Abstract
Objectives
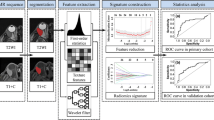
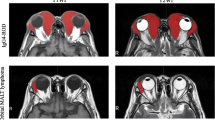
To evaluate the effectiveness of bag-of-features (BOF)-based radiomics for differentiating ocular adnexal lymphoma (OAL) and idiopathic orbital inflammation (IOI) from contrast-enhanced MRI (CE-MRI).
Methods
Fifty-six patients with pathologically confirmed IOI (28 patients) and OAL (28 patients) were randomly divided into training (n = 42) and testing (n = 14) groups. One hundred sixty texture features extracted from the CE-MR image were encoded into the BOF representation with fewer features. The support vector machine (SVM) with a linear kernel was used as the classifier. Data augmented was performed by cropping orbital lesions in different directions to alleviate the over-fitting problem. Student’s t test and the Holm-Bonferroni method were employed to compare the performance of different analysis methods. The chi-square test was used to compare the analysis with MRI and human radiological diagnosis.
Results
In the independent testing group, the differentiation by the BOF features with augmentation achieved an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.803 (95% CI: 0.725–0.880), which was significantly higher than that of the BOF features without augmentation and that of the texture features (p < 0.05). In addition, the same radiomic analysis with pre-contrast MRI obtained an AUC of 0.618 (95% CI: 0.560–0.677), which was significantly lower than that with CE-MRI. The diagnostic performance of the analysis with CE-MRI was significantly better than the radiology resident (p < 0.05) but had no significant difference with the experienced radiologist, even though there was less consistency between the radiomic analysis and the human visual diagnosis.
Conclusions
The BOF-based radiomics may be helpful for the differentiation between OAL and IOI.
Key Points
• It is challenging to differentiate OAL from IOI due to the similar clinical and image features.
• Radiomics has great potential for the noninvasive diagnosis of orbital diseases.
• The BOF representation from patch to image may help the differentiation of OAL and IOI.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- BOF:
-
Bag-of-features
- GLCM:
-
Gray-level co-occurrence matrix
- GLRLM:
-
Gray-level run length matrix
- IOI:
-
Idiopathic orbital inflammation
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- OAL:
-
Ocular adnexal lymphoma
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
References
McKelvie PA (2010) Ocular adnexal lymphomas: a review. Adv Anat Pathol 17:251–261
Decaudin D, de Cremoux P, Vincent-Salomon A, Dendale R, Rouic L (2006) Ocular adnexal lymphoma: a review of clinicopathologic features and treatment options. Blood 108:1451–1460
Kharod SM, Herman MP, Morris CG, Lightsey J, Mendenhall WM, Mendenhall NP (2018) Radiotherapy in the management of orbital lymphoma: a single institution’s experience over 4 decades. Am J Clin Oncol 41:100–106
Uno T, Isobe K, Shikama N et al (2003) Radiotherapy for extranodal, marginal zone, B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue originating in the ocular adnexa: a multiinstitutional, retrospective review of 50 patients. Cancer 98:865–871
Espinoza G (2010) Orbital inflammatory pseudotumors: etiology, differential diagnosis, and management. Curr Rheumatol Rep 12:443–447
Swamy N, McCluskey P, Nemet A et al (2007) Idiopathic orbital inflammatory syndrome: clinical features and treatment outcomes. Br J Ophthalmol 91:1667–1670
Rubin P, Foster C (2004) Etiology and management of idiopathic orbital inflammation. Am J Ophthalmol 138:1041–1043
Brannan P (2007) A review of sclerosing idiopathic orbital inflammation. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 18:402–404
Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R et al (2012) Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur J Cancer 48:441–446
Woolf DK, Ahmed M, Plowman PN (2012) Primary lymphoma of the ocular adnexa (orbital lymphoma) and primary intraocular lymphoma. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 24:339–344
Haradome K, Haradome H, Usui Y et al (2014) Orbital lymphoproliferative disorders (OLPDs): value of MR imaging for differentiating orbital lymphoma from benign OPLDs. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:1976–1982
Cytryn AS, Putterman AM, Schneck GL, Beckman E, Valvassori GE (1997) Predictability of magnetic resonance imaging in differentiation of orbital lymphoma from orbital inflammatory syndrome. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 13:129–134
Xian J, Zhang Z, Wang Z et al (2010) Value of MR imaging in the differentiation of benign and malignant orbital tumors in adults. Eur Radiol 20:1692–1702
Ben Simon GJ, Annunziata CC, Fink J, Villablanca P, McCann JD, Goldberg RA (2005) Rethinking orbital imaging establishing guidelines for interpreting orbital imaging studies and evaluating their predictive value in patients with orbital tumors. Ophthalmology 112:2196–2207
Oses P, Renault M-A, Chauvel R et al (2009) Mapping 3-dimensional neovessel organization steps using micro-computed tomography in a murine model of hindlimb ischemia-brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:2090–2092
Kapur R, Sepahdari A, Mafee M et al (2009) MR imaging of orbital inflammatory syndrome, orbital cellulitis, and orbital lymphoid lesions: the role of diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:64–70
Ro S-R, Asbach P, Siebert E, Bertelmann E, Hamm B, Erb-Eigne (2016) Characterization of orbital masses by multiparametric MRI. Eur J Radiol 85:324–336
Hiwatashi A, Togao O, Yamashita K et al (2018) Diffusivity of intraorbital lymphoma vs. inflammation: comparison of single shot turbo spin echo and multishot echo planar imaging techniques. Eur Radiol 28:325–330
Sepahdari AR, Aakalu VK, Setabutr P, Shiehmorteza M, Naheedy JH, Mafee MF (2010) Indeterminate orbital masses: restricted diffusion at MR imaging with echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging predicts malignancy. Radiology 256:554–564
Sun B, Song L, Wang X et al (2017) Lymphoma and inflammation in the orbit: diagnostic performance with diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 45:1438–1445
Roshdy N, Shahin M, Kishk H et al (2010) MRI in diagnosis of orbital masses. Curr Eye Res 35:986–991
Xu X, Hu H, Liu H et al (2017) Benign and malignant orbital lymphoproliferative disorders: differentiating using multiparametric MRI at 3.0T. J Magn Reson Imaging 45:167–176
Lambin P, Leijenaar R, Deist T et al (2017) Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:749–762
Huang Y, Liu Z, He L et al (2016) Radiomics signature: a potential biomarker for the prediction of disease-free survival in early-stage (I or II) non-small cell lung cancer. Radiology 281:947–957
Nie K, Chen J-H, Yu HJ, Chu Y, Nalcioglu O, Su M-Y (2008) Quantitative analysis of lesion morphology and texture features for diagnostic prediction in breast MRI. Acad Radiol 15:1513–1525
Lakshmanaprabu S, Sachi-Nandan M, Shankar K, Arunkumar N, Ramirez-Gonzalez G (2019) Optimal deep learning model for classification of lung cancer on CT images. Futur Gener Comput Syst 92:374–382
Juntu J, Sijbers J, De Backer S, Rajan J, Van Dyck D (2010) Machine learning study of several classifiers trained with texture analysis features to differentiate benign from malignant soft-tissue tumors in T1-MRI images. J Magn Reson Imaging 31:680–689
Fruehwald-Pallamar J, Hesselink JR, Mafee MF, Holzer-Fruehwald L, Czerny C, Mayerhoefer ME (2016) Texture-based analysis of 100 MR examinations of head and neck tumors - is it possible to discriminate between benign and malignant masses in a multicenter trial? Rofo 188:195–202
Huang Y-q, Liang C-h, He L et al (2016) Development and validation of a radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 34:2157–2164
Liu C, Ding J, Spuhler K et al (2019) Preoperative prediction of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer by radiomic signatures from dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 49:131–140
Qu J, Shen C, Qin J et al (2019) The MR radiomic signature can predict preoperative lymph node metastasis in patients with esophageal cancer. Eur Radiol 29:906–914
Guo J, Liu Z, Shen C et al (2018) MR-based radiomics signature in differentiating ocular adnexal lymphoma from idiopathic orbital inflammation. Eur Radiol 28:3872–3881
Yu J, Qin Z, Wan T, Zhanga X (2013) Feature integration analysis of bag-of-features model for image retrieval. Neurocomputing 120:355–364
Dardas NH, Georganas ND (2011) Real-time hand gesture detection and recognition using bag-of-features and support vector machine techniques. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 60:3592–3607
Nowak E, Jurie F, Triggs B (2006) Sampling strategies for bag-of-features image classification. Computer Vision - ECCV, Pt 4, Proceedings 3954:490–503
Luo J, Ning Z, Zhang S, Feng Q, Zhang Y(2018) Bag of deep features for preoperative prediction of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. Phys Med Biol 63:245014
Mizener JB, Podhajsky P, Hayreh SS (1997) Ocular ischemic syndrome. Ophthalmology 104:859–864
Ding ZX, Lip G, Chong V (2011) Idiopathic orbital pseudotumour. Clin Radiol 66:886–892
Ren J, Yuan Y, Wu Y, Tao X (2018) Differentiation of orbital lymphoma and idiopathic orbital inflammatory pseudotumor: combined diagnostic value of conventional MRI and histogram analysis of ADC maps. BMC Med Imaging 18:6
Funding
This study has received funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61971350), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M653717), Shaanxi Key R&D Plan (2020SF-036), Xi’an Science and Technology Plan Project (GXYD18.3), and the Scientific Research Foundation of Xi’an Fourth Hospital (FZ-50).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Fengjun Zhao.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
One of the authors has significant statistical expertise.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• retrospective
• diagnostic or prognostic study
• performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Y., Xie, X., Chen, J. et al. Bag-of-features-based radiomics for differentiation of ocular adnexal lymphoma and idiopathic orbital inflammation from contrast-enhanced MRI. Eur Radiol 31, 24–33 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07110-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07110-2