, Pietruski P, Maślińska M, Zakrzewski J, Kwiatkowska B (2022) Shear wave elastography as a potential additional diagnostic tool in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: an observational study. Rheumatol Int 42(9):1579–1587
Turnaoglu H, Kural Rahatli F, Pamukcu M, Haberal KM, Uslu N (2018) Diagnostic value of acustic radiation force impulse imaging in the assessment of salivary gland involvement in primary Sjögren’s sydrome. Med Ultrason 20(3):313–318
Zhang X, Zhang S, Feng R, Yao H, Tang S, He J (2021) Sonoelastography of salivary glands for diagnosis and clinical evaluation in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol 39(Suppl 133):184–189
Shiboski SC, Shiboski CH, Criswell LA et al (2012) American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: a data-driven, expert consensus approach in the Sjögren’s International Collaborative Clinical Alliance cohort. Arthritis Care Res 64(4):475–487
Dewall RJ (2013) Ultrasound elastography: principles, techniques, and clinical applications. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 41(1):1–19
Bamber J, Cosgrove D, Dietrich CF et al (2013) EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 1: basic principles and technology. Ultraschall Med 34:169–184
Cosgrove D, Piscaglia F, Bamber J et al (2013) EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 2: clinical applications. Ultraschall Med 34:238–253
ToanNK ASG (2021) Aging-related metabolic dysfunction in the salivary gland: a review of the literature. Int JMol Sci 22:5835
Maślińska M, Przygodzka M, Kwiatkowska B, Sikorska-Siudek K (2015) Sjögren’s syndrome: still not fully understood disease. Rheumatol Int 35(2):233–241
Jiali C, Yuebo J, Jing Li, Shi C, Jing He (2018) Gender differences in clinical and immunological characteristics and the pathogenic study of primary SjiJgren s syndrome. Chin J Rheumatol 22(8):526–531
Fujibayashi T, Sugai S, Miyasaka N et al (2004) Revised Japanese criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome (1999): availability and validity. Mod Rheumatol 14:425–34
Vitali C, Del Papa N (2017) Classification and diagnostic criteria in Sjögren’s syndrome: a long-standing and still open controversy. Ann Rheum Dis 76(12):1953–1954
Yanqing W, Fang N, Longli W, Yangyang Z, Yuting T (2021) Clinical value of virtual touch tissue imaging quantification in diagnosing salivary gland Sjögren’s syndrome. Chin J Med Ultrasound (Electronic Edition) 18(1):11–16
Giuseppetti GM, Argalia G, Salera D, Ranaldi R, Danieli G, Cappelli M (2005) Ultrasonographic contrast-enhanced study of sicca syndrome. Eur J Radiol 54(2):225–232
Samier-Guérin A, Saraux A, Gestin S et al (2016) Can ARFI elastometry of the salivary glands contribute to the diagnosis of Sjögren’s syndrome? Joint Bone Spine 83(3):301–306
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Xin Sui.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
One of the authors (Xinpeng Dai) has significant statistical expertise.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was not required for this study because this study is a systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was not required because this study is a systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies.
Methodology
•Systematic review
• Meta-analysis
• Performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, X., Sui, X., Chen, S. et al. The diagnostic performance of salivary gland ultrasound elastography in Sjögren’s syndrome and sicca symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 34, 1545–1555 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-023-10166-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-023-10166-5